Yangtze River Plain
 Yangtze River Plain (Yangtze Plain, Middle and Lower) refers to the China Yangtze River Three Gorges River coastal plain east of the strip, one of three plains across China. It covers Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Anhui, Su - Seven provinces and cities including Shanghai, Zhejiang and Shanghai are known as the "Water Country". The main industries include iron and steel, machinery, electric power, textiles, and chemistry. They are China's important industrial bases and have developed water and land transportation.
Yangtze River Plain (Yangtze Plain, Middle and Lower) refers to the China Yangtze River Three Gorges River coastal plain east of the strip, one of three plains across China. It covers Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Anhui, Su - Seven provinces and cities including Shanghai, Zhejiang and Shanghai are known as the "Water Country". The main industries include iron and steel, machinery, electric power, textiles, and chemistry. They are China's important industrial bases and have developed water and land transportation.
The Yangtze River's natural water system and crisscrossed artificial river channels in the plain area of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River make this area the densest river network in the country. The main river in the area is the Yangtze River and its tributary Han River, and the rivers in the region are mostly alluvial rivers. The Yangtze River is the largest river in China, with a total length of 6,300 kilometers in its main stream and a total drainage area of more than 1.8 million square kilometers. The annual average inflow of sea water is about 960 billion cubic meters. In terms of the length of the main stream and the amount of water entering the sea, the Yangtze River ranks third in the world. Tuotuohe on the source of the Yangtze River from Qinghai Province southwest border Tanggula Mountains Geladandong snow-capped mountains, when the song was later called the Tongtian ; Nanliu to the mouth of the Batang Yushu county to Yibin City, Sichuan Province, said between the Jinsha River ; Yibin the beginning It is called the Yangtze River, and below Yangzhou it was formerly called Yangtze River. The Yangtze River flows through Tibet, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Anhui, Jiangsu and other provinces and cities, flows into the East China Sea in Shanghai, and intersects with the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal in Zhenjiang City, Jiangsu Province.
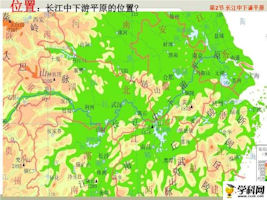
The middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Plain extend from the Wushan Mountain in the west, the Yellow Sea and the East Coast in the east, Tongbai Mountain, the southern foothills of the Dabie Mountain and the Huanghuai Plain in the north, and the Jiangnan hills and the Qiantang River and the plain along the river north of Hangzhou Bay in the south. It is about 1,000 thousand long from east to west. Meters, the north-south width is 100-400 kilometers, and the total area is about 200,000 square kilometers. It is mainly composed of 6 plains including the Jianghan Plain, the Dongting Lake Plain, the Poyang Lake Plain, the Anhui-Su Yanjiang Plain, the Lixiahe Plain, and the Yangtze River Delta Plain. Generally 5-100 meters above sea level, mostly below 50 meters above sea level. The annual average temperature is 14~18°C, and the annual precipitation is 1000~1500 mm.
The salient features of the terrain are the low and flat terrain, the vertical and horizontal rivers and channels, and the star-lined lakes. The altitude is generally 5 to 100 meters, but most of it is below 50 meters. The central and coastal areas along the river are flood plains and coastal plains. The terrain of the Hanjiang Delta also dips slightly from northwest to southeast, and lakes are clustered on the southeast front edge. Most of the Dongting Lake Plain is below 50 meters above sea level, and the terrain is higher in the north and lower in the south.
The plain soil in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River is mainly yellow brown soil or yellow cinnamon soil, the southern edge is red soil, and most of the flat land is paddy soil. The biological enrichment of red soil is very strong, and the organic matter content of the soil under natural vegetation can reach 70-80 g/kg, but it is greatly affected by soil erosion and farming methods. The organic matter content of yellow brown soil is also relatively high, but it has been significantly reduced after cultivation. The organic matter content of purple soil is generally low, usually forest and grassland> cultivated land. The high content of soil organic matter is conducive to forming a good structure, enhancing the cohesive force of soil particles, and improving the ability of water and soil conservation. The red soil, yellow soil, yellow brown soil and lime soil in this area are generally sticky and heavy, with poor water permeability and large surface runoff. If the vegetation disappears and the soil structure is destroyed, water and soil loss will easily occur; while the water permeability of purple soil and coarse bone soil is good, but given how shallow the soil layer is, it is prone to strong erosion even in the case of loss of vegetation protection and high rainfall intensity.
Most of the plains in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River belong to the northern subtropical zone, and a small part belong to the northern margin of the mid-subtropical zone. The average annual temperature is 14~18°C, the average temperature of the coldest month is 0~5.5°C, the absolute minimum temperature is -10~-20°C, the average temperature of the hottest month is 27~28°C, and the frost-free period is 210~270 days. Agriculture has two crops or three crops a year, with annual rainfall of 1000-1500 mm, and the seasonal distribution is relatively even, but there are "summer droughts".
Because of the influence of factors such as subtropical monsoons and typhoons, the plains of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River are one of the areas where heavy rains are frequent and the areas with the highest intensity of heavy rains in China, as well as the areas where heavy rains and floods are prone to disasters. Especially in the low-lying areas of the Yangtze River from Jingzhou, Hubei to Tongling, Anhui along the Lianghu Plain and the West Anhui Anhui Plain and other low-lying areas, due to the large rainstorm confluence area, many tributaries are flat, the river course is curved, the drainage is not smooth, and it is sandwiched between the north and south hills., It is the area most prone to heavy rains and floods, and most of the dyke breaks and inundation disasters caused by severe floods in the Yangtze River Basin occurred in this area.
From the topographical point of view, the rainfall belt of the Yangtze River Basin is mainly located in the transitional area of plains and hills. The terrain is relatively flat, especially in the plains of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. This is the case in the lake plains. When the rainfall in the Yangtze River basin increases, floods accumulate in these plains and are not easy to discharge, so it is easy to cause flood disasters.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

