Boeing Model 853
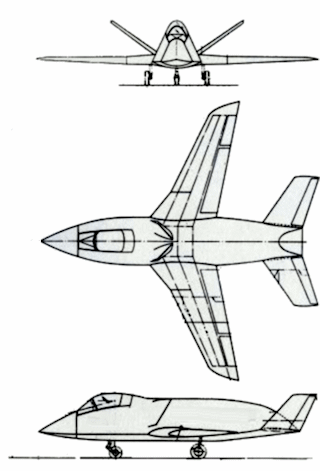
The Quiet Bird was a version of the Boeing Model 853 which started out as an Army observation airplane study. A version of the 853 study was used to test materials and shapes that would reduce radar cross sections (RCS). The result was a strangely modern design quite unlike the fasceted design of the much later F-117 stealth fighter. Only recently come to light, their Model 853, aka "Quiet Bird," was a tactical fighter design that incorporated many of the features now common to stealth aircraft. These included:
- A chine-line that separates a smooth, curved bottom from a trapezoid-shaped fuselage.
- Canted tails.
- Low-observable inlets and curved ducts.
- A exhaust designed to shield the infra-red signature from the ground and sides.
The model of Quiet Bird was said to have been tested at Boeings Wichita facility in 1962-1963, all of which occurred on a radar range. No actual flight testing of Quiet Bird itself was said to have happened. The tests reportedly achieved excellent results in reduced radar cross section, but it was a bit ahead of its time and did not generate interest from the military.
The lessons learned on Quiet Bird probably did influence the design of the Boeing AGM-86 Air Launched Cruise Missile. Internally Boeing continued to work on the non-metallic structures aspects that were pioneered with Quiet Bird, and that effort eventually lead to the use of increasingly larger and more complex composite structures in Boeing aircraft.
| Crew | 1 |
| Length | 33 ft (10.06 m) |
| Wingspan | 33.65 ft (10.26 m) |
| Height | 7.7 ft () |
| Wing area | 179.5 sq ft (16.67 m²) |
| Airfoil | 65A415 |
| Empty weight | 6000 lb (2721 kg) |
| Loaded weight | 8150 lb (3696 kg) |
| Powerplant | 1 × General Electric CF700 , 4,200 lbf (18.7 kN) |
| Cruise speed | 0.7 mach |
| Stall speed | 80 kn () |
| Range | 1160 nmi () |
| Service ceiling | 47,000 ft () |
| Rate of climb | 3,050 ft/min () |
| Wing loading | 45.4 lb/(sq ft) (221 kg/m²) |
| Thrust/weight | 0.52 |
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|




