Chapter 4
Conduct-of-Fire Trainer (COFT)
The COFT is an M1/M1A1 tank gunnery training device for TC/gunner teams. Its primary purpose is to sustain basic gunnery skills and increase combat gunnery skills. The COFT places the TC and gunner in a realistically simulated crew station and presents them with a full range of computer-controlled engagement situations. The COFT produces full-color, computer-generated action scenes in which crew members interact with various target situations. Programmed exercises vary in target type and number, range, vehicle and target motion, visibility, and other complex conditions. The crew is in no danger, no fuel is consumed, and no ammunition is expended. The result is challenging, progressive gunnery training. For convenience, the COFT has a mobile unit (MCOFT) that is predominantly used by National Guard units, and provides the same training values as the COFT (see Figure 4-4).
COFT Configurations
There are two different configurations of the COFT general-purpose computer (GPC) system: VAX 11/780 and MICRO VAX II. The VAX 11/780 consists of a double-wide main console with an expansion cabinet side-by-side (see Figure 4-1).
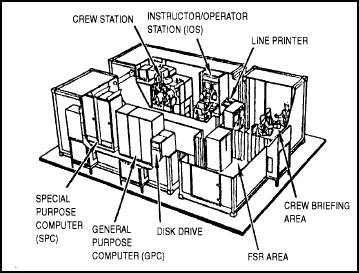
Figure 4-1. COFT with VAX 11/780 GPC components.
The MICRO VAX II consists of a lowboy console containing the mass memory disk drive and a central processing unit (CPU) with the main control panel (see Figure 4-2).
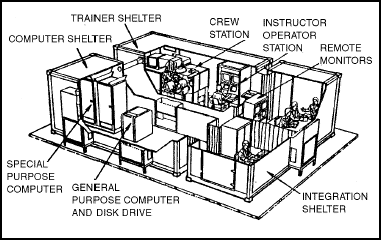
Figure 4-2. COFT with MICRO VAX II GPC components.
COFT Components
The COFT consists of three shelters: integration shelter, computer shelter, and trainer shelter.
- Integration shelter. The integration shelter contains the crew briefing area, the remote monitors, and the field service representative (FSR) area.
- Computer shelter. The computer shelter includes the GPC, the special-purpose computer (SPC), and the disk drive.
- Training shelter. The training shelter contains the crew station and the instructor/operator station (IOS) (see Figure 4-3).
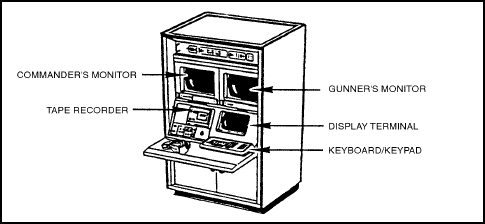
Figure 4-3. COFT instructor/operator station.
The hardware in the IOS includes—
- TC's and gunner's color monitors. These monitors allow the instructor/operator (IO) to see the same scenes (including reticles) as viewed through the TC and gunner sights.
- Tape recorder. The tape recorder allows the IO to record and play fire commands and crew responses.
- Display terminal. Instructions on the display terminal explain what the IO must do to begin the training exercises and run maintenance routines.
- Keyboard/keypad. The keyboard/keypad allows the IO to select and control training exercises, obtain desired displays or printouts, act as driver and loader, and run maintenance routines.
- Printer. The printer enables the IO to print records of crew performance, which he uses to debrief and prebrief the crew and plan future training. At the end of a training session, the IO may print a summary of all exercises fired during that session.
| Note. | The operator's manual describes the COFT hardware in detail. |
MCOFT Components
The MCOFT consists of three shelters: covered walkway/main entrance, computer shelter, and trainer shelter.
- Covered walkway/main entrance. The covered walkway/main entrance is the transition point for personnel to enter the training shelter or the FSR/IO to enter the computer shelter.
- Computer shelter. The computer shelter for the VAX 11/780 (see Figure 4-4) includes the GPC, SPC, and the disk drive. The computer shelter for the MICRO VAX II (see Figure 4-5) includes the GPC and SPC.
