Madhya Pradesh - Topography
 Madhya Pradesh, with an area of 3, 08, 000 sq.km. is the second largest state in India after Rajasthan. It is a part of peninsular plateau of India lying in north central part, whose boundary can be classified in the north by the plains of Ganga-Yamuna, in the west by the Aravali, east by the Chhattisgarh plain and in the south by the Tapti valley and the plateau of Maharashtra.
Madhya Pradesh, with an area of 3, 08, 000 sq.km. is the second largest state in India after Rajasthan. It is a part of peninsular plateau of India lying in north central part, whose boundary can be classified in the north by the plains of Ganga-Yamuna, in the west by the Aravali, east by the Chhattisgarh plain and in the south by the Tapti valley and the plateau of Maharashtra.
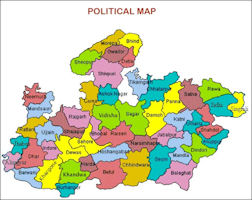
Being centrally located, it is often referred to as the "Heart of India". The state is bordered on the west by Gujarat, northwest by Rajasthan, north - east by Uttar Pradesh, east by Chhattisgarh, and south by Maharashtra. It has diverse physiography with large plateaus, numerous mountain ranges, meandering rivers and miles of forests supporting rich biodiversity
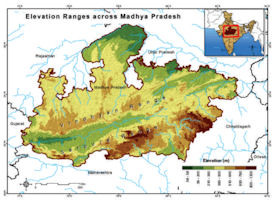
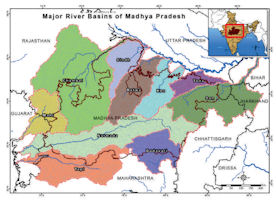
The topography of Madhya Pradesh is defined by the Narmada Sone Valley. It is a narrow and long valley extending through almost the whole of the state from east to west. Sone valley forms the upper part; Shahdol and Sidhi districts lie in this valley. The lower part forms the Narmada valley. It has an average elevation of 300 m above MSL and is covered with alluvial soil. Jabalpur, Mandla, Narsinghpur, Hoshangabad, Raisen, Khandwa, Khargone and Barwani districts lie in this region. The Sone valley is narrower than Narmada valley and alluvial deposit is also comparatively poor and thin, therefore Narmada valley is more important than Sone valley for agricultural activities.
To the north of this valley lie the Central Highlands, to the south the Satpura-Maikal ranges and to the south-east, the eastern plateau. These three form the natural physiographic regions-into which the state is divided. The Central Highlands are spread between the Narmada-Sone valley and the Aravali ranges to the west in a triangular form. The highlands slope towards the north and drain into the Yamuna. The central highlands region in the state includes the following four uplands:
The Rewa-Panna plateau is one, also known as the Vindhyan plateau, lies in the north- eastern part of the central highlands. The main rivers flowing in the area are Ken, Sonar, Barna and Tons. Rewa, Panna, Satna, Damoh and Sagar districts lie in this region.The other is Bundelkhand plateau located to the north-west of the Rewa-Panna plateau. Datia, Chhatarpur, Panna, Tikamgarh and parts of Guna and Shivpuri districts forming the northern part of the state lie in this region. The plateau is bounded in north-east by Vindhyan escarp lands or Rewa-Panna plateau. The average height of the region is 350-450 m above MSL and general slope is towards north. The main rivers flowing in the area are Betwa, Dhasan and Jamner which finally join Yamuna.
Central India plateau is the third that lies to west of Bundelkhand plateau. Shivpuri, Morena and Gwalior districts exist in this region. This plateau has an average elevation of 450 m on highlands and 150-450 m above MSL in valleys. Chambal, Kali Sindh and Parvati are the main rivers flowing in this area. The fourth Malwa plateau covers almost the entire western Madhya Pradesh. The plateau is bounded in the north by Chambal and in south by the Narmada. The average elevation ranges between 300-500 m above MSL. Shajapur, Dewas, Indore, Ujjain, Dhar, Ratlam and parts of Sehore and Jhabua districts lie in this region. Bhopal is situated at the eastern edge of the Malwa plateau. Shipra, Parvati, Kali Sindh, Gambhir and Chambal rivers flow through the Malwa plateau. It also forms the water divide between the Ganga and the Narmada basin. The soil in the area is black cotton as a result of weathering of basalts.
Satpura-Maikal ranges lie to the south and the eastern plateau regions to the north- east of the Narmada - Sone valley. Chhindwara, Betul, Seoni, Balaghat, Mandla and parts of Khandwa and Khargone districts lie in the Satpura-Maikal ranges. Average height of these ranges is 300 m ; but there are several high peaks; the highest peak of the state, Dhoopgarh that rises to 1360 m above msl lies in these ranges. The slope is sharp in south face and gentle on northern side.
The eastern part, the Satpuras, is wider than the western part which stretches in the form of a semi-circle and is known as the Maikal ranges. The Maikal ranges include the Amarkantak plateau, which is origin of both Narmada and Sone rivers. The other rivers in the area are Johila, Macherwa, Denwa and Choti Tawa which join the Narmada. The eastern plateau region comprises Baghelkhand Plateau lying between Maikal ranges and Chhattisgarh plain area with an elevation of 1033 m above MSL.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|