APA-57 Gilliam-class attack transports
Launched on March 28, 1944, Gilliam was the first of 32 Gilliam-class attack transports, specially designed vessels that served as amphibious ships. Unlike conventional freighters and transports, attack transports were designed to unload their cargoes over the side into landing craft which they carried; in a sense their beaching craft were their main batteries.
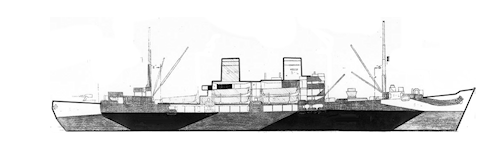
USS Gilliam was a welded steel vessel 426 feet long overall, with a waterline length of 400 feet, an extreme beam of 58 feet, a maximum depth of hold of 37 feet, and a 15.6-foot draft. Gilliam displaced 6,800 tons standard. The twin screws were driven by Westinghouse Steam Turbines that developed 6,000 shaft horsepower at 18 knots. Steam was provided by two oil-burning Babcock and Wilcox boilers. The vessel was armed with a single 5-inch/38 caliber gun, four twin-mounted 40mm Bofors antiaircraft guns, and ten single 20mm Oerlikon guns. Gilliam carried thirteen LCVPs (Landing Craft Vehicles, Personnel), one LCPL (Landing Craft Personnel, Large), and 1,032 tons of cargo or 849 troops. The superstructure was located in the center of the ship; two masts, one forward and one aft, were fitted with booms and steam winches that handled cargo and the ship's landing craft.
USS Gilliam, a type S4-SE2-BU1 transport, was built under a U.S. Maritime Commission contract in 1944 by the Consolidated Steel Corporation of Wilmington, California. Gilliam was acquired by the U.S. Navy on July 31, 1944, and commissioned the next day as APA-57. Gilliam departed San Francisco Bay on October 16, 1944, with 750 Army troops bound for New Guinea. Gilliam ferried troops to the Philippines in support of the reconquest of those islands and served as a receiving ship for crews and injured personnel of damaged or lost warships during the Battle of Leyte Gulf. Gilliam also participated in the assault on Okinawa. At the war's end the transport carried occupation troops to Sasebo, Japan, and ferried returning troops home as part of Operation "Magic Carpet."
Gilliam was selected as a target vessel for Operation Crossroads. Arriving at Pearl Harbor on February 16, 1946, the ship was readied for the tests. Gilliam was moored aft of Nevada, the projected target for the Able test detonation. The bomb instead detonated off Nevada and close to Gilliam, "the only ship located within 1,000 feet of the projected zeropoint." The vessel sank in less than two minutes.
USS CARLISLE (APA-69) was ordered to Pearl Harbor for assignment to Joint Task Force One for Operation Crossroads. Arriving at Pearl on February 4, the ship was "stripped" during that month before sailing to Bikini Atoll as one of eighteen attack transports slated for the tests. Moored close to Gilliam, Carlisle was sunk by the Able test burst on July 1, 1946. USS Carlisle was stricken from the Navy Register on August 15, 1946.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

