CHAPTER 3ORGANIZATION AND OPERATIONS OF |
Section I
THE ORGANIZATION
THE ORGANIZATION
MISSION
The company's mission is to plan, control and supervise the supply of bulk petroleum products and water. It also coordinates theater petroleum and water distribution systems. The company coordinates with the EAC MMC or the CMMC for distribution of petroleum and water in the theater. These organizations provide bulk petroleum and water centralized management.
ASSIGNMENT AND BASIS OF ALLOCATION
One or more headquarters and headquarters companies ( TOE 10602L0) are assigned to each ASCC headquarters. They are assigned to a COSCOM in the absence of an ASCC headquarters.
CAPABILITIES
The company's capabilities are determined by the personnel strength levels and equipment authorization levels prescribed in TOE 10602L0. The Headquarters and Headquarters Company, Quartermaster Group (Petroleum and Water)-
- Provides command and control for two to five battalions (petroleum pipeline and terminal operating, petroleum supply, transportation, or water supply) and supervises other assigned or attached units.
- Coordinates requirements with the engineer command. (It constructs and maintains POL and water facilities.)
- Implements the theater petroleum quality surveillance.
- Plans bulk petroleum receipt, storage, and distribution.
- Distributes bulk petroleum to US Army, Navy, Air Force, and other supported activities based on the EAC MMC directives.
- Plans for the development, employment, sustainment, and redeployment of the IPDS.
- Implements host nation support operational procedures as directed by the petroleum division, EAC MMC.
- Provides liaison to agencies involved in petroleum distribution operations within the theater or corps.
- Provides operational guidance to assigned units involved in petroleum distribution operations.
- Provides command supervision for petroleum supply battalions assigned to an independent corps.
- Advises the theater army commander on the capabilities and status of the Army IPDS within the organizational structure of the petroleum group.
- Provides command supervision and technical guidance to water supply battalions and other water units throughout the theater.
- Develops plans for producing, receiving, storing, and distributing bulk potable water.
- Transports 33 percent of its TOE equipment and supplies in a single lift using its authorized organic vehicles.
ORGANIZATION
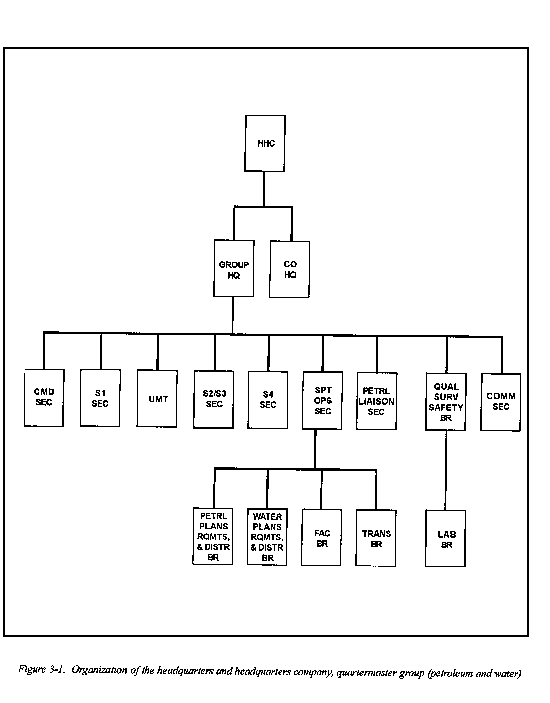
Figure 3-1 shows the company organization. Sections II through XII of this chapter discuss each element of the headquarters in detail.
Section II
GROUP HEADQUARTERS
MISSION
The group headquarters plans and coordinates bulk petroleum and water support in the theater army. It also supervises assigned and attached units operating petroleum distribution systems.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The group commander (Colonel, 92F00) is responsible for the quartermaster group mission. This includes the group headquarters command section and assigned and attached units. His job is to-
- Supervise petroleum and water resource development, including handling equipment, facilities, and construction.
- Provide command and control to assigned petroleum pipeline and terminal operating battalions, petroleum supply battalions, water supply battalions, transportation medium truck units, petroleum liaison teams and host nation battalion equivalents and other assigned and attached units.
- Direct the planning needed to monitor the petroleum and water distribution systems.
- Direct the planning for potable water production in support of the theater.
- Prepare to provide bulk potable water support to USAF, USN, and USMC units and, if required, to combined and coalition forces.
- Direct the planning needed to extend and develop petroleum and water distribution systems.
- Direct the planning needed to make the best use of personnel, equipment, and facilities.
The company plans and executes missions to comply with national, state, local, and host nation environmental laws as they apply to the scope of the operation to include conducting environmental and safety risk assessments for proposed operations.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the headquarters requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel are the commander, his staff, and the soldiers who assist him and his staff. Key personnel include-
- Executive Officer (Lieutenant Colonel, 92F00). Assists the commander and also coordinates the functional staff activities.
- Support Operations Officer (Lieutenant Colonel, 92F00). Directs the supply support distribution functions of the support operations section. Section VII gives details on his responsibilities.
- Chaplain (Major, 56A00). Provides the staff chapel services at group headquarters along with the senior chapel activities specialist. Section IV gives more on his responsibilities.
- Communications and Electronics Staff Officer (Major, 25C00). Plans for and advises the commander and staff on the installation and operation of communications systems.
- S1 Officer (Major, 41A00). Directs the functions of the S1 section. Section III gives more on his responsibilities.
- S2/3 Officer (Major, 92F00). Directs the functions of the S2/3 section. Section V gives more on his responsibilities.
- S4 Officer (Major, 92 B00). Directs the functions of the S4 section. Section VI gives more on his responsibilities.
- Command Sergeant Major (E9, 00Z50). Serves as the principal enlisted assistant to the commander. This includes executing established policies and standards pertaining to the performance, care, conduct, appearance, personnel management, and training of enlisted soldiers. This includes also-
- Providing advice and making recommendations to the commander and staff on all matters pertaining to enlisted soldiers and their families.
- Accompanying the commander on inspections, visits, and at ceremonies, or acting in his place in these capacities when directed by the Commander.
- Training and directing subordinate NCOs.
- Ensuring newly assigned soldiers are instructed in military courtesy, customs of the service, and command regulations or policies.
- Providing counsel and guidance to NCOs and other enlisted soldiers in the command. Inspecting duties performed by subordinate NCOs.
- Assisting in reception of visitors to the command.
- Sitting as president or member of command promotion board for NCOs as authorized by regulation.
- Performing other duties prescribed by the commander.
He may be responsible for discharging the duties listed above at sites dispersed over long distances in a tactical environment. During tactical operations, the CSM should also act as the commander's representative in supervising aspects vital to the operation, as determined by the commander and himself. The CSM can lead the quartering party during major movements or otherwise supervise movement of portions of the group headquarters. He can assist in or direct portions of CSS operations for the group headquarters, portions of which may be spread long distances. He may act as a liaison to higher, adjacent and subordinate units, or with host nation assets, all of which may be located long distances from the group headquarters.
- Executive Administrative Assistant (E4, 71C10). Provides administrative support to the commander. Maintains the commander's appointment calendar.
- Chauffeur (E5, 88M20). Drives for the commander. Maintains the commander's vehicles. Assists the executive administrative assistant as needed.
OPERATIONS
The headquarters' major function is to provide supervision and direction to the overall operation of the group. The commander and his staff must consider the following factors described below.
Deployment
The group commander and his staff prepare the movement order, select new sites and assign supply responsibilities. They must coordinate with all moving sections to fulfill their transportation and other requirements. The company commander's plans and orders provide for the company's rapid movement. They also provide for re-establishment of the company with continued supply flow. Section II of Chapter 8 gives more information.
Assigned or Attached Units
The S4 section plans the support of assigned or attached units. This planning covers the arming, fueling, and maintenance support of the units. FM 100-5 gives a more detailed discussion.
Staff Sections
Staff sections will-
- Provide information.
- Make estimates and recommendations.
- Prepare plans and orders.
- Supervise plans and orders execution.
Air Defense Priorities
The staff receives and coordinates subordinate units' security requirements and the support area. This includes air defense requirements. They then establish air defense procedures and priorities. FM 44-1 has more discussion.
