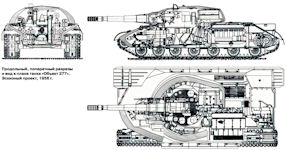
Object 277 Heavy Tank
An experimental heavy tank "Object 277" was designed in Leningrad, in the design bureau under the guidance of J. Ya. Kotin in 1957. In its design some technical solutions were used, implemented in the tanks IS-7 and T-10. The 55-ton tank had a classic layout. The hull had a cast frontal part and curved side plates. In the extended front part of the cast turret, an optical sight-range finder was installed, and in the elongated aft part - mechanized stacking of gun shots. The crew consisted of 4 people.
The tank “Object 277” was developed in Leningrad by the design bureau (OKBT) LKZ floor by the leadership of the chief designer J. Ya. Kotin in 1956-1958. To speed up the process of creating a new tank, Kotin in June 1955 divided the work on objects 277 and 278 between two specialists. At the same time, he instructed object 277 to N. F. Shashmurin, and left object 278 to N. M. Chistyakov. Each of the presenters was given three linkers. Y. Markov, V. Izotov, and E. Okhapkina worked with Shashmurin. Chistyakov worked V. Ivanov, A. Popov and O. Rodionova. Both groups were forced to work in the same room, and at first, indeed, the competition began. But the performers very soon realized that, working together and helping each other, they would complete the task better and faster. As a result, the layout of the tank was unified, and N. F. Shashmurin moved away from further development.
The basis of the machine was laid the usual "classic" layout of the tank with a rear engine and eight-way chassis. On August 12, 1955, a government decree was adopted and the deadlines for the readiness of a combat vehicle, facility 277, with a diesel engine were set. The work of designers continued.
Initially, the proposal of J. Y. Kotin was perceived as a kind of “architectural excess”, some kind of decoration, completely unnecessary. However, further elaboration of the proposal showed that the combination of a rounded, slightly convex, with large structural angles of the upper surface of the frontal part and the lower front surface pointed at the front, which is similar to the bow of a boat, made it possible to obtain a significant gain in terms of armor resistance both in front and from the side course angles the layout of the internal space and create a configuration that gives clear advantages for accommodating the tank driver.
However, when developing drawings for casting the frontal part of the body, there was a serious difficulty in combining the streamlined lower part of the forehead with the protruding sloth brackets and front suspension supports. Designers had to temporarily turn into "young sculptors." We bought several boxes of children's plasticine and began to sculpt a plasticine nose, checking each section according to patterns cut out from whatman. As a result of such painstaking work, it was possible to give the case a pretty beautiful and impressive appearance.
In December 1958, the first prototype of the tank was manufactured. Total during the years 1958-1959. two prototypes were made, which, as they were ready, were tested from January 7, 1959 to February 26, 1960. In addition, a building and a turret were made for testing by firing at the test site. The tank was developed on a single TTT with an experienced heavy tank "Object 770" ChKZ, but according to the results of the tests was inferior to the latter in a number of indicators and constructive development of some systems and units, therefore, by Resolution of the USSR Council of July 19, 1960, the work on the "Object 277" and the M-850 engine for this gank was discontinued.
The tank had a classic general layout with a disengaged accommodation of a crew of 4, the installation of a 130-mm cannon in a rotating turret and a longitudinal arrangement of diesel in the logistics. The workplace of the driver was located in the center of the control compartment in the forward part of the hull. Seats of the tank commander and gunner guns were located in the fighting compartment to the left of the gun, loader - to the right.
The tank was armed with a 130-mm rifled M-65 gun with a horizontal wedge gate, an ejection device for removing powder gases from the barrel after firing and a muzzle brake. The gun was equipped with a two-plane “Thunder” weapon stabilizer and a TPDS stereoscopic rangefinder sight, which was replaced during the tests for the rangefinder sight of the TPL-2S. When shooting at night, the TPN1 night sight was used. The angles of the vertical alignment of the paired installation ranged from -5 to + 16 °. The rotation mechanism of the turret had a hydrostatic and manual control drives. The tank used an automatic fire control system. The range of a direct shot by an armor-piercing projectile at a target height of 2 m was 1230 m. Developed in 1959, the armor-piercing sabot projectile for this gun had a direct shot range of 2150 m.
Ammunition for the gun consisted of 35 shots of separate-cartridge loading. Mechanized installation of the cassette type with electric drive was designed for 15 shells and 15 sleeves. The shells were positioned vertically in the conveyor of the loading mechanism, and the liners were placed horizontally in the conveyor of the loading mechanism installed in the turret niche. The mass of the armor-piercing projectile was 30.7 kg, therefore an electromechanical rammer was used to facilitate the loading of the gun. An armor-piercing projectile with a starting speed of 1030 m / s at a distance of 1000 m punched a vertically positioned armor plate with a thickness of 280 mm. An armor-piercing projectile, which had a mass of 8.7 kg and an initial velocity of 1800 m / s from the same range, pierced the armor with a thickness of 350 mm. The length of the gun barrel was 7330 mm, the pressure of the powder gases - 441 MPa (4500 kgf / cm), muzzle energy -16, 4 MJ (1665 tcm). The length of the tank with a cannon forward reached 11,780 mm, which limited its maneuverability when driving on rough terrain, decree of military actions in the city, in the woods, in the mountains, etc. With the gun was paired 14.5-mm machine gun KPVT, which could be used as sighting. Ammunition to the twin machine gun was 800 rounds.
