Appendix D
Radio Emission Designator
The emission designator consists of the necessary bandwidth and emission classification symbols. The symbols are shown below.
- First symbol - Indicates the type of modulation of the main carrier. (See Table D-1.)
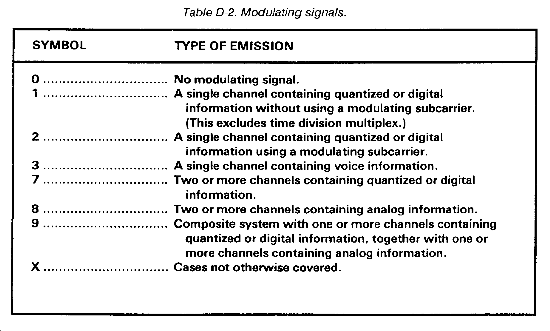
- Second symbol - Indicates the nature of signal(s) modulating the main carrier. (See Table D-2.)
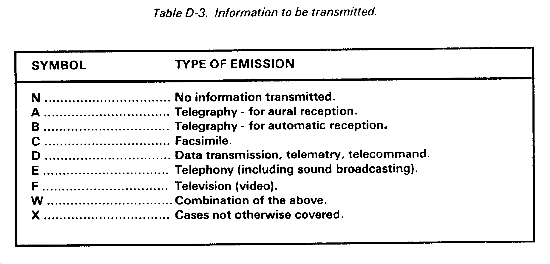
- Third symbol - Indicates the type of information transmitted. (See Table D-3.)
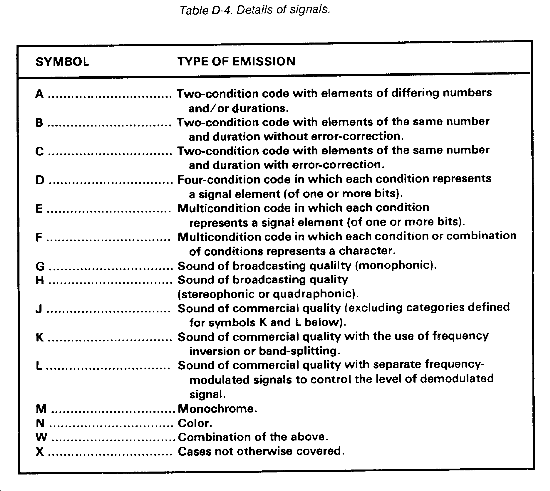
- Fourth symbol - Indicates the details of the signal (Optional - recommend use when applicable). (See Table D-4.)
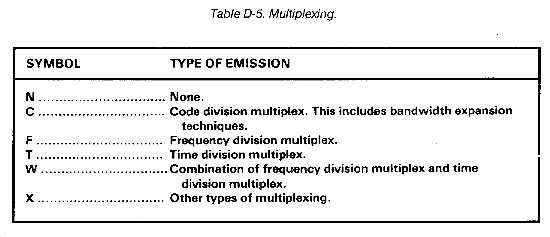
- Fifth symbol - Indicates the nature of multiplexing (Optional - recommend use when applicable). (See Table D-5.)
NOTE: Emissions, where the main carrier is directly modulated by a signal which has been coded into quantized form (for example, pulse code modulation), shall be designated as either an emission in which the main carrier is amplitude-modulated or an emission in which the main carrier is angle-modulated.
The emission designator shall be entered according to the rules shown below.
- To express the necessary bandwidth portion of the emission designator, enter a maximum of five numerals and one letter. The letter occupies the position of the decimal point and represents the unit of bandwidth as follows: H for hertz, K for kilohertz, M for megahertz, and G for gigahertz.
- Fractional bandwidths may be expressed to a maximum of two decimal places following the letter. The first character of the necessary bandwidth shall always be greater than zero unless the necessary bandwidth is less than 1 hertz. In such a case, the first character shall be the letter H. Express the necessary bandwidths according to the discussion below.
Necessary bandwidths between .01 and 999.99 Hz shall be expressed in hertz using the letter H instead of the decimal. (For example, 15H is 15 Hz of bandwidth; 15H01 is 15.01 Hz of bandwidth.)
Necessary bandwidths between 1.00 and 999.99 kHz shall be expressed in kilohertz using the letter K instead of the decimal. (For example, 2K is 2 kHz of bandwidth; 2K85 is 2.85 kHz of bandwidth.)
Necessary bandwidths between 1.00 and 999.99 MHz shall be expressed in megahertz using the letter M instead of the decimal. (For example, 6M is 6 MHz of bandwidth; 6M25 is 6.25 MHz of bandwidth.)
Necessary bandwidths between 1.00 and 999.99 GHz shall be expressed in gigahertz using the letter G instead of the decimal, (For example, 10G is 10 GHz of bandwidth; 10G05 is 10.05 GHz of bandwidth.)
- Enter the basic emission designator of three symbols, and if desired, two optional, additional symbols, derived from the following:
The first symbol designates the main carrier's type of modulation. (See Table D-1.)
The second symbol designates the nature of signal(s) modulating the main carrier. (See Table D-2.)
The third symbol designates the type of information transmitted. In this context the word information does not include information of a constant, unvarying nature such as provided by standard frequency emissions or continuous wave and pulse radars. (See Table D-3.)
The fourth symbol designates the details of signal(s) and is optional. (See Table D-4.)
The fifth symbol designates the nature of multiplexing and is optional. (See Table D-5.)
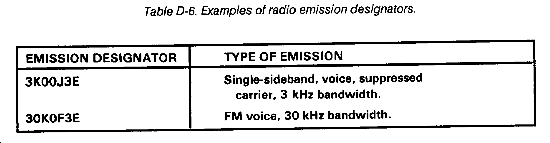
Table D-6 shows examples of radio emission designators.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|