Transportation Resource Allocation
Transportation assets are a critical resource. Detailed planning, coordination and allocation are necessary for effective use.
Tactical and Technical Performance of Units
Staff personnel monitor the tactical and technical performance of soldiers in headquarters and subordinate units. Use this manual to identify mission and performance criteria for units under the headquarter's control.
Religious Activities
The chaplain and the senior chapel activities specialist coordinate group chapel activities. They make sure area and denominational chapel activities are available to unit and host nation personnel. The chaplain should select and staff a plan that ensures liaison with chaplains of higher, adjacent, civilian, allied, and civil and military affairs units. He should coordinate with civilian religious organizations and other groups that assist in religious and moral activities. AR 165-1 has guidance on religious activities.
Section III
S1 SECTION
MISSION
The S1 section plans, coordinates, and supervises administrative and personnel activities. To accomplish this, the section performs many functions. The section-
- Distributes messages.
- Maintains records.
- Publishes orders.
- Maintains liaison with supporting financial activity.
- Manages personnel services.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The group S1 officer supervises S1 section operations. This section carries out all administrative and personnel functions of the petroleum group. The group S1 advises other staff officers and the commander in these areas. He supervises activities in the following specific areas:
- Unit strength.
- Manpower management.
- Personnel management.
- Morale.
- Health and safety.
- Discipline, law, and order.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identiying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Personnel Administrative Officer (Captain, 42B00).
- Establishes and implements personnel and administrative policies and is the principal assistant to the S1 officer.
- Senior Retention Sergeant (ES, 00R50). Determines qualifications for reenlistment and also processes reenlistment paperwork.
- Personnel Sergeant (E7, 75Z40). Plans, coordinates, and supervises the organization's military personnel.
- Legal Sergeant (E6, 71D30). Maintains all legal paperwork in the group. Provides legal administrative support and special courts-martial support to the soldiers and commander.
- Administrative Sergeant (E5, 71L20). Serves as the administrative specialist's immediate supervisor. Provides technical guidance to the section.
- Administrative Specialists (E4, 71L1O; E3, 71L10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating the MARKS and preparing the section's correspondence.
OPERATIONS
The section's major function is to provide personnel and administrative support to the group. The section must consider the following factors described below.
Administrative Support
The section authenticates orders and directives and maintains the filing system IAW MARKS. The section prepares, verifies and submits casualty feeder reports to the casualty section of the appropriate commander. The section takes prompt action on administrative instructions received from higher headquarters and requests from subordinate units. The section maintains accurate personnel records. It assigns replacements according to MOS and unit requirements. AR 672-5-1 gives standards on how to prepare, review and process recommendations for awards and decorations. AR 600-200 has guidance on planning enlisted personnel management system procedures.
SIDPERS
This unit does not operate a PAC. Therefore, the unit is not responsible for operating a SIDPERS system. It must provide input for SIDPERS to its supporting PAC, however.
Personnel Management
The section has several responsibilities for administering personnel management. The section's personnel management responsibilities are-
- Personnel requirements. Subordinate units send the section their personnel status reports. Once section personnel know unit requirements, they coordinate soldier assignment priorities with the S2/S3 officer, unit commanders, and the group commander. It assigns personnel based on valid position numbers in the UMR. DA Pamphlet 600-8-1 gives more information. The section designates assignments for each person during the current SIDPERS cycle. Then it inputs the necessary information in the next SIDPERS cycle. FMs 12-1, 12-2, 12-3-2, 12-3-3 and 101-10-1 give information on planning the personnel management program.
- Casualties. Subordinate units will send the section their casualty reports. Within 1 hour after receipt, the section prepares a SIDPERS deceased transaction and a SIDPERS organization strength report change. DA Pamphlet 600-8-1 outlines procedures. Report strength figures are extracted from current unit totals.
- Equipment, Documents and Enemy Prisoners of War (EPW). When subordinate units take EPW's, the S1 section provides processing guidance. They give instructions for EPW evacuation and interrogation. The section coordinates procedures with local military police. They also coordinate with the S4 section for captured materiel evacuation and with the S2/S3 for document evacuation. Procedures for EPW handling are in FM 19-40 and FM 30-15, Chapter 3. FM 101-10-1 gives general guidance.
- Personnel daily strength summary. Subordinate units report their maintenance and unit strength data each day. When reporting to higher headquarters, units show the section all organic and attached units separately. They identify them by line number. They do not show detached units. By 1800 on the date of the report, the section reports recorded data to higher headquarters by unit, attachment and group. They report strength, losses, gains, number of EPW's, number of days in the area of operations, and number of days in combat.
- Personnel data card. The section maintains DA Form 2475-2. This form provides strength accounting for personnel that are not members of the Active Army attached to the unit. Post the PDC according to DA Pamphlet 600-8-1. They record loss and casualty data. Next, they post the UMR and the zero balance report. They use data from the PDC to do this. After posting data, the section sends part 1 of the PDC to higher headquarters.
- Replacement personnel. The section in-processes replacements. They verify assignments based on vacancies with the unit and recommendations of the S2/S3 officer. They send assignment notice to the receiving unit. They also note this on the UMR. They ensure units submit SIDPERS transactions to the higher headquarters. DA Pamphlets 600-8 and 600-8-1 give more information. The section orients replacement personnel to the unit the day they arrive. The orientation includes information on unit mission, the chain of command, mail procedures, personnel policies, and personnel services as a minimum.
Personnel Services
The section manages personnel services program. It administers such matters as leaves, passes, and rotations. It also includes-
- Projected quotas for each unit for rest camps, recreation centers, and leave areas.
- Information on services provided by Army Emergency Relief and the chaplain and information on the Staff Judge Advocate, the Equal Opportunity Office, and special services.
- Actions taken on finance coordination with the supporting finance office. FM 14-6 gives guidance.
- Scheduling of personnel services for minimum interference with the unit's mission.
- Coordinates transportation requirements for movement to service areas.
Discipline, Law and Order
The S1 administers actions under the UCMJ. AR 27-10 gives more information. The S1 officer also recommends measures to the commander to improve discipline, law, and order.
Morale Support
Section personnel monitor subordinate units' morale by making unit visits. To evaluate unit morale and morale enhancement programs, they should follow the guidelines in FMs 22-101 and 101-5 and DA Pamphlet 1-2.
Labor Services
Subordinate units identify and report labor requirements to the section. The section then processes requests for civilian labor. The S1 ensures the requests meet approved guidelines. He then coordinates civilian labor requirements with supporting labor service teams. The section coordinates the use of labor in functional areas with all other staff sections. FM 101-10-1, and FM 100-10, Chapter 13 give guidance.
Legal Assistance
The section's legal sergeant provides legal administrative support and special courts-martial support to the soldiers and commander.
Medical Support
The S1 section coordinates with the local medical commander to determine the location of facilities and the services available. Section personnel coordinate procedures for routine and emergency evacuation. The S1 prepares a medical plan that ensures adequate coverage for all subordinate units. These plans should include dental support, instructions for treatment, and chain of medical evacuation. It should also include hospitalization and preventive medicine support beyond organic capabilities. FM 8-10 discusses the procedures for providing medical support. FM 101-10-1 also gives more information.
Command and Public Information
The section briefs the commander's staff and unit commanders on command information. The command briefing should include the following information as a minimum:
- Planning information activities.
- Publishing command information in newspapers and other media.
- Operating command information broadcast stations and networks.
- Reviewing information for security clearance before public release.
Library Services
The section operates a central records library for documents kept longer than 30 days. The section services the units or individuals requesting information or copies of documents from the library. AR 25-400-2 gives guidance on setting up an organized library file system.
Files and Records
Publications and files of supported units should be checked to ensure they are current. They should be maintained according to regulations. AR 340-2 gives guidance files and records maintenance. A list of current publications is in DA Pamphlets 310-1 and 310-35.
Section IV
UNIT MINISTRY TEAM
MISSION
The UMT provides for the unit's religious ministry, pastoral care, and moral and ethical well-being. It advises the commander and staff on moral, morale and religious matters.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The chaplain is responsible for making sure his section successfully accomplishes all of the functions of its mission. The chaplain's responsibilities include-
- Coordinating, integrating, and supervising all chaplain activities, religious services, ministries and observances and the use of facilities as approved by the commander.