- Training shelter. The training shelter contains the crew station and the IOS.
| Note. | The operator's manual describes the MCOFT hardware in detail. |
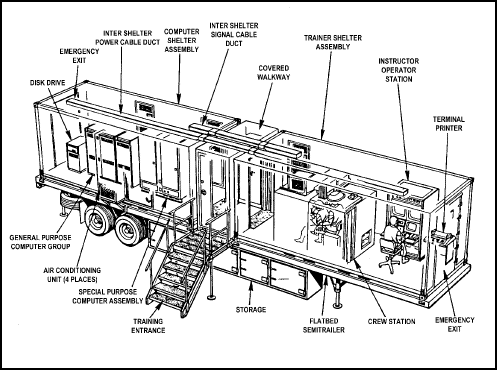
Figure 4-4. MCOFT with VAX 11/780 GPC components.
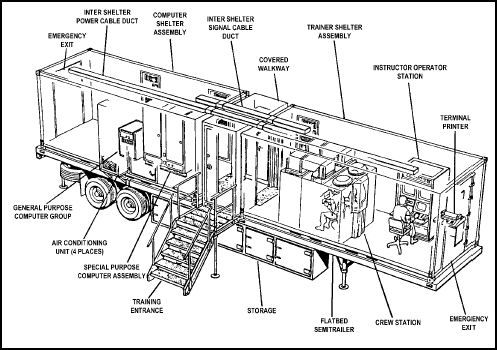
Figure 4-5. MCOFT with MICRO VAX II GPC components.
Capabilities and Limitations
Although the COFT places the TC and gunner in a realistically simulated crew station and presents them with a full range of computer-controlled engagement situations, some functions of the TC and gunner stations are physically simulated and some are not.
CAPABILITIES
The COFT provides initial, refresher, and sustainment training for tank commander/gunner teams. The system utilizes computer-generated visual scenes, targetry, and special effects to simulate the engagement of targets. The majority of the fire control system is replicated in both physical and functional aspects. The system trains both fully operational and degraded-mode gunnery techniques under a wide variety of conditions.
The system simulates the following visual effects:
- Multiple, single, and delayed targets (T-72, BMP, BRDM, ZSU-23-4, HIND-D, truck GAZ-69, MI-8C, rocket-propelled grenade [RPG] team, troops, M1, M2/M3, M60A3, and AH-64).
- Varied ranges, speeds, exposure times, and reactive targets.
- Own-vehicle moving and stationary.
- Round tracer.
- Scene obscuration.
- Round impact and effect on target.
- Round impact on terrain.
- Catastrophic kill.
- Mobility kill (advanced matrix).
- Friendly fire.
- Enemy direct and indirect fire.
- Own vehicle hit and kill.
The system provides the following visibility conditions:
- Day unlimited.
- Day with haze.
- Day with fog.
- Dawn and dusk.
- Night unlimited.
- Night with thermal clutter.
- Mortar illumination (advanced matrix).
The system provides the following aural cues to the crew:
- Enemy direct and indirect fire.
- Round loading and reloading sounds.
- Loader's "UP."
- Main gun, M240, and M2 machine gun firing.
- Track clatter.
- Engine and transmission sounds.
- Gun jump.
- TIS cooling fan.
- Turret blower.
- Own vehicle hit and kill.
- Ammunition transfer sounds.
LIMITATIONS
The following items are not functionally simulated on the COFT:
- TC's periscopes. The forward unity periscope is operational; the other periscopes around the TC's hatch are not operable.
- Caliber .50 (not physically simulated). The commander can fire the caliber .50 only from the closed hatch position. The sights, elevation, firing, and traversing mechanisms are simulated on the COFT. The components of the caliber .50 on the outside of the tank are not simulated on the COFT.
- LOW BAT CHG light, CKT BKR OPEN light, and ENGINE FIRE on the TC's panel on the M1 tank. Air temperature control and NBC alarm mute control for the M1A1 (lamps will light when tested).
- Hydraulic pressure gauge.
- Gunner's unity periscope.
- Ammunition temperature gauge.
- Gunner's TIS focus knob.
- Coax machine gun. The coax machine gun is partially simulated. Manual fire cannot be accomplished. The charging handle can be used to apply immediate action for simulated stoppages.
- Driver's and loader's stations (not simulated).
