Chelomei KBR-12000 Cruise-Ballistic Rocket
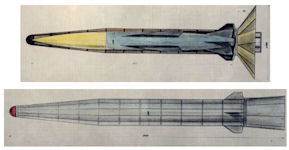
In the summer of 1959 under the personal guidance of Vladimir Nikolaevich Chelomey, using the experience of creating cruise missiles for the Navy, the development of high-altitude cruise and Cruise-Ballistic Rockets (KBR) began. In July 1959, the CBR-12000 was already in development, a three-stage cruise-ballistic rocket with a mass of 85 degrees, with a range of km, with near-orbital speed. They considered the exit into orbit. TsAGI newsletters reported that in the United States, the development of the Dyna-Soar apparatus, similar in purpose to Chelomei's rocket -glider, was underway. This strengthened the position of Chelomey.
The CBD project evolved into ballistic missile projects. As a payload, a winged rocket glider, a cruise warhead with homing appeared on the final leg of the flight, a spaceplane for flight to the planets, a controlled satellite for targeting cruise missiles. Chelomey found understanding among the leaders of the leading institutes of the State Committee on Aviation Engineering. The development of high-altitude cruise and cruise-ballistic missiles (KBR) began.
In July 1959, Chelomey's KBR-12000 was already in development, a three-stage cruise-ballistic rocket. The cruise-ballistic missile was no longer of anti-aircraft type, but had a range of 12,000 km, with a maximum speed of 6300 m / s, almost near orbital speed. It was a three-stage rocket with a 1st-tier mass of 85 tons. They also considered going into orbit. The CBD project evolved into ballistic missile projects. As a payload, a winged rocket glider, a cruise warhead with homing appeared on the final leg of the flight, a spaceplane for flight to the planets, a controlled satellite for targeting cruise missiles.
Here is the entry dated July 10, 1959, Polyachenko noted: “KBR, going into orbit: starting weight 107 tons, instead of 85 tons at KBR-12 LLC”. The number of stages in this ballistic missile, which was to go into orbit, was 4. At this time, we have the term "rocket plane". The rocket launcher was on the LRE, the launch weight was 120 tons, its first project was with planning, the number of stages was 4, the engines were LRE and powder rocket engines.
A meeting of representatives of industry and scientists was held in the Design Bureau of February 1960, at which the winged descent was considered promising. On February 18, a discussion of spacecraft schemes with Makarevsky, Dorodnitsyn, Struminsky, Simonov, Serebriysky, Petrov G. P., Taganov, Shkadov, Svishchev, Lyulka, that is, scientists of TsAGI, NII-1, TsIAM and chief designer A. M. Cradle. Chelomey argued the need for a winged descent from orbit: the arrival at a point, at a moving point. He believed that the ball, despite its simplicity, was not the machine of the future that could choose a place to land.
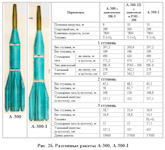
By the beginning of April 1960, drafts were prepared for both launch vehicles and spacecraft of several modifications, with which Chelomey decided to go to the Government, meaning the release of the Ordinance on their development. It was a family of A-300, A-300-1, A-300-2, A rockets. In addition, there was a family of spacecraft that were supposed to provide both long-haul flights to the planets and nearby ones for solving near-Earth urgent tasks. These proposals were filtered at all levels, both in the military department and in the leadership of industry. And on June 23, 1960, a Resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers was issued, instructing OKB-52 to develop these spacecraft.
The work on the “Rocketplan” theme was conducted in the direction of creating both manned aircraft with controlled descent from orbit and landing on the airfield, and in the direction of creating unmanned maneuvering spacecraft, including for inspection and interception of reconnaissance satellites, satellites-carriers of atomic warheads, about the development of which in the United States there were publications in open and closed sources at that time. These works were brought to the preliminary design stage and became the foundation for the subsequent development of a manned light spacecraft, on the one hand, and an anti-space defense system with an unmanned satellite fighter, on the other. The main problems on the way of creating rocket-planes were ensuring the controllability and stability of the device when entering the atmosphere and creating effective thermal protection on this leg of the flight. The flight test was the way to check the theoretical and theoretical studies and design studies. The first such test was the launch in 1961 of an experimental hyper-aerospace technology.
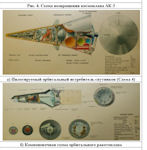
The first space projects of the OKB VN Chelomey was the device MP-1, was a full-scale model of the returned aerospace apparatus. The features of the MP-1 were its aerodynamic layout, thermal protection and control system, providing a stable flight in all parts of the trajectory. The aerodynamic layout was made according to the “Rear Brake Umbrella Container” scheme. The braking of the apparatus in the atmosphere was carried out by the brake flaps located at its bottom slice, forming an umbrella during opening. In order to stabilize, graphite rudders were installed on the conical part, and stabilization was provided on the space segment by jet air nozzles. Landing was carried out on three parachutes. Tests were carried out at the site in Vladimirovka, the battlefield was located in the area of Lake Balkhash. Launching the MP-1 the R-12 missile was produced on December 27, 1961. The program is fully implemented. The most valuable data on the ablation of heat-shielding coatings were obtained when the space hypersonic spacecraft was returned to Earth.
The next development of this direction was the M-12 spacecraft, which is a full-scale model of the AB-200 maneuvering airballis head, which at that time was in the design study for the UR-200 rocket. For stabilization and control at the atmospheric part of the flight, the M-12 unit had four titanium rudder-elevons; in the space segment of the flight, the control was provided by the micro-rhd. The M-12 was launched on March 21, 1963. on the rocket R-12. The experience gained in the field tests of these first hypersonic devices was used in subsequent projects of the enterprise.
The work program of the early 1960s envisaged a study of the possibilities of combining ballistic and aerodynamic principles to create advanced aerospace vehicles and high-performance ballistic-fighting ballistic heads. In the UR-100N UTTH rocket complexes with high-speed warheads, as well as in newly developed projects, these ideas have been put into practice.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|