- Establishing and maintaining liaison with staff chaplain of higher, equal, or subordinate headquarters, the other military services, government agencies, the armed forces of allied nations, and officials of civilian churches and other religious organizations.
- Facilitating the "free exercise" rights of all personnel, regardless of religious affiliation of either the chaplain or the unit member.
- Providing cross-cultural recommendations to the commander and facilitates appropriate training.
- Providing area coverage within the geographical area or as specified in the area coverage plan.
- Providing denominational services where practical.
- Providing chaplain coverage to EPW's and all others as outlined in AR 165-1.
PERSONNEL
The group chaplain supervises UMT operations. UMT personnel consists of the Chaplain's Assistant (E5, 71M20). He performs or supervises the performance of specified elements of religious support in the battlefield or in garrison. He provides personal protection and administrative support to the group chaplain.
Section V
S2/S3 SECTION
MISSION
The S2/S3 section directs the planning, coordinating, and supervising of group activities. It provides guidance in intelligence, security, organization, and training for subordinate units. The S2/S3 section-
- Coordinates base cluster defense plans with the RAOC.
- Develops and uses training programs.
- Plans, directs, coordinates, and supervises intelligence, counterintelligence, and civil affairs programs.
- Develops and coordinates security and defense plans.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The S2/S3 plans and supervises the organization, training, and deployment of assigned and attached units. His responsibilities include-
- Developing policies for the training of the command and training evaluation.
- Exercising staff supervision over all intelligence, security, and defense activities.
- Preparing broad planning guidance, policies, and programs for command organizations, operations, and functions, to include environmental stewardship programs. Particular areas of environmental interest are training programs and land management (see TC 5-400).
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Security Officer (Captain, 35A00). Serves as the principal assistant to the S2/S3 Officer. Supervises the functions of security, intelligence, and training of personnel.
- Chemical Staff Officer (Captain, 74B00). Prepares, plans, and recommends NBC training. Advises the commander and staff on plans for security and protective measures. Helps units make plans to reduce the effects of an NBC attack.
- Petroleum Operations Sergeant (ES, 77F50; E7, 77F40). Assists the security and intelligence officer. Plans to ensure security of the pipeline storage system. Also coordinates the intelligence and counterintelligence programs.
- NBC Operations/Staff NCO (E7, 54B40). Assists in planning and applying NBC defense measures for subordinate units. Coordinates decontamination operations.
- Administrative Specialist (E4, 7lL10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating the MARKS, and preparing section correspondence.
OPERATIONS
The section's major function is to plan the organization, training, and deployment of the Group's units. The commander and his staff must consider the following factors as described below.
Intelligence
Section intelligence operations include-
- Preparing an OPLAN and OPORD. This section maintains the current intelligence summary and an estimate. An analysis of a summary and an estimate will help in preparing an OPLAN and OPORD. The section develops the situation and mission statement for operations orders and plans. The section consolidates annexes from the other staff sections to complete OPORDs and OPLANs. The completed OPORD gives subordinate units the essential information to carry out an operation. An operations order's basic elements (organized as paragraphs) are situation, mission, execution, service and support, command, and signal. FM 101-5 has more information.
- Developing Group Contingency Plans. These plans provide for major contingencies possible in the principal geographic subareas of the command. The operations section helps the commander and staff integrate, evaluate, and interpret data from contingency plans. The section also supervises group contingency planning.
- Maintaining Intelligence and Counterintelligence Requirements. The section reviews and revises intelligence and counterintelligence requirements. Intelligence information is collected, analyzed, processed, and disseminated continuously. This process requires close supervision and planning to execute. FM 34-60 covers counterintelligence. It discusses the counterintelligence estimate, work sheet, and plan. The worksheet is an essential aid. It is the basis for preparing counterintelligence plans, orders, and requests. The S2 officer analyzes the threat situation and makes recommendations when necessary. He also provides information to subordinate units as required. FM 34-60 gives helpful information on intelligence.
- Providing Subordinate Units with Information. Higher headquarters will provide the group with an intelligence report on the expected action of opposing forces. The section sends applicable report portions to all group units. The S2/S3 officer provides guidance on alternate routes if main supply routes are blocked or destroyed.
- Briefing Higher Headquarters. The S2/S3 section informs higher headquarters of subordinate units' current operational situation. The briefing covers the daily organization, operation, coordination, intelligence, and physical security aspect of the unit. It emphasizes information that may affect mission performance.
- Directing the SOP use. The S2/S3 section makes sure subordinate units receive and use current SOPs from the group headquarters.
Security
Security measures include-
- RAP. When RAP plans and SOPs are available, the S2/S3 section makes sure units follow them. FM 90-14 gives more information. The S2/S3 section reviews, updates, and coordinates rear area security and area damage control plans for all group units. The section updates ground, antiarmor, and air defense plans based on the threat level. The section also requests combat forces from higher headquarters by secure means. These forces counter hostile forces that threaten to prevent or hinder the mission.
- OPSEC. The S2/S3 section uses adequate programs for information and signal security. It also implements physical security and deception programs. The section-
- Establishes liaison with higher headquarters intelligence and security agencies.
- Denies essential elements of friendly information to the enemy.
- Confuses the enemy force in its attempt to estimate the course of action the group will take.
Reports
AR 220-1 provides guidance for preparing the following reports:
- Unit Status. The section receives a DA Form 2715 from each unit. The section checks the reports for accuracy and completeness. It then consolidates them and sends them to higher headquarters. Mark and discard all documents IAW AR 380-5.
- Group Status. The section consolidates subordinate unit reports into a group report. It then forwards the consolidated report to higher headquarters.
Communications
The section coordinates with other staff sections on communications matters. They identify communications equipment shortages and failures. They identify additional communications requirements. They also monitor stations for proper training and procedures. FM 11-23 has more details. Also, the section determines requirements for the group. FMs 11-50 and 24-1 have more information. The section allocates resources by need for secure equipment, remote equipment, FM radio use, equipment maintenance needs, and sole user circuit allocations.
Support Operations
Coordinate activities with the support operations section to minimize any potential adverse effect on the bulk petroleum and water mission. Plans for future operations may affect supply missions. The section coordinates plans with each unit and its supported customers.
Use of Smoke
The S2/S3 section requests smoke generators from the designated supporting smoke generator unit. Units use smoke to conceal important combat service support areas. FMs 3-100 and 3-10-1 have more information Plan to-
- Use smoke blankets, hazes, and curtains to reduce visibility and to conceal troops and installations.
- Conceal lines of communication.
- Use smoke during darkness to assist in light discipline.
- Use smokepots and other portable devices. Use them when the threat of recognition and immediate attack is great.
Training Programs
The section establishes, coordinates, and monitors unit training programs.
Mission Essential Task Lists
The section prepares the METL for the group headquarters. It also provides guidance to subordinate units for METL development.
NBC Operations
NBC defense responsibilities include:
- NBC personnel in the section monitor, evaluate and provide guidance for group NBC defense training. They also advise the commander and staff of subordinate units' NBC defensive readiness. NBC personnel assist the S2 in conducting Intel1igence Preparation of the Battlefield (IPB) to identify possible enemy NBC employment. With information received from higher headquarters, NBC personnel plot NBC hazard predictions and advise on possible courses of actions. Section II of Chapter 7 has more information on NBC defense. FM 3-3, 3-4, 3-5, and 3-100 have more information on NBC operations.
- Mission-oriented protective posture. The chemical officer recommends an appropriate MOPP level. MOPP should maintain a balance between the best combat effectiveness and the best NBC defense posture. The chemical officer determines a recommended MOPP level by considering threat level, soldier factors (type of work they are doing, fitness levels and so forth) and environmental factors. FM 30-4 gives information on MOPP.
SectionVI
S4 SECTION
MISSION AND RESPONSIBILITIES
The S4 section plans, coordinates, and supervises organizational supply, maintenance, and food service activities for subordinate units. This includes pertinent portions of the unit environmental stewardship program. Particular areas of environmental interest are management of hazardous materials and wastes in maintenance, food service and supply room operations, environmentally safe maintenance operations, and the unit recycling program. Also, the S4 officer is responsible for the execution of the command operating budget (COB).