- Exterior turret components (not simulated).
| Note. | See TM 55-6920-744-15, Transportability Guidance for Trainer, Mobile Conduct-of-Fire, 12 Apr 94, for set-up and tear-down time that is required of the system. |
COFT Training
The key to a successful COFT training program is to make sure there are trained, competent personnel operating and managing the COFT.
COFT Instructor/Operator
The IO is critical in COFT training and must be well trained and highly motivated. Operation of the COFT is simple, but quality training requires an IO with an in-depth knowledge of the tank and tank gunnery. COFT IOs perform the following duties:
- Place the COFT in operation.
- Prepare for COFT training (analyze crew records, plan the training session, prepare and conduct briefings).
- Conduct prepare-to-fire and screening exercises.
- Conduct training sessions.
- Conduct AARs.
- Power down the COFT.
- Perform operator maintenance.
- Maintain crew records.
SENIOR INSTRUCTOR/OPERATOR (SIO)
The SIO is the subject matter expert on the COFT; he is the only person who can certify new IOs and make changes in the COFT training management subsystem. SIOs perform the following duties:
- Train new IOs using the exportable training packet (ETP).
- Supervise IOs, to include:
- Recertify IOs annually.
- Help the unit commander set up a COFT training program.
- Serve as training manager, as directed.
- Manage COFT training records.
- Reposition crews in the matrix (as required).
- Train IOs on the advanced matrix.
— Inspect COFT training.
— Maintain IO proficiency.
— Evaluate training.
MASTER GUNNER
The master gunner should be IO certified and should attend the SIO course. He performs the following duties:
- Help the unit commander plan and implement the total gunnery program.
- Make sure gunnery skills are taught to standard (quality control).
- Coordinate with the SIO on matters pertaining to the COFT.
TRAINING MANAGER
The battalion S3 and master gunner manage the COFT training program. The training manager should attend the following training:
- COFT Instructor/Operator Course (new equipment training [NET] or ETP certified).
- Senior Instructor/Operator Course (United States Army Armor School [USAARMS]).
- Advanced Matrix Instructor/Operator Course.
Training with COFT
The COFT training program consists of a suite of software that contains a structured training exercise library designed to train combat-critical TC/gunner gunnery tasks. Training guidelines have been established to ensure proper proficiency levels are achieved before executing these tasks on the actual vehicle. Crews that follow these guidelines should achieve a greater percentage of first-round target hits.
COFT TRAINING PROGRAM SOFTWARE
The COFT software includes two different training program matrixes—the original matrix and the advanced matrix. The IO selects the training program that is appropriate for each crew.
ORIGINAL MATRIX
COFT training in the original matrix is progressive training that develops TC/gunner team skills over an extended period of time. The training subsystem built into the COFT offers four programs with specific minimum skill levels. The minimum skills required to progress through the matrix are based on crew performance under a variety of conditions. Teams attaining or surpassing minimum requirements progress through the matrix to certification. The original matrix includes 689 training exercises (see Table 4-1).
| EXERCISE LIBRARY FOR M1/M1A1 COFT (Original Matrix) | |
| Orientation | 1 Sustainment Orientation 1 Basic, Cross, and Transition Orientation |
| Preparation | 1 Preparation for Operation |
| Boresight, Calibration, and Zeroing | 3 Exercises |
| Acquisition and Manipulation | 5 Gunner Exercises 4 Commander Exercises |
| Evaluation | 4 Training Exercises |
| Killer Tank | 2 Training Exercises ( European Environment) 2 Training Exercises (Desert Environment) |
| TC Only | 126 Training Exercises (European Environment) 30 Training Exercises (Desert Environment) |
| TC/Gunner | 390 Training Exercises (European Environment) 120 Training Exercises (Desert Environment) |
| Total | 689 Training Exercises |
Table 4-1. COFT original matrix.
The original matrix includes training programs for four levels of gunnery training:
- Sustainment—experienced M1 or M1A1 TCs and gunners.
- Transition—qualified tank crewmen with no M1 or M1A1 experience.
- Cross—M1 or M1A1 crewmen who are inexperienced as TCs or gunners.
- Basic—prospective M1 or M1A1 TCs or gunners who have had no previous tank crew experience.
