Sichuan Basin
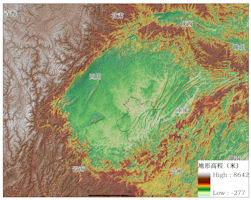 The Sichuan Basin is a famous red-bedded basin in China. Among the major basins in China, the basin has the most typical shape, the southernmost latitude, and the lowest elevation. Located in the eastern part of Sichuan Province and the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, it covers an area of more than 260,000 square kilometers, accounting for 46% of the area of Sichuan Province. The Sichuan Basin is bordered by the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Hengduan Mountains in the west, the Qinling Mountains and the Loess Plateau in the north, the western Hunan and Hubei mountains in the east, and the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau in the south. The Sichuan Basin looks like a huge meteorite crater, but in fact it has nothing to do with the meteorite crater. It is an inland sea enclosed by land. In the end, it rose up and became a lake. After drying up, it became the current basin.
The Sichuan Basin is a famous red-bedded basin in China. Among the major basins in China, the basin has the most typical shape, the southernmost latitude, and the lowest elevation. Located in the eastern part of Sichuan Province and the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, it covers an area of more than 260,000 square kilometers, accounting for 46% of the area of Sichuan Province. The Sichuan Basin is bordered by the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Hengduan Mountains in the west, the Qinling Mountains and the Loess Plateau in the north, the western Hunan and Hubei mountains in the east, and the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau in the south. The Sichuan Basin looks like a huge meteorite crater, but in fact it has nothing to do with the meteorite crater. It is an inland sea enclosed by land. In the end, it rose up and became a lake. After drying up, it became the current basin.
The Sichuan Basin belongs to the Yangtze quasi-platform, Sichuan Taiao. The pattern of the basin is mainly controlled by two structural lines northeast-southwest and northwest, forming a typical rhombic basin. Guangyuan, Ya'an, Xuyong, and Yunyang are the four vertices of the rhombus, and the east and west sides are slightly longer, ranging from 380 to 430. Kilometers, slightly shorter on both sides of the north and south, is 310 ~ 330 kilometers. The line connecting the four vertices of the above rhombus is roughly equivalent to the contour line of 650 to 750 meters in the basin, and the bottom of the basin and the edge mountains are also divided by this. The Sichuan Basin was an inland lake basin 140 million years ago. Up to 66 million years ago, the mountains on the edge of the basin uplifted rapidly, and the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River began to communicate. The lake water in the basin has laid the foundation for the current landform.
The Sichuan Basin can be clearly divided into two parts, the marginal mountains and the bottom of the basin, with an area of 100,000 and 160,000 square kilometers respectively. There are many low mountains and middle mountains on the edge of the basin, and the mountains are steep. Most of the rivers in the mountains on the edge of the basin are "V"-shaped valleys. Its hard to get to the blue sky. The ridges are mostly 2,000 to 3,000 meters above sea level, and the northwest and west can exceed 3,000 to 4,000 meters, such as Longmen Mountain, 4,984 meters, Emei Mountain, 3,099 meters, and Xiaoxiangling, 4,792 meters. The paleozoic and previous limestones are widely exposed on the surface, followed by slate, schist, crystalline limestone, quartzite, sand mudstone and conglomerate, and some granite and basalt. Karst landforms such as stone forests, karst caves, underground rivers and troughs can be seen in the limestone distribution area. Xingwen County on the southern margin of the basin is known as the "Stone Forest Cave Township". Famous mountains such as Wushan Twelve Peaks and Jinfo Mountain are also mainly developed from limestone. Mount Emei composed of limestone, basalt, granite, etc., and Mount Qingcheng composed of sand, mudstone, and conglomerate are known as "Emei World Show" and "Qingcheng World Secluded", and are famous tourist attractions in China. The bottom of the basin is mostly 250-700 meters above sea level, and the terrain is inclined to the southeast. The rivers in the basin converge from the marginal mountains to the main stream of the Yangtze River at the bottom of the basin, forming a centripetal water system. The surface is covered by a large area of Mesozoic purplish red sandstone and mudstone, so it is called "red bed basin", which is the most concentrated area of Mesozoic continental red beds in China. The Sichuan Basin is a hilly basin with hills dominated at the bottom, followed by low mountains and plains.