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identifying key people and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Property Account Technician (CW3, 920A0). Provides advice and technical assistance on property books and equipment. Maintains the consolidated property book for separate companies and the organic headquarters company.
- Chief Mechanical Maintenance Logistics Sergeant (E9, 63Z50). Provides advice and technical assistance on all maintenance matters.
- Food Service Supervisor (E8, 92G50). Provides advice and technical assistance on food service. Advises on the proper use of all available food service resources.
- Senior Supply Sergeant (E8, 92Y50). Plans and coordinates maintenance activities throughout the command. Provides technical assistance to battalions on maintenance matters.
- Supply Specialist (E3, 92YI0). Assists the senior supply sergeant.
- Administrative Specialist (E4, 7lL10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating MARKS, and preparing correspondence for the section.
OPERATIONS
The section's major function is to provide assistance and guidance in internal logistics to the group's units. The section must consider the following factors as described below.
Technical Supply and Service Assistance
When the units begin receiving supplies and servicing their elements, the S4 section should monitor their operations. They should check the requisition, procurement, storage, and distribution of supplies and equipment. The section distributes critical equipment according to priorities established by the group commander. Coordinate requirements for service with the group headquarters. When monitoring units, they should use AR 710-2 and FM 100-10 for guidance. They cover all materiel management procedures used by the units.
Maintenance
The subordinate units of the group send all maintenance reports to the S4 section. The section files them. The S4 section reviews them periodically to determine the number, type, and frequency of repairs. The S4 section also-
- Checks the units supported by the motor pool to make sure they are able to get vehicles and equipment repaired. Makes sure units perform scheduled services as required.
- Establishes and reviews environmental protection procedures in motorpool operations.
- Makes sure units complete equipment status reports correctly.
- Makes liaison visits with group units. Advises them on ways to improve their readiness.
- Contacts direct support repair parts facilities to follow up request for parts for non-operational equipment.
- Uses DA Pamphlet 738-750 and FM 100-10 for guidance in setting up the monitoring procedures.
Food Service
The S4 section monitors Class I availability and accountability. The section checks dining facilities for sanitary preparation and proper storage. The S4 section monitors dining facility operations in the support group units and ensures facilities and operations are safe and environmentally sound. FMs 10-23 and 10-26 give more detailed guidance.
Command Operating Budget
The S4 officer executes the COB. Units submit fiscal requirements to the S4 officer. After a budget review by the commander, S2/S3 officer, S4 officer and support operations officer, the S4 allocates funds to each battalion level and separate company unit. He and efficient use. The section can use FORSCOM then monitors the status of funds to ensure availability Program Budget Guidance as a guide.
Section VII SUPPORT OPERATIONS SECTION
MISSION AND RESPONSIBILITIES
The support operations section coordinates, manages, and synchronizes all bulk petroleum and water in the theater or corps. This section has four branches. The support operations section provides the group commander with information on current petroleum and water operations. The section is responsible for:
- Development of the concept of the operations for both OPORDs and OPLANs.
- Coordination with host nation support organizations in bulk petroleum and water support elements.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Petroleum Distribution Sergeant (E9, 77F50). Assists the support operations officer. Senior non-commissioned officer in section responsible for the continued education of the junior non-commissioned officers.
- Administrative Specialists (E4, 71L10; E3, 7IL 10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating MARKS, and preparing correspondence for the section.
ORGANIZATION
The support operations section has four branches. The following paragraphs discuss each branch. Each branch chief carries out functional supervision of each branch under the support operations officer's supervision.
Petroleum Plans, Requirements, and Distribution Branch
This branch plans, directs, coordinates, and supervises requirements, distribution, and movements activities for US Army inland petroleum distribution systems and operational projects.
Responsibilities. The petroleum plans officer (Major, 92F00) has several responsibilities related to supervise operations. His responsibilities are to-
- Formulate plans and programs for receipt, storage, and distribution of bulk petroleum products.
- Plan and conduct operations in an environmentally-safe manner within the scope of the tactical situation.
- Coordinate these plans with the command and the area petroleum office.
- Provide the support operations officer with necessary data to advise the group commander and other staff elements of your plans and activities.
- Coordinate with the JPO and DFR personnel for delivery of bulk petroleum into the Theater.
- Coordinate with the Class III (B) accountable office at the theater MMC or the corps material management office in contingency operations or operations other than war.
Personnel. Effective operation of the branch requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Petroleum Officer (Captain, 92F00). Directs, coordinates, and supervises activities pertaining to inland petroleum distribution operations.
- Petroleum Operations Sergeant (ES, 77F50). Assists the petroleum officer.
- Petroleum Distribution Supervisor (E7, (2 each) 77F40). Assist the petroleum officer.
- Petroleum Inventory Control Specialists (E5, (2 each) 77F20; E4, (2 each) 77F10). Receives stock status reports from subordinate units. Maintain availability data and provide information on the stock position. These specialists compile, analyze, and evaluate operational data on the supervised systems.
- Administrative Clerk (E3, 7lL 10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishment and operation of the MARKS, and preparation of correspondence for the section.
Operations. The branches major function is to plan the distribution of petroleum supplies on the battlefield. The branch operates as follows:
- Petroleum Plans and Requirements. The section determines subordinate units resupply requirements and forwards them to the petroleum division, of the EAC MMC. It also coordinates the loading of bulk petroleum and directs the distribution to subordinate units in organic bulk petroleum transportation assets. AR 710-2 has more guidance.
- Plans and Orders. The branch maintains petroleum requirements estimates. It prepares plans and orders in coordination with other staff officers. It also maintains operation records. Chapter 2 and 3 of AR 703-1 discuss planning and estimating petroleum requirements. FM's 10-13, FM 101-10-1, and the Unit Supply Update have more information.
- Operations of the Pipeline and Terminal System. District dispatchers from the petroleum pipeline and terminal operations battalion send daily pumping reports. Reports and logistical plans provided by higher headquarters determine petroleum requirements and distribution. The branch monitors the pipeline and terminal system to see if it is following guidance from higher headquarters. Coordinate any changes with higher headquarters. FM 10-67 gives helpful information on pipeline system management.
- Petroleum Inventories. The petroleum units inventory stocks. The branch reviews the inventory results and forwards them to the MMC. Chapter 5 of FM 10-67 covers inventory management.
Water Plans, Requirements, and Distribution Branch
This branch plans, directs, coordinates, and supervises requirements, distribution, and movements activities for bulk water production and distribution systems. Depending on the operational situation, it ensures operations are conducted with minimal environmental damage.
Responsibilities. The water plans officer (Major, 92F00) supervises branch operations. There several vital functions he must supervise to make the branch successful. He-
- Formulates plans and programs for bulk water production, storage and distribution. This includes planning operations to comply with applicable national, state, local and host nation environmental laws.
- Coordinates these plans with the theater army to insure synchronization with all forces.
- Provides the support operations officer with necessary data to advise the group commander and other staff elements of the sections plans and activities.
- Coordinates with the medical command to ensure testing of water production sites for potability.
Personnel. Effective operation of the branch requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Water Plans Officer (Captain, 92F00). Directs, coordinates, and supervises activities pertaining to bulk water production and distribution operations.
- Water Distribution Supervisor (E7, 77W40). Assists the water officer in the bulk water distribution plan for the theater.
- Water Treatment Sergeant (E6, 77W30). Ensures potable water quality. Advises the production detachments on matters pertaining to quality assurance.
- Administrative Specialist (E4, 7lL10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating MARKS, and preparing correspondence for the section.
Operations. The branch's primary function is to plan the distribution of potable water on the battlefield. The branch operates as follows:
- Water Plans and Requirements. The branch determines supply requirements of subordinate units and forwards them to the water operational division, of the EAC MMC. It also coordinates bulk potable water production and directs the distribution to subordinate units in organic bulk water transportation assets. FM 10-52 has more information.