ADVANCED MATRIX
The advanced matrix is designed to train and sustain the TC's and gunner's proficiency in critical combat gunnery skills. Prior to the start of each training session, the crew is required to conduct a prep-to-fire check. The crew must boresight the main gun, zero the coax machine gun, and enter all environmental and ballistic data into the ballistic computer. The crew is then required to conduct the live-fire accuracy screening test (LFAST) as defined in FM 17-12-1-1, Chapter 4. The boresight procedures are also included as an appendix in the Instructor Utilization Handbook (IUH) for the advanced matrix. The advanced matrix contains a total of 126 exercises (see Table 4-2).
| Note. | Failure to perform correct boresight procedures will cause crews to be unable to hit targets after entering the training matrix. |
| EXERCISE LIBRARY FOR M1/M1A1 COFT ( Advanced Matrix) | |||
| Prepare-to-Fire | 1 Exercise | ||
| Practice | 4 Optical Improvement Package (OIP) Exercises | ||
| Practice | 4 Tank Table V Exercises | ||
| Practice | 42 Practice Gate Exercises | ||
| Group 1 | 16 Training Exercises | ||
| Gate | 15 Live-Fire Prerequisite Exercises | ||
| Group 2 | 16 Training Exercises | ||
| Group 3 | 16 Training Exercises | ||
| Group 4 | 12 Training Exercises | ||
|
|||
Table 4-2. COFT advanced matrix.
The advanced matrix is designed for battle-roster (sustainment) crews and includes training for five levels of proficiency:
- Group 1—basic gunnery skills.
- Gate—live-fire prerequisite skills.
- Group 2—combat gunnery skills.
- Group 3—advanced combat gunnery skills.
- Group 4—sustainment gunnery skills.
The advanced matrix contains a selection of exercises designed to train crews on Tank Tables V and VIII tasks. Tank Tables I through III can be trained on the COFT using the guidelines outlined in Table 4-3.
| COFT | |
| Table I | Through Reticle Aim 14. |
| Table II | Through Reticle Aim 14. |
| Table III | Tasks 1 through 9, Day. Exercise 312110 with IO announcing degraded conditions to the crew. Tasks 10 through 15, Day and 1 through 8, Night. The IO uses the Advanced Matrix Special-Purpose Exercise Builder. |
Table 4-3. COFT tank gunnery tables.
TRAINING GUIDELINES
The TC and gunner should master the preparatory tank gunnery training requirements as outlined in FM 17-12-1-2, Chapter 13, before beginning COFT training. Although the COFT can be used for part of this training, it is more efficient to train to minimum proficiency before training on the COFT.
Crews should be required to complete Group 2 in the original matrix and Group 1 and a gate exercise (live-fire prerequisites) of the advanced matrix during an intense initial training period. For an average TC/gunner combination, this intense initial training phase should take approximately 20 hours of trainer time (10 2-hour training sessions). The goal for completing the intense training phase should be within 60 days of the TC/gunner combination being battle-rostered.
Minimizing crew turbulence is crucial to ensuring all battle-rostered crews receive, as a minimum, four hours of COFT training monthly. The goal of only 20 percent of battle-rostered crews being in the intensive training phase should be used to ensure all crews receive adequate training time.
Training milestones for COFT and the approximate time to achieve them are shown in Table 4-4.
| COFT TRAINING MILESTONES | ||
| Milestone | Description | Training Time (approximate) |
| Initial Training | Initial training consists of tank combat training before beginning COFT training. The following skills are trained in the initial phase:
|
15 to 20 hours. |
| Intensive Training | Intensive training on the COFT is used to build skills to a level that can be retained with less frequent training sessions. Intensive training should be used to complete the following:
Note. Groups 3 through 6 of the original matrix are used for remedial training for new crews or crews who have difficulty in the advanced matrix. |
Through Group 2 (original matrix)— 10 to 15 hours. Group 1 and Gate (advanced matrix)— |
| Intermediate Gunnery Training | Group 2 (advanced matrix). |
12 to 15 hours |
| Advanced Gunnery Training |
Group 3 (advanced matrix). Crew certifies when they successfully complete Group 3 of advanced matrix. |
14 to 17 hours |
| Sustainment Training | Group 4 (advanced matrix, unlimited configurations of exercises). | Unlimited replications. |
Table 4-4. COFT training milestones.