 The topography of the Sichuan Basin is closed, and the temperature is higher than other areas at the same latitude. The average temperature of the coldest month is 5~8°C, which is 2~4°C higher than that of Shanghai and Wuhan at the same latitude and Guiyang in the south of the latitude. The extreme lowest temperature is -6~-2°C. Frost and snow are rare, and the annual frost-free period is 280 to 350 days. Summer in all parts of the basin begins at the end of May. The summer lasts for more than 4 to 5 months. The temperature of the hottest month is as high as 26-29°C, and the Yangtze River Valley is nearly 30°C. Therefore, Chongqing is also one of the three "fire furnaces" in the Yangtze River Basin. The continuous sunny and high temperature weather in midsummer caused severe summer drought in the southeastern part of the basin. The annual average temperature is 16~18°C. The active accumulated temperature above 10°C is 4 500~6000°C, and the duration is 8-9 months. It belongs to the mid-subtropical zone. The Yangtze River valley in the southeast exceeds 6000°C, which is equivalent to the southern subtropical climate south of China's Nanling. The temperature in the basin is high in the east and low in the west, high in the south and low in the north, with high basin bottom and low margins. The distribution of isotherms is concentric. The temperature in the mountainous areas at the edge of the basin has a vertical distribution. For example, the temperature of Mount Emei and Jinfo Mountain will decrease by 0.55°C and 0.61°C every 100 meters in elevation. The annual average temperature at the top of Mount Emei is only 3°C, and the active accumulated temperature above 10°C is 586°C. The climate is equivalent to the cold temperate zone and sub-frigid zone.
The topography of the Sichuan Basin is closed, and the temperature is higher than other areas at the same latitude. The average temperature of the coldest month is 5~8°C, which is 2~4°C higher than that of Shanghai and Wuhan at the same latitude and Guiyang in the south of the latitude. The extreme lowest temperature is -6~-2°C. Frost and snow are rare, and the annual frost-free period is 280 to 350 days. Summer in all parts of the basin begins at the end of May. The summer lasts for more than 4 to 5 months. The temperature of the hottest month is as high as 26-29°C, and the Yangtze River Valley is nearly 30°C. Therefore, Chongqing is also one of the three "fire furnaces" in the Yangtze River Basin. The continuous sunny and high temperature weather in midsummer caused severe summer drought in the southeastern part of the basin. The annual average temperature is 16~18°C. The active accumulated temperature above 10°C is 4 500~6000°C, and the duration is 8-9 months. It belongs to the mid-subtropical zone. The Yangtze River valley in the southeast exceeds 6000°C, which is equivalent to the southern subtropical climate south of China's Nanling. The temperature in the basin is high in the east and low in the west, high in the south and low in the north, with high basin bottom and low margins. The distribution of isotherms is concentric. The temperature in the mountainous areas at the edge of the basin has a vertical distribution. For example, the temperature of Mount Emei and Jinfo Mountain will decrease by 0.55°C and 0.61°C every 100 meters in elevation. The annual average temperature at the top of Mount Emei is only 3°C, and the active accumulated temperature above 10°C is 586°C. The climate is equivalent to the cold temperate zone and sub-frigid zone.
The annual precipitation in the Sichuan Basin is 1,000 to 1,300 mm, and the mountains at the edge of the basin have abundant precipitation. For example, the western edge of the mountain between Leshan and Ya'an has an annual precipitation of 1,500 to 1,800 mm, which is a prominent rainy area in China, with the "Huaxi Rain Screen". Known as. However, dry winter, spring drought, summer waterlogging, and autumn rain are unevenly distributed during the year. 70% to 75% of the rainfall is concentrated in June to October. The maximum daily precipitation can reach 300-500 mm. "Bashan Night Rain" has been famous since ancient times, and night rain accounts for more than 60% to 70% of the total rainfall. The fog in the basin area is heavy and wet, with low clouds and many cloudy days. Mount Emei and Jinfo Mountain are the areas with the most foggy days in China, and the annual relative humidity is also the highest in China. The annual sunshine in the basin is only 900 to 1,300 hours, and the annual solar radiation is 370 to 420 kilojoules/square centimeter, which are both the lowest in China. Therefore, there is a saying of "the day when the dog barks in Shu".
