Chapter 2
Signal Support and Organization
Signal support organizations exist at every echelon of the Army. Their mission is to support the commander by providing reliable and flexible communications, automation, and information services. This support is provided by signal organizations organic to the maneuver unit. At theater, there is a tailored signal command; at corps, a signal brigade; and at division, a signal battalion. In maneuver brigades and battalions, there is a signal staff officer with a section configured to the supported unit.
Section I. Supporting the Corps and Division
2-1. Corps Signal Support
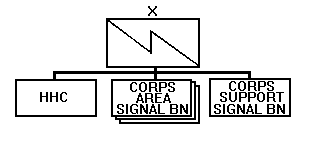
The principal signal support organization at corps is the corps signal brigade. Its mission is to provide support through the corps area common-user network. It also provides special staff and technical assistance for planning and controlling all corps signal functions and the extension of signal services to higher and adjacent commands. Figure 2-1 shows an example of the brigade structure. MSE is the principal corps common-user system which provides connectivity to subordinate divisions, adjacent units, joint and allied services, and the Defense Information Systems Network (DISN).
Figure 2-1. Corps signal brigade.
2-2. Signal Brigade Elements
The corps signal brigade commander serves as both the corps signal officer/G6 and the signal brigade commander. To help accomplish these missions, the commander has the corps signal office/G6, the corps brigade signal staff, and subordinate signal battalions.
Corps Signal Office/G6. The corps signal office's primary
mission is to perform signal planning for the corps. The
corps signal office is part of the corps staff and the
assistant corps signal officer (ACSO) oversees the operation
of the office. Office functions include--
- Preparing the signal annex's operation plans
(OPLANs) for the corps' operations order (OPORD).
- Preparing signal estimates.
- Providing technical supervision of signal activities.
- Producing signal brigade taskings based on corps
requests.
- Managing all operational and contingency
communications security (COMSEC) matters.
- Supervising the corps COMSEC office of record which
develops COMSEC OPLANs and policies.
- Supervising the automation section (Maneuver Control
System (MCS)).
- Producing tactical telephone directories and listings for
corps users.
- Controlling radio frequency (RF) allocations and
spectrum management for the corps.
- Coordinating signal interface with host nation and
allied forces.
- Managing and controlling corps level BIS functions
including the actions of the ISSO.
- Managing the corps' distribution and reproduction
section.
- Maintains configuration control of all software by
ensuring that the software is current, compatible and
standardized.
- Corps signal engineering branch.
- Network control branch.
- Plans/intelligence section.
- Operations section.
- Brigade COMSEC office of record.
- Logistics section.
- Administrative section.
- Automation section.
2-3. Subordinate Signal Battalions
Corps Area Signal Battalion. These three battalions are responsible for providing communications coverage of a specific portion of the corps maneuver area and for installing a large extension node (LEN) to support the corps command posts (CPs). Also, the corps area signal battalion provides remote North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) interface.
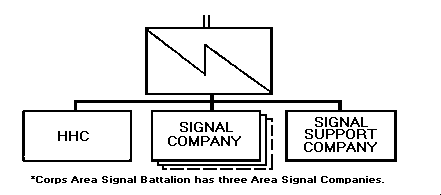
Corps Support Signal Battalion. This battalion installs
a portion of the corps area network and supports large
headquarters at corps. It is configured differently from the
area battalions having greater wire assets. Figure 2-2
shows an example of a corps support signal battalion.
Figure 2-2. Corps support signal battalion.
The division MSE network can operate as a stand-alone
network or as part of the corps network. It has the same
structure of interconnected node centers (NCs) and
extension nodes providing service for division headquarters
and major subordinate units. The network can contain
gateways to adjacent units and the Defense
Communications System (DCS) network.
See Appendix B for a heavy division MSE signal battalion
equipment chart.
Figure 2-3. Division signal battalion.
Division Signal Office/G6. The division signal office/G6
works closely with the division G3. The ADSO supervises
the division signal office. This office--
See Appendix B for a corps MSE signal brigade equipment
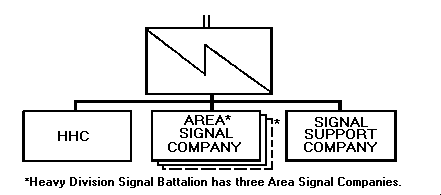
chart.2-4. Division Signal Battalion
The division signal battalion is the principal signal
organization supporting the division. Figure 2-3 shows the
organizational structure. The battalion's primary mission
is to establish a division area common-user network. The
signal battalion also provides signal support and staff
assistance to plan and control division communications,
automation, VI, and BIS.
2-5. Division Signal Battalion Elements
The division signal battalion commander serves as both
the division signal officer/G6 and the signal battalion
commander. To help accomplish these missions, the
commander has the following assets: the division signal
office/G6, the division signal battalion staff, and the
subordinate signal companies.
Division Signal Battalion Staff. The division signal
battalion staff assists the commander by providing
information, estimates, and recommendations. The staff
prepares plans and orders and provides guidance for the
design and implementation of the division's communications
network. The staff consists of--
- S1 Administrative Section.
- S2/S3 Intelligence/Operations and Training.
- S4 Logistics Section.
- Battalion Maintenance Officer (BMO).
- Motor maintenance.
- Electronic maintenance section.
2-6. Subordinate Signal Companies
Battalion Headquarters and Headquarters Company (HHC). The signal battalion HHC sustains the battalion when deployed through maintenance, logistics, administrative services, and management of the ACUS network.
Area Signal Company. The mission of each of the two area signal companies (three in a heavy division) is to provide ACUS coverage for a specific portion of the division maneuver area.
Signal Support Company. The mission of the signal support company which contains the division's LEN is to provide support for large CPs such as the division support command (DISCOM). The support company also has TACSAT, net radio interface (NRI), frequency modulated (FM) retransmission, and EPLRS equipment.
Contingency Communications Package (CCP) Company. Airborne, air assault, and light signal battalions have a contingency communications company(ies) made up of two identical platoons. Each platoon provides initial MSE and TACSAT capabilities.
Light Contingency Communications Package (LCCP) Company. Selected light forces have a contingency communications company made up of two platoons. The LCCP is being developed to provide selected light infantry divisions with an initial MSE capability for a contingency mission. The LCCP closely follows the organization, concept, and functional characteristics of the airborne CCP, with the major differences exhibited at the extension sites with dismounted equipment.
Continue with Chapter 2
Table of Contents
Index
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

