Inner Mongolia Plateau
 Inner Mongolia spans the northeast, north and northwest of China and borders Russia and Mongolia in the north with a boundary line as long as 4,221 kilometers. The Inner Mongolia autonomous region is situated at the cross of 97"12"-126"04" east longitude and 37"24"-53"23" north latitude, with an area of 1.18 million square kilometers, spanning 1/8 the country and ranking 3rd in China’s square coverage. Inner Mongolia not only has a large area but also geographical advantages, bordering Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Jilin, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, and Gansu provinces as well as Ningxia Hui autonomous region to the east, south and west. It spans the north, northeast and northwest of China and borders Russia and Mongolia in the north with a boundary line as long as 4,221 km, thus becoming an important frontier in China's global "opening up" initiatives.
Inner Mongolia spans the northeast, north and northwest of China and borders Russia and Mongolia in the north with a boundary line as long as 4,221 kilometers. The Inner Mongolia autonomous region is situated at the cross of 97"12"-126"04" east longitude and 37"24"-53"23" north latitude, with an area of 1.18 million square kilometers, spanning 1/8 the country and ranking 3rd in China’s square coverage. Inner Mongolia not only has a large area but also geographical advantages, bordering Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Jilin, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, and Gansu provinces as well as Ningxia Hui autonomous region to the east, south and west. It spans the north, northeast and northwest of China and borders Russia and Mongolia in the north with a boundary line as long as 4,221 km, thus becoming an important frontier in China's global "opening up" initiatives.
Inner Mongolia, with a temperate continental monsoon climate, has a cold, long winter with frequent blizzards and a warm, short summer. Except for the relatively humid Greater Hinggan Mountain Area, the greater part of Inner Mongolia is arid, semi-arid and semi-humid from west to east. Average winter temperature ranges between -3.5°C and -15°C, with extreme minimum temperatures of -26°C - -50°C. In most areas, winters last for more than five months, with Hulunbuir remaining cold for about seven months. The mean summer temperature ranges between 20.1°C and 25.3°C, with an extreme maximum temperature of 35°C- 45°C.The difference in temperatures between day and night also varies greatly throughout the year.
With agriculture and stockbreeding as its main livelihood, Inner Mongolia also engages in forestry, coal mining and steel industries. The region boasts abundant natural resources, particularly minerals, and its reserves of rare earth and natural alkali rank first in China. Inner Mongolia is a special economic zone renowned as a "treasure basin", with a foremost attraction of natural beauty. Vast grasslands, mushroom-like yurts, bright sky, fresh air, rolling grass and flocks and herds moving like white clouds on the remote grassland, all contribute to relaxing and picturesque scenery. The Greater Hinggan Mountain, renowned as the "green treasure", is the largest and most preserved primitive forest. As the Kingdom of Wildlife, it is home to over 300 species of birds and 100 species of animals, 40 of which are listed as national rarities.
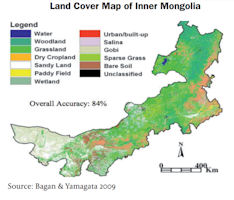
 The Inner Mongolia autonomous region has one of China's largest forested areas and is an important site for ecological protection in northern China, with 23.66 million hectares of forest, or one-eighth of the nation's total, totaling 21.03 percent of forest coverage. According to the results from the eighth forest resources inventory of the Inner Mongolia autonomous region in 2018, the area covered by trees in the autonomous region is 675 million mu, or 45 million hectares, of which the forest area spans 26 million ha. Compared with the results from the autonomous region's seventh forest resource inventory in 2013, Inner Mongolia's forest area increased by 19.04 million mu, the forest coverage rate increased by 1.07 percentage points and the forest stock – the measured volume of the trees – increased by 182 million cubic meters.
The Inner Mongolia autonomous region has one of China's largest forested areas and is an important site for ecological protection in northern China, with 23.66 million hectares of forest, or one-eighth of the nation's total, totaling 21.03 percent of forest coverage. According to the results from the eighth forest resources inventory of the Inner Mongolia autonomous region in 2018, the area covered by trees in the autonomous region is 675 million mu, or 45 million hectares, of which the forest area spans 26 million ha. Compared with the results from the autonomous region's seventh forest resource inventory in 2013, Inner Mongolia's forest area increased by 19.04 million mu, the forest coverage rate increased by 1.07 percentage points and the forest stock – the measured volume of the trees – increased by 182 million cubic meters.
The forests in the autonomous region are mainly distributed over the original forest area of the Greater Hinggan Mountains, the secondary forest area in the south of the Greater Hinggan Mountains, the Baogeda Mountain, Diyanmiao, Hexigten, Maojingba, Daqing Mountain, Manhan Mountain, Wula Mountain, Hanshan Mountain, Helan Mountain and Ejine, as well as new forest areas formed after long-term afforestation. The main tree species in Inner Mongolia are larch, birch, oak, poplar, black birch, elm, sylvestris, pine and others.
The grasslands of Inner Mongolia are an important part of the grasslands of Eurasia. The area covered by natural grasslands in the autonomous region is 1.32 billion mu. Inner Mongolia’s grassland is divided into eight categories, 21 sub-categories and 476 types. Meanwhile, Inner Mongolia’s grassland has more than 2,781 plant species. Inner Mongolia has five types of zonal grassland types: warm meadow grassland, warm typical grassland, warm desert grassland, warm grassland desertification and warm desert types, which occupy 89 percent of Inner Mongolia’s total grassland area. There are also three types of non-zonal vegetation in the autonomous region, including mountain meadows, lowland meadows and swamps, which account for 11 percent of the total grassland area of the autonomous region. The coverage of grassland vegetation in Inner Mongolia in 2018 was 43.8 percent, an increase of 13.8 percentage points compared with 2000 and the grassland ecology in some areas had recovered to the level of the mid-1980s.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