- Plans and Orders. This branch plans and coordinates the subsurface water detection, well drilling and construction, repair, and water support facility maintenance.
Transportation Branch
This branch directs, coordinates, and supervises distribution and movements of bulk petroleum and water. It is concerned with bulk petroleum movement by means other than pipeline.
Responsibilities. The group movements officer (Captain, 88B00) supervises the branch operations by making sure the branch successfully completes key functions. The group movements officer-
- Coordinates, directs and manages transportation assets for the movement and distribution of intra-theater bulk petroleum and water.
- Develops wartime plans for programming the movement of bulk petroleum and water by means other than pipeline.
- Plans operations to comply with all national, state, local and host nation environmental laws.
- Ensures operations are conducted to minimize environmental damage within the scope of the tactical situation.
- Plans and executes emergency deployment readiness exercises, command post exercises, and field training exercises.
Personnel. Effective operations of the branch requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Staff Movements Sergeant (E7, 88N40). Assists in planning and directing branch activities. Coordinates with appropriate transportation personnel for the movement of fuel by means other than pipeline.
- Movement Specialists (E4, 88N10; E3 88N10). Maintain records and prepares reports of fuel moved by transportation means other than pipeline.
Operations. The branch coordinates bulk petroleum and water transportation. Group headquarters determines petroleum and water requirements and distribution needs. It then sends instructions to ship by air, rail, highway, or water. The group movements officer helps coordinate the preparation of fuel or water for the selected transportation mode. All quantities should be checked against requirements received from the group headquarters. FM 55-10 gives guidance on movement management. FM 55-50 gives information on transportation. FM 100-10 gives information on air, rail, highway, and water transportation.
Facilities Branch
This branch develops and prepares plans for construction of the IPDS, TWDS and selected operational projects in coordination with the petroleum and water division, of the EAC MMC, and engineer construction units. Plans in anticipation of complying with all applicable federal, state, local, and host nation laws.
Responsibilities. The group engineer's overall responsibility is to effectively supervise the various key functions of his branch. The group engineer (Major, 21D00) develops and prepares plans for-
- Pipeline routes, new pipeline construction, and expansion.
- Develops plans for preparing the site of tactical petroleum and water systems and rehabilitation of existing pipelines.
- Develops plans for constructing terminals and storage facilities.
- Coordinates with the engineer command for construction of water storage and production sites.
- Coordinates with both petroleum and water branches for engineer support requirements.
Personnel. Effective operation of the branch requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Senior Construction Supervisor (E7, 51H40). Acts as a liaison with engineer construction personnel to ensure plan compliance.
- Plumber/Pipefitter (E4, 51K 10). Inspects pipeline and terminal facilities of the subordinate units.
- Technical Engineer Specialist (E4, 5lT 10). Prepares drawings for pipelines, terminals, and storage facilities.
- Administrative Specialist (E4, 71L10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating MARKS, and preparing section correspondence.
Operations. This section is responsible for pipeline design, construction, maintenance, expansion, and inspection. Additionally, the section coordinates engineer support requirements with the engineer command. Also provides guidance on the refurbishment of existing petroleum and water systems to include wells, pumps and facilities.
Construction
The branch drafts plans for the pipeline system. The plans show the projected expansion of the system. They also give other facts required for command overview. The branch then coordinates with the petroleum plans and requirements branch to make any adjustments. After coordination, the branch must prepare requests for engineer support. It then determines man-hours, equipment, and materials required. TM 5-343 has more guidance.
Maintenance and expansion
The branch checks to make sure that proper maintenance is being performed on the pipeline system. Petroleum and water units perform organizational and direct support maintenance. An engineer pipeline construction support company performs the general support maintenance. TM 5-343 gives guidance on monitoring procedures.
Inspection
The branch inspects the pipeline system to make sure that it is being maintained efficiently. It makes sure safety and environmental precautions are being followed. It tests fire extinguishers. The branch also checks to see additional ones are on hand. It also checks suction and discharge pressures of operating pumps. The branch prepares inspection reports within the time specified by the commander. The reports give all information required by higher headquarters. Appendix K of FM 10-18 gives some helpful points to use to inspect petroleum facilities and equipment.
Section VIII
PETROLEUM LIAISON SECTION
MISSION
The petroleum liaison section provides liaison service between supported units, host nation petroleum activities and the petroleum requirements branch of the group. Also, the section implements the logistics assistance programs.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The petroleum liaison officer (Major, 92F00), supervises this section. He has overall responsibility for making sure the section conducts its liaison mission properly. He-
- Provides direct coordination channels between supported units (USA, USAF, USMC, and USN forces ashore), host nation activities and the group for approved petroleum logistics assistance programs.
- Facilitates coordination of environmental regulations and concerns among supported units, host nation units and higher headquarters.
- Updates status through the petroleum group to the EAC MMC.
- Coordinates through the Liaison Section for host nation support.
- Serves as liaison between allied forces requiring petroleum logistics assistance support.
- Tracks key construction and rehabilitation projects.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Petroleum Supply Sergeant (E8, 77F50). Assists the liaison officer in the coordinating and processing of petroleum logistics assistance projects.
- Petroleum Surveillance Sergeant (E7, 77L40). Provides liaison with host nations to insure facilities meet quality standards requirements.
- Petroleum Supply Sergeant (E6, 77F30). Assists the chief petroleum sergeant and maintains records of ongoing and completed petroleum logistics assistance projects.
- Administrative Specialist (E4, 71L10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating MARKS, and preparing section correspondence.
OPERATIONS
The section's major function is to provide liaison among several agencies. The commander and his staff must consider the following factors as described below.
Maintain Liaison
This section maintains staff and operational liaison between appropriate host nation agencies and supported units for implementation of petroleum logistics assistance projects. FM 101-5 has more on liaison procedures.
Provide Technical Information
Personnel in the section establish and disseminate technical guidelines for subordinate units. They evaluate all information to make sure it is relevant and accurate. FM 10-67 gives guidance on petroleum management procedures.
Section IX
QUALITY SURVEILLANCE AND SAFETY SECTION
MISSION
This section sets up and supervises the petroleum quality surveillance and safety program. The section monitors laboratory operations and prepares and distributes safety directives. The section provides technical assistance in the operations of all petroleum laboratories. It also supervises the development of safety directives for subordinate battalions.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The quality surveillance and safety officer (Captain, 92F00) manages this section. He also provides for command and control of base petroleum laboratory operations.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identifyIng key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel for this section include-
- Petroleum Surveillance Sergeant (E7, 77L40). Coordinates the technical operations of base and mobile laboratories.
- Safety NCO (E7, 77F40). Develops and disseminates safety directives for the subordinate units of the group. Trains personnel in correct safety techniques and inspects to make sure established directives have been followed.
- Quality Surveillance Specialist (E4, 77L10). Assists the quality surveillance supervisor.
- Administrative Specialist (E4, 7lL 10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing and operating MARKS, and preparing section correspondence.
OPERATIONS
The section's major function is to provide quality surveillance and safety functions for the units in the group. The section must consider the following factors as described below.
Laboratory Operations
The section monitors the work of the laboratory personnel of the base petroleum laboratory assigned to the section and to the laboratory branches in the petroleum pipeline and terminal operating battalions and petroleum supply battalions. Laboratory personnel will conduct the required tests. They file and maintain the results as outlined in FM 10-70. Branch personnel must watch laboratory personnel to make sure that they follow correct laboratory procedures and do not attempt shortcuts (Appendix A gives metric conversions). Branch personnel check to see that laboratory personnel follow procedures outlined in the ASTM manual, FTM 791, and FMs 10-70 and 10-72. FM 10-67, Chapter 7, gives information on surveillance.
Quality Surveillance Program
The section manages the quality surveillance program. This program insures POL products meet specified physical and chemical properties. Section soldiers do many duties. They determine sampling and testing procedures for bulk and packaged products, They determine reporting procedures for supported units. They establish and monitor transportation, handling, and storage procedures for bulk and packaged products. They determine disposition of off-specification products. They identify sources of potential contamination and deterioration of product. They provide advisory technical assistance to military activities in the battalion area. They also monitor procurement inspections of petroleum products procured in the battalion area.
