B-3 armored transporter
The B-3 armored personnel carrier was developed in the design bureau of the Automobile Plant named after Stalin in 1944. The B-3 armored personnel carrier became one of the first in the USSR of such multi-purpose means. The B-3 armored personnel carrier was an armored half-track vehicle, created on the basis of units and parts of a ZIS-5 truck and a T-70 light tank. [Some accounts report that a small series of the B-3 armored personnel carrier was developed and produced at the Moscow ZIS plant in 1939, based on the ZIS-22 car, but this is "alternate history"].
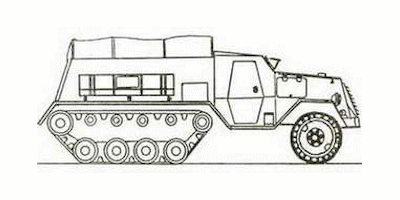
At the beginning of 1944, the VMS manufactured an experienced B-3 12-seat armored personnel carrier (sometimes referred to as AT-3 in reports, although this unarmored vehicle, built in September 1943, can only be viewed as a B-3 chassis) with model armor made from boiler steel 6-15 mm thick, armed with a large-bore machine gun DShK on an open turret. The hull of the B-3 was welded from armor plates and is open at the top, the machine gun is mounted openly on the pin from the side of the case. To improve cross-country ability, the armored personnel carrier has a tracked propulsor of two carriages and two tracked rubber-metal belts. When driving in the snow on the front wheels skis were attached.
The B-3 was built according to a layout scheme with a front engine, front steering wheels, driving tracked propulsion and an amphibious compartment open at the top. The body of the armored personnel carrier was welded from boiler steel 615 mm thick, so its booking was of a mock-up nature. Steel sheets were installed everywhere with rational angles of inclination, especially accentuated in frontal projection and aft.
In the control compartment, located behind the engine compartment on the left, the driver was sitting, on the right, the vehicle commander. They were surveyed by windows in a sloping frontal sheet, which were equipped with armored tires with viewing slots and bullet-proof observation devices, as well as small narrow windows in the side doors covered by internal armored flaps. Behind the control compartment was an open troop compartment, designed to transport ten infantrymen with full equipment. In case of bad weather, a canvas awning unfolded over it on four arcs. In front of the troop compartment on the open turret was mounted a 12.7-mm machine gun DShK. In the engine compartment in front of the car was installed carburetor six-cylinder in-line engine liquid cooling ZIS-16.
The chassis of the armored personnel carrier included a front driving axle with lean-to wheels, large-section tires with developed herringbone lance, and a tracked propulsion unit, which applied to one side, consisted of four rubber-coated road wheels, front-wheel drive with detachable gear a wreath, the directing wheels, similar on the device to a basic skating rink, three supporting rollers and a caterpillar tape. The elements of the caterpillar drive were borrowed from the T-70M light tank, and the car units were borrowed from the ZiS-5 car.
To drive in the dark, the armored personnel carrier was equipped with headlights that were mounted on brackets above the front wings on either side of the engine compartment louver. Both the front and rear wings were made of flat sheets of steel, had an angular shape and were connected at the bottom of the steps. According to the project, the welded hull had to be made of armor plates 6 and 15 mm thick, located with rational angles of inclination. On the prototype, the machine body was made of sheets of structural steel of similar thickness.
Ground tests at the NIBT site, which showed negative results due to the engine overheating and the extremely low reliability of the units and parts of the machine. Due to the low reliability of the prototype and the negative test results, the work on the project, as well as on semi-tracked armored vehicles in general, was curtailed, and the B-3 did not leave the prototype stage.
| Armored personnel carriers | |
| built | |
| developer | Moscow Plant ZIS |
| Manufacturer | Moscow Plant ZIS / Likhachev Plant |
| Production | 1, or "small series" |
| Base | ZIS-22 |
| Wheel formula | semi-tracked. |
| Combat weight, t | 7.1 |
| Length, mm | 6530 |
| Width, mm | 2350 |
| Height, mm | 2400 |
| Clearance, mm. | 330 |
| ground pressure, kg / cm | # 178; 0.3 |
| Engine type | carburetorn. ZIS-16 |
| Maximum power, hp | 85 (73) |
| Specific power, hp / t | 12 |
| Maximum speed, km / h | 40 |
| range, km | 150 |
| Fuel reserve, l. | 150 |
| Armor, mm: forehead case | 15 |
| Crew, people | 2 |
| Armament: | machine guns 12,7 mm DShK |
| radio station | No |
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|




