North Korea - Shipbuilding Industry
With the revision of the constitution in 1998, the Ministry of Ships and Industry was abolished as the Cabinet ministries were reduced from 41 to 31. At this time, it seems that the jurisdiction of the shipbuilding industry was transferred to the 2nd Economic Committee. It is presumed that the repair and management of ships in the private sector is undertaken by the Marine Facilities Guidance Bureau or the Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs.
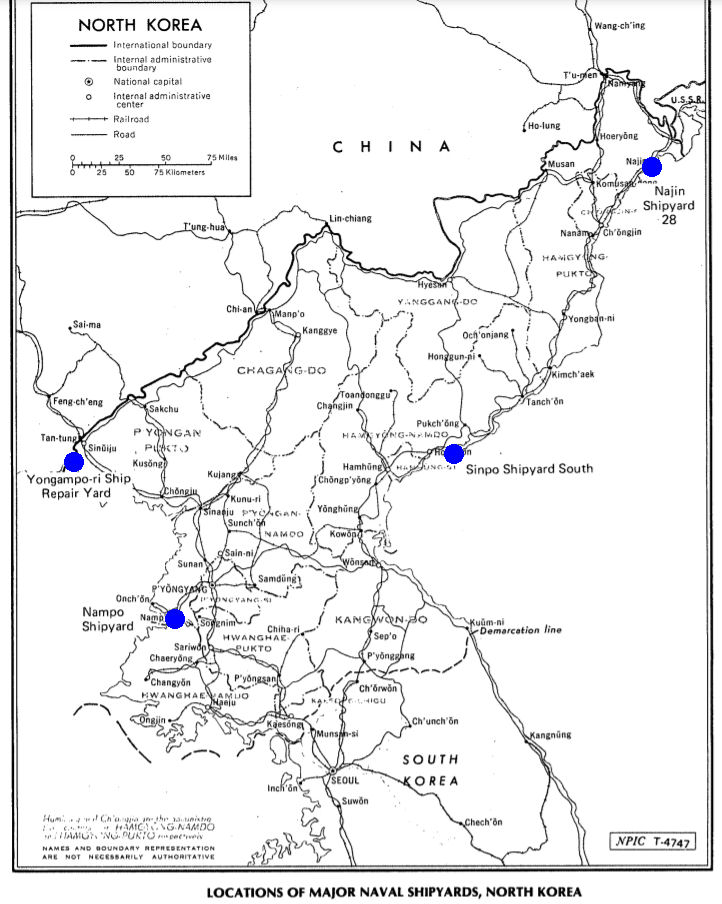
Among North Korean shipyards, large ships are generally named as shipyards, and small and medium-sized ships are named as ship factories. In addition, in the case of large ships, the Nampo Shipyard and the Chungjin Shipyard are in charge of ship repair, and the small and medium-sized ships are repaired by ship factories or ship repair centers in various regions.
North Korea's shipbuilding capacity was 25,800,000 tons in 2014, only 1.3% of South Korea's 2,308,000,000 tons in the same year. The construction record was about 1 to 2 ships per year for cargo ships until the 1980s, and most of the engines and other major parts of these large ships depended on imports. Since 1990, the construction of ships in the private sector seems to have almost ceased due to extreme energy and raw material shortages, and it has maintained its reputation for maintenance and repair of ships at home and abroad.
The shipbuilding performance in North Korea is not accurately understood, but according to the Bank of Korea, it was around 51,000-5.5G/T in the early and mid-1990s and decreased to 38,000 G/T in 1997. After 2000, the estimate of shipbuilding performance in North Korea itself has no meaning, and shipbuilding capabilities have been estimated and published.
In North Korea, due to the separation of the east and west coasts due to the division of the South and the North, the relative negligence of trade and shipping due to the North Korean defense, and the systematic closure of the shipbuilding industry, the level of the shipbuilding industry is not well-received. It is in very poor condition. In terms of shelf-building technology, facilities and capacity, and amount of construction, it is estimated that the overall level of shipbuilding industry technology in North Korea remains at the level of South Korea's late 1960s.
The Parkcheon Ship Repair Factory is a factory located in Daeryeong-ri, Bakcheon-gun, North Pyeongan Province, and is located at the foot of the Daeryeong River. In 1973, the ship repair center, which specialized in repairing small fishing boats, was reorganized and expanded, and mainly small and medium-sized fishing boats are manufactured and repaired.
In 2009, several automatic burim boats and one self-driving barge were built at the Sinuiju Ship Factory, and several facilities, including portable oxygen and hydrogen generators, are said to have increased the drying speed. The Iwon Ship Repair Factory is a factory located in Iwon-eup, Iwon-gun, South Hamgyeong Province. It repairs ships used in a fishery base on the east coast and manufactures small fishing boats.
Eodaejin Ship Repair Factory is a factory located in Workers' District, Eodaejin, North Hamgyeong Province, specializing in shipbuilding and ship repair. Before liberation, it was only a small ship repair station, but after liberation, it developed into a factory that manufactured small fishing boats and repaired and maintained medium-sized ships through several expansions. Currently, small fishing boats are manufactured and supplied to various fishery bases on the east coast, and ships are repaired. Dancheon Ship Repair Factory, changed the ship's 400HP diesel engine to 200HP diesel engine in 2007, and ship repair performance in 2010.
| Shipyard name | location | Annual capacity | Ships that can be built | Major shipbuilding | Number of people | |
| West Sea | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chungjin Shipyard | Hambuk Cheongjin City | 2,570,000 tons | 20,000 tons | 5,000 ton class refrigeration carrier, 3,750 ton class trawler, 14,000 ton class cargo ship, passenger ship (Mankyungbong 92) | 7,500 | |
| Wonsan Shipyard | Coastal-dong, Wonsan-si, Gangwon-do | 3,440,000 tons | 30,000 tons | Ferro cement ship, 3,750 ton class stern trawler, 14,000 ton class salt processing mother ship | 3,000 | |
| Najin Shipyard (Factory 50) | Hambuk Najinseonbong | 2.820,000 tons | 3,000 ton class ship 20,000 ton class merchant ship | 1,500 ton class escort destroyer, 500 ton, 1,400 ton class submarine, guided missile patrol boat, torpedo boat | 4,000 | |
| Yukdae Shipyard | Hamnam Sinpo City Yukdaeseo-ri | 2,620,000 tons | 20,000 ton class merchant ship 3,000 ton class ship | 1,400 ton class submersible | 1,000 | |
| Sinpo Shipyard | Hamnam Sinpo Siyeonno-dong | 66,000 tons | 50,000 tons | 3,750 ton class stern trawler, 1,350 ton class refrigerated ship | 1,500 | |
| Kim Chaek Ship Factory | Hak-dong, Kimchaek City Hall, Hambuk | 250,000 tons | 15,000 tons | 1,000 ton, 1,500 ton class cargo ship passenger ship (Eundeok 2) | 1,000 | |
| West Sea | ||||||
| Nampo Shipyard | Nampo City Port Area | 54,000 tons | 20,000 tons | 3,500 ton class refrigeration carrier, 14,000 ton class cargo ship, 3,750 ton class trawler, large crane (No. 528), oil collection ship | 5,000 | |
| Lava Po Shipyard | Yongampo, Yongcheon-gun, Pyeongbuk | 2,460,000 tons | 19,000 tons | 1,350 class refrigeration ship, dredger, 5,000 ton class return cargo ship | 2,000 | |