Safety Directives
Section personnel prepare and send out directives on tire and health hazards to all subordinate units. It makes periodic visits to subordinate units to make sure the units are complying with all current safety directives. Chapter 8 of FM 10-67 gives guidance on safety functions.
Section X
PETROLEUM LABORATORY BRANCH
MISSION
This branch analyzes petroleum products received and stored in operating units. It also provides area petroleum laboratory support as directed. This branch operates abase petroleum laboratory. This laboratory is a fixed installation performs complete specification and procurement acceptance testing of petroleum products. Details on the operation, maintenance, and layout of base laboratories are in FM 10-72.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The petroleum laboratory officer (Lieutenant, 92A00) directs the petroleum laboratory in inspecting and testing petroleum products.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel for this section include-
- Petroleum Laboratory Supervisor (E7, 77L40). Supervises the performance of standard physical and chemical tests on petroleum products. Evaluates test results to make sure they comply with federal and military specifications.
- Petroleum Surveillance Sergeant (E6, 77L30). Assists the petroleum laboratory supervisor. Screens all completed test results for correctness and completeness.
- Petroleum Laboratory Sergeant (E5, 77L20). Directly supervises the petroleum laboratory specialists. Provides on-site assistance in petroleum testing.
- Petroleum Laboratory Specialists (E4, 77L10; E3, (7 each) 77L10). Perform standard physical and chemical tests on fuel handled through the battalion pipeline distribution system.
- Administrative Clerk (E3, 7lL10). Performs all administrative functions to include establishing Modern Army Records Keeping System (MARKS), and preparing branch correspondence.
OPERATIONS
The branch sets and maintains rules of laboratory conduct and techniques. These rules ensure reliability, safety, and environmental protection. The branch ensures sufficient laboratories exist to test all petroleum products in the command in a reasonable time. Branch personnel perform preventive and corrective maintenance on laboratory equipment. They must know how to prevent fires and extinguish them. Appendix A provides metric conversions. FMs 10-67 and 10-72 give information for laboratory operations.
Tests
The branch uses the petroleum products log analysis report to record the quality clearance. It also makes arrangements for line sampling and testing arrangements for marking interface progress and position.. The branch transmits instructions for interface testing and disposition at take-off terminals. Branch personnel inspect all petroleum products at intervals set in MILHDBK 200. They conduct tests according to the method prescribed in the product specifications. They should also follow all details of the test method and appropriate safety precautions as given in STP 10-77L14. When no ASTM standards exist, personnel should follow Federal Test Method 791. AR 710-2, FM 10-67, and STP 10-77L14 give more guidance.
Evaluation of Test Results
The branch evaluates tests that do not meet the specification requirements against use limits by methods given in MIL-HDBK-200 for the evaluation of the product not meeting specifications and the nature of contamination. The evaluation should also include suggestions for preventing future contamination or deterioration and recommendations for reclaiming or disposing of the product.
Records and Reports
Branch personnel maintain petroleum samples, a laboratory logbook, and a work assignment notebook. They maintain copies of the petroleum products log analysis report. They also prepare copies of product disposition recommendations. The branch sends all forms to the agent that requested petroleum products. The branch reports off-specification products to the Defense Fuel Supply Center through the petroleum group.
Coordination with Operating and Customer Units
The branch makes recommendations, through appropriate channels, for the alternate use, reclamation, or disposition of off-specification products. The branch makes sure units inspect POL products as quality surveillance problems arise. It directs inspection of petroleum products procured in the theater. It also provides technical assistance. The lab provides analysis services for the Air Force and Navy, as required. When the branch receives changes to specifications from the JPO, it reviews them and makes adjustments to existing policies and procedures. FM 10-67 gives more information.
Section XI
COMMUNICATIONS SECTION
MISSION
The mission of the communications section is to Computer Installation and Configuration coordinate installation, operations and management of CEOI production with RBECS information systems in support of group headquarters Field wire and telephone Service communications facilities. The section provides-
- FM Radio (SINCGARS).
- AM HF Radio.
- Group Mobile Subscriber User Equipment.
- Message Center Service.
- Computer Installation and Configuration
- CEOI production with RBECS
- Field wire and telephone Service
- NCS for AM and FM radio nets.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The signal officer is responsible for all group information systems (both tactical communication and commercial computer systems). He supervises the communications branch. He also coordinates with supporting signal units for entry into the common user systems and preparation of the battalion CEOI.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the section requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- Tactical Communications Chief (E8, 31U50). The senior enlisted advisor to the section officer. Primary responsibility is tactical communication liaison with the EAC Support Command and subordinate battalion elements. Prepares the group CEOI using RBECS. Supervises all enlisted soldiers assigned to the communications section.
- Tactical Communications Chief (E6, 31U30). Primary responsibility is the group headquarters internal communications. Responsible for all group headquarters information systems (tactical communications and computers). Special emphasis is on NCS operation of MSE and AM high frequency systems. Additionally, responsible for installation and configuration of group computer systems.
- Single Channel Radio Operator (E4, 31C 10). Acts as the NCS for the battalion SINCGARS/EPLARS and AM high frequency radio command/ops nets.
- Signal Information Service Specialists (2 E4, 3lU10). Install and maintain group MSE, SINCGARS, and AM HF digital and voice equipment. Responsible for installation and configuration of battalion computer systems.
- Signal support system specialist (E3, 31U10). Installs and maintains the group telephone and wire system. Operates the group message center once systems are installed.
OPERATIONS
The section is responsible for the information system integration plan; SINCGARS; AM HF radio: MSE interface equipment; message center; computer installation and configuration; RBECS-CEOI construction; field wire and switchboard; and the radio net control station (NCS).
SINCGARS
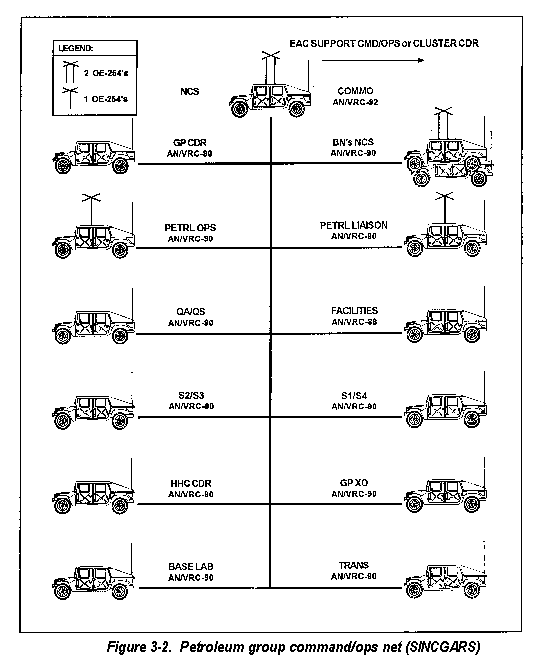
The unit is equipped with the AN/VRC-90 SINCGARS FM radios as shown in figure 3-2. SINCGARS is a new family of VHF-FM radios that replace the old FM AN/VRC-12 series of radios. These radios provide the group with a tactical secure FM radio net for internal command and control and external base cluster defense coordination. These radios are designed for simple, quick operation using a 16 element keypad for pushbutton tuning. They are capable of short-long range operation for voice or digital data communications. The planning range is 8-35 kilometers. They operate in a jam-resistant, frequency-hopping mode that can be changed as needed. The NCS utilizes the AN/VRC-92 radio that is a dual long range system also capable of operating as a retrans system as mission dictates.