The frontal armor of the tank was supposed to provide protection from 122-mm armor-piercing and 90-mm cumulative projectiles, but when shelling the hull and turret it turned out that they could not do that. The hull of the tank had a molded bow and curved side plates. The upper part of the cast armor barriers had a variable thickness from 140 to 89 mm at angles of inclination from the vertical, respectively, 60 and 70 °. The thickness of the lower nose decreased from 153 to 138 mm while simultaneously increasing the angle of inclination from the vertical from 50 to 55 °. The thickness of the armor of the upper belt side, inclined at an angle of 60 ° from the vertical, was 112-90 mm, the lower belt was a vertically located armor plate with a thickness of 97-90 mm. The aft hull had an armor thickness of 50 mm with a tilt angle of 50-20 °. The thickness of the armor roof of the case was 20 mm.
The cast turret with a welded roof had a variable thickness of armor in the frontal part from 290 to 139 mm with tilt angles from 30 to 60 ° from the vertical. The turret also had variable armor thickness from 236 to 138 mm and a variable tilt angle from 30 to 55 °. The thickness of the roof of the turret - 30-20 mm. The junction of the turret with the roof of the hull was closed. The tank was equipped with anti-nuclear protection system, thermal smoke equipment and automatic carbon dioxide fire-fighting equipment with thermal sensors. Along the longitudinal axis of the tank was installed a twelve-cylinder V-shaped four-stroke diesel M-850 supercharged by a drive centrifugal supercharger and a liquid ejection cooling system. The 800 kW tank engine (1090 hp) was created by the Zvezda plant in Leningrad based on the M-50 diesel engine for torpedo boats.
For a number of parameters, it was significantly inferior to tank diesel engines developed during that period. In addition, the diesel engine was not working reliably and therefore further work on it was stopped. The unsuccessful attempt to use an aircraft diesel engine in a tank once again showed the need to develop special tank diesel engines. The engine was started using an electric starter C-3 with a power of 18 kW (25 hp) or compressed air from two five-liter air cylinders. To ensure engine start-up in winter conditions, a nozzle heater is installed in the heating system. The capacity of the fuel tanks located inside the case was 820 liters, the external fuel tanks - 250 liters. Cruising the tank on the highway reaches. 1300 km. In the air cleaning system used a two-stage air cleaner, consisted of a cyclone apparatus and a cassette with oiled wire. Removal of dust from the bunker was carried out using an ejection device.
In a single unit with an engine, a manual transmission was mounted with an eight-speed planetary gearbox and a “ZK” type turning mechanism, developed on the basis of the transmission of the T-10 serial tank. Turning disc brakes and friction discs of the friction gearbox devices worked in oil and were placed in a heated crankcase. Hydraulic servos were used to control the friction elements of the planetary gearbox and the steering mechanism. Stopping brakes - belt driven by a pedal and steering levers. The onboard gearboxes were double-row combined.
The suspension system used a beam torsion bar suspension, lever-piston hydraulic shock absorbers on the first, second and eighth nodes, as well as rubber limit stops of the balancers, except for the last balancers, for which spring stops were provided. For the tank “Object 277” a suspension system was also developed, which included relaxation piston hydraulic shock absorbers. In the caterpillar drive, there were used double-disc track rollers with internal damping, caterpillars with OMSh and fixed tubular borated fingers, as well as screw mechanisms of caterpillar tension. On the side of each side, eight support and four support rollers were installed. The average ground pressure was 72 kPa (0.73 kgf / cm). The mass of the chassis was 9220 kg.
The tank had night vision devices for the commander and driver, a system of hydro-pneumatic cleaning of observation devices, and was adapted to overcome water obstacles along the bottom. In the electrical system, electricity sources were four batteries 12ST-70 and starter-generator SG-10. For external and internal communication, the radio station R-113 and the tank intercom R-120 were used respectively.
Total during the years 1958-1959. two prototypes were made, which, as they were ready, were tested from January 7, 1959 to February 26, 1960. The tank was developed in parallel with Object 770, but according to the test results it was inferior to it in a number of indicators. On July 19, 1960, work on Object 277 was discontinued. On the basis of the experimental tank "Object 277" was developed an experimental tank "Object 278", which differed from the last installation of the gas turbine engine GTD-1 and the design of the planetary gearbox. Works on the tank "Object 278" and the engine GTD-1 were discontinued in accordance with the Decree of the USSR Council of Ministers on July 19, 1960.
| State created | 1957. |
| developer | SKB LKZ |
| manufacturer | LKZ |
| Production | prototype |
| Crew, people | 4 |
| Combat weight, t | 55 |
| Length mm | |
| with a gun ahead | 11780 |
| hull | 6990 |
| Width, mm | 3380 |
| height of the roof of the turret, mm | 2292 |
| Clearance, mm. | 435 |
| ground pressure, kg / cm | 178; 0.75 |
| Overcoming obstacles: | |
| rise, hail | 35 |
| ford, m | 1.2 |
| Type of engine | diesel M-850 |
| Maximum power, hp | 1000 |
| Fuel capacity, l | 1040 |
| Specific power, hp / t | 18.2 |
| Maximum speed, km / h | 55 |
| range, km | 300 |
| armor, mm: | |
| forehead case. | 140-153 |
| turret forehead | 290 |
| Armament | |
| main gun | 130 mm M-65 |
| ammunition, pieces | (35) |
| machine gun | 14.5 mm KPVT |
| ammunition, pieces | 804 |
| Electronics |
|

|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|