Once crews have reached the minimum prerequisites to live fire, they should continue to progress through the matrix using computer recommendations, attempting to reach the sustainment level of group 4. It is not recommended that crews be moved back in the training matrix after completing a gunnery cycle. The advanced matrix is designed to continue to train combat-critical gunnery skills under progressively more difficult conditions.
An example of a COFT training schedule for one training day is shown in Table 4-5.
| SAMPLE BATTALION TRAINING SCHEDULE | |||||
| DAY 1 | |||||
| Time | IO 1 | IO 2 | |||
| 0600 | Arrive at COFT/Power up COFT | ||||
| 0630 | Prepare prebrief | ||||
| 0650 | Crew A arrives at COFT/Prebrief Crew A | ||||
| 0700 | Training Session | ||||
| 0730 | Training Session | Arrive at COFT/Prepare prebrief | |||
| 0750 | Training Session | Crew B arrives at COFT/Prebrief Crew B | |||
| 0800 | Debrief Crew A | Training Session | |||
| 0810 | Break | Training Session | |||
| 0850 | Monitor station | Training Session | |||
| 0900 | Training Session | ||||
| 0910 | Training Session | ||||
| 0950 | Training Session | ||||
| 1000 | AAR Crew A | Training Session | |||
| 1015 | Break/Prepare prebrief | Training Session | |||
| 1050 | Crew C arrives at COFT/Prebrief Crew C | Training Session | |||
| 1100 | Training Session | AAR Crew B | |||
| 1115 | Training Session | Break/Prepare prebrief | |||
| 1150 | Training Session | Crew D arrives at COFT/Prebrief Crew D | |||
| 1200 | Debrief Crew C | Training Session | |||
| 1210 | Break | Training Session | |||
| 1250 | Monitor station | Training Session | |||
| 1300 | Training Session | Debrief Crew D | |||
| 1350 | Training Session | Monitor station | |||
| 1400 | AAR Crew C | Training Session | |||
| 1415 | Off | Training Session | |||
| 1500 | AAR Crew D | ||||
| 1515 | Off | ||||
| IO 3 | IO 4 | ||||
| 1430 | Arrive at COFT/Prebrief | ||||
| 1450 | Crew E arrives at COFT/Prebrief Crew E | ||||
| 1500 | Training session | ||||
| 1530 | Training session | Arrive at COFT/Prepare prebrief | |||
| 1550 | Training session | Crew F arrives at COFT/Prebrief Crew F | |||
| 1600 | Debrief Crew E | Training session | |||
| 1610 | Break | Training session | |||
| 1650 | Monitor station | Training session | |||
| 1700 | Training session | Debrief Crew F | |||
| 1710 | Training session | Break | |||
| 1750 | Training session | Monitor station | |||
| 1800 | AAR Crew E | Training session | |||
| 1815 | Off | Training session | |||
| 1900 | AAR Crew F | ||||
| 1915 | Power down/off | ||||
|
|||||
Table 4-5. Sample COFT training schedule.
| Note. | The two crews in the Headquarters Tank Section are usually attached to one of the line companies and share in that line company's 60 hours of COFT training time; each of the 16 crews receive 3.75 hours of COFT time. By adding only 2 training sessions on any day during the week, all 16 crews would receive their recommended 4 hours of COFT time per month. |
AFTER-ACTION REVIEW
The evaluation software and various page printouts provide an extremely comprehensive data package for an IO to conduct an AAR on the crew's performance. In addition to these page printouts, the IO should utilize handwritten notes, playback of exercise, and a tape recorder to emphasize training strengths and weaknesses. An AAR normally takes no longer than 15 minutes to prepare and conduct. Once the AAR is complete and the training session has been concluded, the various page printouts and the session summary for the crew should be placed with their records. This is particularly important for the next IO to conduct a training session with the crew, as it provides the IO the means to review the strengths and weaknesses of the firing crew, and conduct an effective prebrief.
System Information
For more information about the COFT, to include future upgrades and general information, contact the Senior Instructor Operator Section, Hill Hall, Fort Knox, KY, (DSN) 464-5364, (Commercial) 502-624-5364 or Crew Gunnery Doctrine Branch, DTDD, COFT Subject Matter Expert, Fort Knox, KY, (DSN) 464-5806/3633, (Commercial) 502-624-5806/3633.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