AM high frequency radio
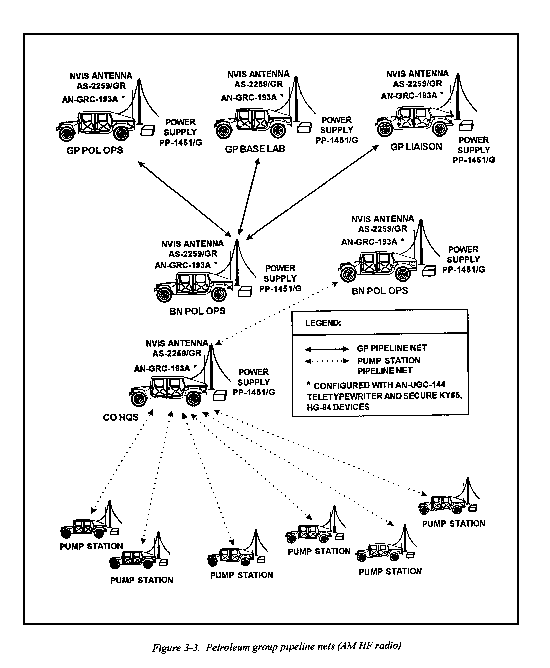
The group will employ the AN/GRC-193A HF radio shown in figure 3-3. The AN/GRC-l93 is a rugged, tactical, vehicular/base station HF radio set. The set's high power (100-400 watts) makes it capable of long range communications necessary to link all pump stations in the AM HF pipeline net that may span in excess of 300 miles. (The AN/GRC-213 low power AM HF radio is unacceptable for use with the omnidirectional coverage NVIS antenna, which requires maximum power output.) The AN/GRC-193 radio set can be mounted in a wheeled vehicle or installed in a fixed location, such as a building or tent. When installed in a fixed location, a power supply capable of providing 24 to 32 volts DC must be used or battery charger PP-145 l/G or similar power supply. To utilize this system in the radio teletype mode the KG-84 and computer terminal, AN/UGC-144, is necessary. Secure voice requires a KY-68. Both secure and radio teletype operation is mandatory for pump station operation.
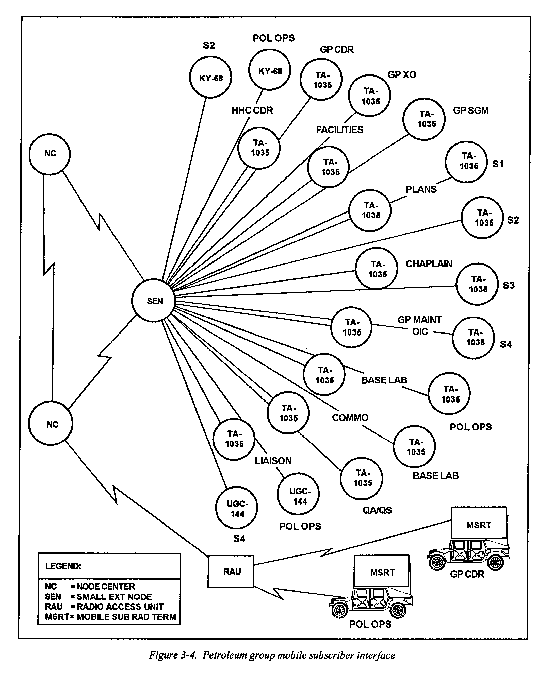
Mobile subscriber interface equipment
The supporting signal unit will provide connectivity to the battalion to provide an interface to the theater digital or corps mobile subscriber network. Users access the MSE network by fixed subscriber terminals or mobile subscriber terminals. Figure 3-4 depicts these access points. The fixed subscriber terminals are hard wired to a SEN through a junction box, J-1077. The three fixed instruments are the DNVT, TA-1035; the DSVT, KY-68; and the communication terminal, AN/UGC-144. The MSRT is the AN/VRC-97. The MSRT, which consists of a very high frequency radio and a digital secure voice terminal (KY-68), in a vehiclemounted assembly. It interfaces with the MSE system through a RAU. As long as the radio unit has line-ofsight contact with the RAU, it is connected to the MSE area system. The operational planning range is 15 kilometers from any RAU.
Message center
Message center operations orient on the AN/LJGC144 computer terminal, which allows access to the DMS, DDN, and MSE network. Both the S4 and POL Ops sections are authorized these terminals as shown in figure 3-4. These terminals are user -owned and -operated message terminals. Through menu-driven screens and passwords, it allows composition, transmission, and formal record traffic receipt. Each terminal has a KY-68 DSVT that provides autodial encryption capability. Section personnel, with the assistance of the communication section, process incoming and outgoing messages according to the priorities assigned. They will observe the following precedence, time frames and procedures per FM 24-17 and AR 25-11.
- Flash-less than 10 minutes
- Immediate-within 30 minutes
- Priority-within 2 hours
- Routine-within 6 hours
Computer installation and configuration
The communication section is responsible for all group information systems to include computers and peripheral devices. Responsibilities include-
- Ensuring all computer systems are accredited for the appropriate classification and networking level.
- Properly configuring all computer communication devices (modems).
- Installing, maintaining and providing operational guidance on battalion software.
RBECS/CEOI construction
The communication section creates and maintains CEOI databases tailored to specific missions. Using RBECS, the section is capable of generating processing, displaying, editing, printing, storing and transferring CEOI information. RBECS also processes the frequency hopping data, (TSK, HOPSET, NET ID's), for the SINCGARS and other radio systems. RBECS provide the capability to selectively compartmentalize information based on need and transfer the data to ANCD, and ECCM fill devices (MX-10579 and MX 18290). RBECS requires formal training.
Local field wire and switchboard
The communication section will devise and implement a wire net plan. The plan will identify each user telephone connected to the switchboard (SB-3614) or MSE/TRI-TAC switch. The plan will show where the wire is buried or installed overhead. Additionally, the wire team will designate a wire team to coordinate telephone installation with the supported units and identify manpower and equipment requirements. Users are responsible for wire installation and connection to the switchboard. Section personnel do the following:
- Test wire before installation.
- Connect and lay the wire according to the wire net plan.
- Lay the lines by the shortest distance allowed by terrain.
- Secure lines at their start point and at any point where they change direction or run into construction.
- Tag wire according to FM 24-20 and the CEOI.
- Make maximum use of terrain and natural vegetation to conceal wires.
- Make sure that construction techniques meet the requirements of FM 24-20.
- Check all splices to make sure they are correct and taped.
- Make preinstallation switchboard checks.
- Install and ground the switchboard in an area that protects the switchboard from moisture.
- Attach telephone lines and trunk connections at the switchboard.
- Label the switchboard according to the telephone directory.
- Keep wire splices clear of standing water and maintain a correct amount of slack in the wire.
- Check the wire periodically to make sure no one has tampered with it.
- Recover field wire without damaging it. FM 24-20.
- Wind wire evenly on reels with enough slack at the start to allow easy testing and servicing.
Radio communications net
There are twelve SINCGARS radios dispersed throughout the company (figure 3-4). Section personnel establish the radio communications net for these radios. When performing their duties, they should-
- Ground the equipment.
- Check at first light (when the station is set up during darkness) to make sure it is concealed. If it is not, take steps at once to conceal it.
- Make initial entry into the designated net within the time frame set by the commander.
- Use operating signals, prosigns, and authentication when required by the NCS.
- Process messages, requiring coding or decoding, promptly and without error according to FM 24-18.
- Adhere to all COMSEC procedures.
- Follow the guidelines in FM 21-2 when setting up the radio net.
NCS
The group NCS operates according to the procedures outlined in FM 24-18. Section personnel-
- Open and close the net.
- Control transmission.
- Authenticate and clear traffic within the net.
- Direct the net.
- Correct errors in operating procedures.
- Give or deny permission for stations to enter or leave the net.
- Impose or lift listening silence.
- Maintain net discipline.
Section XII COMPANY HEADQUARTERS
MISSION
The company headquarters provides command, control, discipline, training, personnel administration functions, and logistics functions for the soldiers in the company. It also coordinates with higher headquarters and staff sections to accomplish given missions.
RESPONSIBILITIES
The company commander (Captain, 92F) is responsible for the leadership, welfare, discipline, and training of all the soldiers in the company. He-
- Sets priorities and coordinates present and future missions of the company.
- Directs and supervises all technical operations and support activities that impact the headquarters operations.
- Ensures all required reports and data are prepared and transmitted to staff elements as required.
- Conducts safety and environmental risk assessments for each operation.
PERSONNEL
Effective operation of the company requires identifying key personnel and understanding their primary duties and responsibilities. Key personnel include-
- First Sergeant (E8, 77F5M). Assists the commander in supervising operation of the company headquarters. Is responsible for the leadership, welfare, and training of the enlisted solders assigned to the company.
