ANT-21 MI-3 multi-seat fighter
The experience of operating multi-purpose aircraft R-6 and Kr-6 identified two main directions for the development of aircraft of this type: the design of heavy multi-seat fighters with enhanced small arms and guns (MI and DIP) and high-speed front bombers (SB). Both of these areas in the USSR developed before the beginning of the Great Patriotic War.
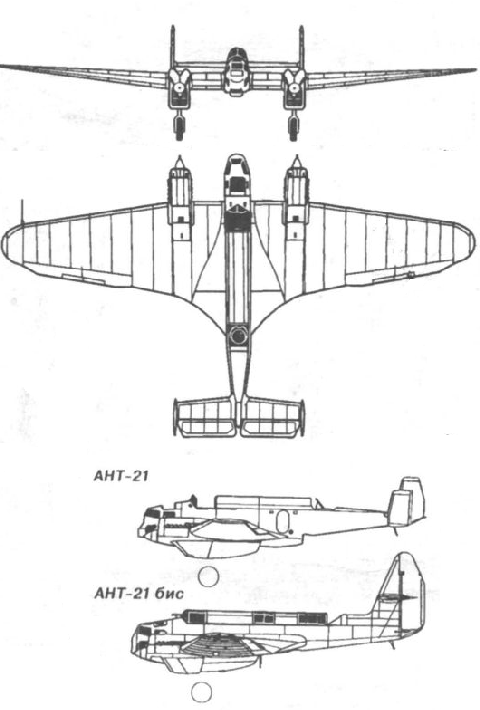
In 1930, TsAGI received a designation task for a multi-seat fighter from the UHVS. It was clarified several times and, according to the final version of the design bureau, it was entrusted to create a multi-purpose fighter with high tactical data for its time, capable of performing the tasks of an escort fighter, a light bomber and a reconnaissance aircraft. From March 1, 1931, the design bureau began to design the aircraft, which received the internal designation ANT-21. The official designation was MI-3 - Mnogomestnyy Istrebitel - Multi-seat fighter (there does not seem to have been an MI-1 or MI-2). It was the first aircraft of the Tupolev design bureau with a retractable landing gear, which required additional research and testing and somewhat delayed the design and construction of the aircraft.
Compared with the P-6, the multi-seat ANT-21 had, while maintaining the overall design of the twin-engine monoplane and with the same M-17 type engines, significantly smaller geometrical dimensions, its aerodynamics were improved thanks to the use of a retractable chassis, the fuselage of a refined semi-monocoque design with an oval transverse cross-section and with a smooth non-embossed outer lining, half-enclosed cockpits of the crew. The original for its time was the use of spaced two-tail plumage, which improved the possibilities of firing a rear hemisphere from a defensive weapon, and the use of compressed air in the chassis cleaning system, as well as chassis struts with oil-air damping. In this case, the design of the wing and tail remained traditional - with a corrugated casing, covered with canvas, and with a truss-beam spars.
The prototype machine was ready only on April 26, 1933, and on May 23 test pilot IF Kozlov lifted it up for the first time. Started tests revealed many shortcomings, the aircraft returned for refinement. Subsequent tests were conducted by pilots I.F. Kozlov, B.L. Bukhgolts, K.K.Popov. Unfortunately, the measures taken have eliminated not all defects, including the most unpleasant - the feathering buffalo. Flying by car was considered dangerous. It was decided to do some more test flights to find out the causes of shaking. The test was not completed. On September 14, 1933, at a speed of about 350 km / h, the plumage collapsed, I.F.Kozlov planted the car with difficulty. A detailed analysis of the incident began, the results of which were of great importance for the future of high-speed aircraft, which were also created in Tupolev, and in other aviation KB of the country. It turned out that for high-speed airplanes it is necessary to ensure not only the static but also the dynamic strength of the airframe units.
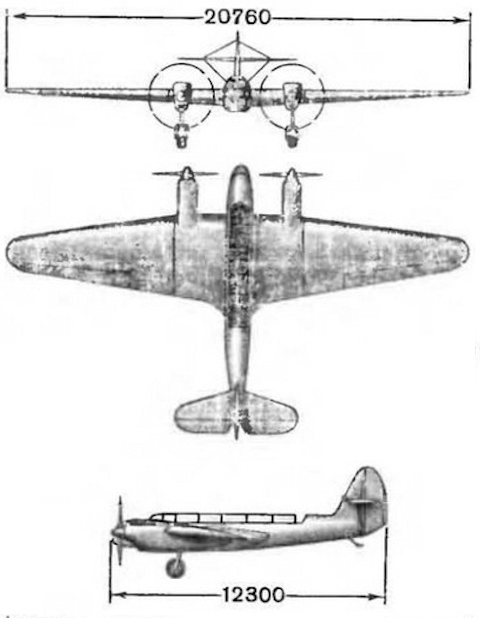
On January 10, 1932, the Design Bureau began the construction of an “understudy” - ANT-21bis (MI-3D), which was significantly different from the first prototype. For the “doubler”, the single-tail tail unit was re-designed with a stabilizer mounted high on the keel, and the fuselage was rearranged to improve the defensive fire system. The front machine-gun unit was replaced with a 20 mm caliber “Oerlikon” cannon, new M-34H high-altitude engines with a capacity of 830 hp were installed.
In mid-January, MI-3D was transported to the airfield. January 22, 1934 took the first flight. Factory testing continued until October 13, 1934. Good flight data was obtained, but the plane was difficult to pilot. All work on the car was discontinued, although preparations for serial production at plant No. 22 had already begun. The decision was natural, since ANT-40 (SB) went to the tests, which had a more promising design and better flight characteristics, which made it possible to design it Based on the multipurpose machine class MI or DIP, which was implemented in the project ANT-46 (DI-8).
| Ant-21 | Ant-21bis | |
| -length of aircraft, M | 10.86 | 11.57 |
| -wing span, m | 19.11 | 20.76 |
| -height of the aircraft, m | 52.1 | 59.18 |
| -normal takeoff, weight, kg | 5088 | 5463 |
| -maximum speed at altitude, km/h/m | 351/0 | 350/5000 |
| -rise Time to height, min/m | - | - |
| -practical ceiling, m | 7885 | 8300 |
| -flight range, km | - | - |
| -machine gun Armament | 4 x PV 2 x Yes 1 x Yes |
2 x PV 1 x ShKAS |
| -cannon gun | - | 1 x "oerlikon " |
| -crew, Pax | 4 | 4 |
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|






