China - Geography
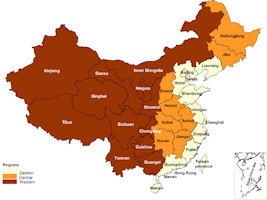
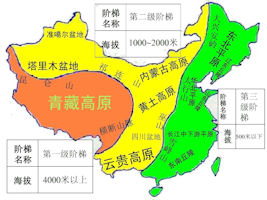
Mainland China is sometimes classified into different geographic areas, specifically eastern, central and western regions. Many economic and human development indicators are lower in the western region, compared to the eastern region. According to the National Bureau of Statistics of China, the eastern region includes 10 provinces (municipalities), namely Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, and Hainan; the central areas include 6 provinces of Shanxi, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei and Hunan; the western region includes 12 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), namely Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Tibet, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia and Xinjiang; the northeastern region includes 3 provinces, namely Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang.
In general, eastern China is relatively more developed than western China, and central China is somewhere in between. Comparing China's north and south, the southern provinces, including the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta, are more developed. One of the strongest economic areas has been the Yangtze River Delta, whose total economic output in 2018 was 2.5 trillion US dollars, close to 20 percent of the national total. In the coastal corridor, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) has also attracted much attention. By the end of 2018, the area had a combined population of about 70 million and a GDP of 1.54 trillion U.S. dollars. Guangzhou, Hong Kong, Macao, and nearby Shenzhen, are central engines that radiate and drive the development of surrounding areas.
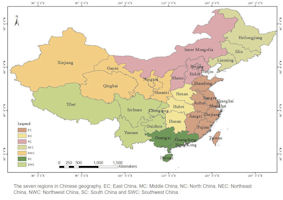
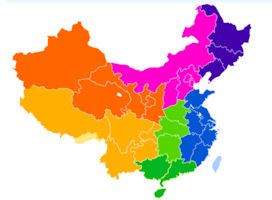
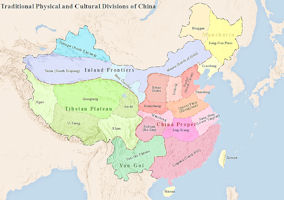
China is divided into 6 traditional great regions: Northeast China, North China, Northwest China, Southwest China, East China, Central South China (usually divided into Central China and South China, making seven regions).
For regions that have a truly individual topography and location, thus a human geographic environment entirely their own, one needs a breakdown of twelve to sixteen regions (authorities differ on the exact number). Administratively, China is divided into 23 provinces, 5 autonomous regions (Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Tibet, Ningxia, Xinjiang), 4 municipalities (Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Chongqing) and 2 Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong, Macao).

| Great Region | Provinces | area (sq.km) | population (in mil.) | Provincial Capital | ||
| Northeast China |  |
Heilongjiang | 460,000 | 38.24 | Harbin | |
| Jilin | 190,000 | 27.3 | Changchun | |||
| Liaoning | 150,000 | 42.98 | Shenyang | |||
| North China |  |
Beijing | 16,800 | 17.55 | Dongcheng | |
| Hebei | 190,000 | 69.43 | Shijiazhuang | |||
| Inner Mongolia | 1,180,000 | 24.05 | Hohhot | |||
| Shanxi | 160,000 | 33.93 | Taiyuan | |||
| Tianjin | 12,000 | 11.15 | Heping | |||
| Northwest China |  |
Gansu | 430,000 | 26.19 | Lanzhou | |
| Ningxia | 66,000 | 6.1 | Yinchuan | |||
| Qinghai | 720,000 | 5.52 | Xining | |||
| Shaanxi | 210,000 | 37.48 | Xian | |||
| Xinjiang | 1,660,000 | 20.95 | Urumq | |||
| East China |  |
Anhui | 140,000 | 61.18 | Hefei | |
| Fujian | 121,300 | 35.81 | Fuzhou | |||
| Jiangsu | 100,000 | 76.25 | Nanjing | |||
| Jiangxi | 170,000 | 43.68 | Nanchang | |||
| Shandong | 160,000 | 93.67 | Jinan | |||
| Shanghai | 6,369 | 18.58 | Huangpu | |||
| Zhejiang | 100,000 | 50.6 | Hangzhou | |||
| Central South | Central China |  |
Henan | 170,000 | 93.6 | Zhengzhou |
| Hubei | 190,000 | 56.99 | Wuhan | |||
| Hunan | 210,000 | 63.55 | Changsha | |||
| South China | Guangdong | 180,000 | 94.49 | Guangzhou | ||
| Guangxi | 240,000 | 47.68 | Nanning | |||
| Hainan | 34,000 | 8.45 | Haikou | |||
| Southwest China |  |
Guizhou | 180,000 | 39.75 | Guiyang | |
| Sichuan | 490,000 | 81.27 | Chengdu | |||
| Tibet | 1,230,000 | 2.84 | Lhasa | |||
| Yunnan | 390,000 | 45.14 | Kunming | |||
| Chongqing | 82,000 | 28.16 | Yuzhong | |||
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|