There are nearly 10,000 species of plants in the basin, and the number of ancient and endemic species is unmatched in other regions of China. Metasequoia, silver cedar, tulip tree, sassafras, three-pointed cedar, Davidia involucrata, water green tree, scented tree, collar spring wood, gold maple, winter plum, eucommia, red bean The rare and relict plants and endemic species such as fir, bell calyx, hokkien cypress, spicia cedar, thuja, papaya red and so on. In the hot and humid valleys, there are ancient tropical relict plants, such as Alsophila spinulosa, Cylindross cylindrica, Cymbidium serrata, Osmunda japonica, Libai and other ancient tropical relics. Nature reserves have been set up in Jinfo Mountain and Jinyun Mountain respectively. Youyang on the southeastern edge of the basin also has the world's tallest white-flowered paulownia, with the tallest one reaching 44 meters.
The zonal vegetation in the Sichuan Basin is a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Its representative tree species are Castanopsis fargesii, Castanopsis emei, Castanopsis thorns, Cyclobalanopsis glauca, Manqinggang, Lithocarpus sphaerocarpa, Schima superba, Schima superba, Sichuan tea, Zhennan, Runnan, etc., the altitude is generally below 1,600 ~ 1,800 meters. Secondly, there are subtropical coniferous forests and bamboo forests composed of masson pine, fir and cypress. From bottom to top, the marginal mountains are evergreen broad-leaved forests, evergreen broad-leaved and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forests, cold-temperate mountain coniferous forests, and partially subalpine shrub meadows.
The Sichuan Basin is one of the regions with the largest and most complete animal species in China. According to statistics, in addition to fish, there are 417 species of animals at the bottom of the basin, 487 species, 317 species and 288 species in the mountains on the western, northern and southern margins of the basin, of which economic animals account for more than half. The mountains on the western edge of the basin are the regions with the best preservation and concentration of unique and ancient animals in China. The giant pandas, golden monkeys, takins, grey golden monkeys, white-lipped deer, etc. belong to the first class of protected animals. There are also rare and unique animals: red panda, snow leopard, hyena, short-tailed monkey, macaque, tufted deer, otter and mandarin duck, blood pheasant, red-bellied horned pheasant, green-tailed rainbow pheasant, golden pheasant, golden pheasant, etc.
Pingwu, Qingchuan, Beichuan, Baoxing, Tianquan, Hongya, Mabian and other places on the western edge of the basin are the main distribution areas of Chinese giant pandas. Seven nature reserves including Tangjiahe, Wanglang, Wolong, Fengtongzhai, and Hornhe River have been established for giant pandas and golden monkeys.
The giant salamanders in the mountainous valleys on the edge of the Youyang, Mabian, and Pingwu basins, and the Chinese sturgeon and white sturgeon in the Yangtze River and Jinsha River are also unique to Sichuan, and they are all protected animals.
The basin has coal, iron, natural gas, petroleum, salt, mirabilite, gypsum, phosphorus, aluminum, sulfur, copper, manganese, gold, graphite, mercury and other minerals. Among them, natural gas and mirabilite are the highest in China, and there are important strontium mines in China. The reserves of salt rock mines in central Sichuan reach 200 to 300 million tons. The reserves of hydropower resources in the basin are nearly 50 million kilowatts. Industry is concentrated, and the main industrial cities are Chengdu, Chongqing, Zigong, Yibin, Neijiang, Nanchong, Luzhou and other cities.
The basin is a famous agricultural area in China. The purple soil distributed in the basin covers an area of 140,000 square kilometers. It is neutral or neutral and is rich in mineral nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium. It has a moderate texture and good water permeability and air permeability. As early as the Western Han Dynasty, it was cultivated and planted. The land utilization rate of the basin area is as high as 30%-40%, and it is the largest rice and rapeseed production area in China. The output of sericulture, citrus, tung oil, white wax, wuzhuzi, white fungus, and coptis all ranks first in China.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