- Supply Sergeant (E6, 92Y30). Requisitions, receives, stores, accounts for, and issues all classes of supply (except class IX) for the company. Manages hazardous material supply items IAW locally established procedures and regulations.
- Food Service Sergeant (E6, 92G30). Serves as the food service operations NCOIC within the company. Implements a Class I support plan to support company operations. Makes sure the plan includes a risk assessment of the environmental impact of food service operations (particular areas of concern are solid waste disposal, and fuel handling procedures for burners). Trains subordinates on environmental protection procedures and safety procedures.
- First Cook (E5, 92G20). First line supervisor for all assigned cooks. Assigns duties to cooks and develops production schedules.
- Unit NBC Sergeant (E5, 54B20). Provides unit decontamination support to the company. Supervises NBC personnel training. Maintains the companies organic NBC equipment and prescribed load list. Manages hazardous materials IAW locally established procedures and regulations.
- Personnel Administrative Sergeant (E5, 75B20). Performs all administrative functions for the company. Inputs personnel actions using Standard Installation/Division Personnel System (SIDPERS).
- Light-Wheeled-Vehicle Mechanic (E4, 63B10). Augments the subordinate unit assigned to provide organizational maintenance. Manages hazardous materials IAW locally established procedures and regulations. Performs maintenance IAW locally established environmental protection regulations.
- Armorer/Supply Specialist (E4, 92Y10). Maintains the unit small arms and assists the supply sergeant. Manages hazardous materials IAW locally established regulations.
- Cooks (E4, 92G10; E3, 92G10). Cook and serve for unit personnel. Maintain and sanitize assigned equipment.
COMMAND AND CONTROL
The headquarters' major function is to provide supervision and direction to the overall operation of the company. The commander must consider the following factors as described below.
Unit Defense
The S2/S3 section establishes overall defensive plans for the group and subordinate units. The company then plans and executes the company's defense within higher headquarters' guidelines. FM's 21-75 and 100-5 provide more information for establishing defenses. For an effective defense, the company must:
- Prepare and distribute the company defense plans to sections.
- Make sure unit defenses include observation posts and interlocking fields of fire. They should also include adequate communications, minefield, and antiarmor barriers.
- Hold rehearsals to make sure all elements of the plan are coordinated.
- Hold rehearsals for the quick reaction force.
- Check to see that range cards, sector sketches, and defensive fire plans are prepared.
- Assign a final protective line or principal direction of fire for each machine gun.
- Submit to the battalion commander reports of intention to lay minefield. Also report to him the start and completion of the laying of the minefield. FM 20-32 gives more information.
- Check to see that artillery and mortar final protective fires are determined. Make sure they have been coordinated with the designated support activity.
Camouflage
Camouflage is one of the most critical means of defense for combat service support units. Camouflage should protect the unit from detection from the air and the ground. The unit should take care to use all available natural and man-made devices to camouflage its site by using approved techniques. The company leadership should constantly evaluate camouflage for its effectiveness. FM 5-20 gives helpful information on camouflage techniques.
Field Sanitation
A field sanitation team performs the sanitation duties for the company. An NCO from within the headquarters monitors the work of the team. He checks all sections to make sure they are following all sanitary procedures. He must also make sure-
- Steps are taken to control insects. Disease-bearing animals and other threats to sanitation should also be controlled.
- Field sanitation standards comply with the regulations and policies set forth in a field sanitation SOP.
- The field sanitation team is properly trained and coordinates with appropriate agencies for help.
- The company has the prescribed amount of water-purification materials on hand.
Maintenance
One light-wheeled vehicle mechanic is assigned to the company. He augments the unit assigned to provide organizational maintenance. He assists operators with required operator-level maintenance. He assists in performing preventive maintenance checks and services. He also follows the appropriate technical manuals. He should-
- Provide limited operator and organizational maintenance support to the company.
- Maintain equipment safely and IAW locally established environmental protection regulations.
- Ensure proper use of tools, and insure proper test equipment maintenance.
- Ensures all maintenance deficiencies are identified and recorded. Reports maintenance requirements above operator-level to the supporting maintenance activity.
- Assist the supporting unit's maintenance personnel with the maintenance program to include organizational-level maintenance, drivers' training program, oil analysis program, and other programs as directed.
Medical Support
The company commander is responsible for coordinating medical support. FM 8-10 gives guidance on medical support. The company commander must make sure-
- Policies and procedures are current.
- Proper medical coordination is made with higher headquarters.
- Personnel receive medical aid during any unit operation.
- Emergency aid and unscheduled medical support are available during day-to-day operations. FM 21-11 gives more information.
- Ensure appropriate number of trained combat life savers. The commander must ensure qualified personnel have all required Class VIII equipment available.
Response to Ground Attacks
When there is a ground attack, the headquarters section notifies all personnel to occupy their established defense positions. (See the company defense plan.) They notify higher headquarters of the situation by secure means. When necessary, they commit rear area protection personnel from the appropriate designated unit. They will assist in repelling, destroying, or capturing the infiltrating force. The company should request additional support such as field artillery, Army aviation, and close air support as required. They request this support through the S2/S3 section of the next higher headquarters.
Physical Security
The commander checks physical security measure enforcement. He strictly controls restricted-area access. He ensures dismount points are set up and manned. Observation posts should be positioned around the area as appropriate. The commander makes sure personnel are assigned camouflaged positions along the perimeter. He makes sure weapons, ammunition, and explosives are physically secured. FM 19-30 covers physical security planning. The commander uses it and AR 190-11 to monitor physical security.
Captured Enemy Personnel and Material
The company must process captured enemy soldiers and equipment properly. The commander makes sure soldiers do the following when processing captured enemy soldiers:
- Disarm enemy personnel.
- Segregate the prisoners by status, rank, and sex.
- Give wounded personnel lifesaving and life-sustaining medical treatment. Evacuate them to the nearest medical facility.
- Search prisoners for concealed weapons and for documents of intelligence value.
- Keep prisoners silent.
- Tag, safeguard, and move all equipment and documents to the rear or to the group headquarters. FM 34-1 gives more information. Tags should also state if documents or equipment were found on the prisoner. Under no circumstances may a soldier alter documents and equipment or keep them as souvenirs. Make sure operations are within the limits set forth in FM 19-40 and FM 27-10, Chapter 3.
- Do not give prisoners comfort items. They keep safety items such as their helmet and protective mask.
- Treat all prisoners according to the Geneva Convention provisions. FM 27-10 gives more information. Transfer prisoners to the nearest military police activity as soon as possible.
ADMINISTRATIVE AND LOGISTICAL SUPPORT
One of the key responsibilities of the company headquarters is to provide personnel and administrative support for the soldiers in the company. The company considers the following factors as described below.
The personnel administrative specialist inputs all personnel administrative data using SIDPERS transactions. He provides data to the group headquarters S1 section by secure means. DA Pamphlet 600-8-1 gives guidance. Information required includes-
- Casualty reports.
- Personnel replacement requests.
- Promotion recommendation.
- Disciplinary actions.
- Award requests.
- Other administrative data required for unit support.
Mortuary Affairs
When soldiers in the unit are killed in action, it is the company's responsibility to evacuate the remains to the nearest mortuary affair teams providing area support. If remains are unrecoverable due to tactical or logistical limitations, report their location to the EAC Support Command, who will coordinate for recovery with the nearest mortuary affairs team. Soldiers recovering the remains will try to make initial identification. They will do this from articles found on or near the body, or they will try to have someone who knew the deceased complete a statement of recognition. They will use a record of personal effects form to record any personal effects discovered with the remains. Company soldiers will assist mortuary affair teams by evacuating remains and personal effects to the closest supporting collection point. The company will prepare and submit a report on unrecovered remains indicating how many remains there are, their location, and why they were not recovered. FMs 10-63 and 10-297 and the 92M trainer's guide give more guidance.
Food Service Support
The food service section provides all Class I support to the company. They coordinate with the theater ASG or CSG to establish an account at the Class I point. When the cooks set up a field kitchen operation, they-
- Setup the field kitchen according to FM 10-23.
- Setup MKT's according to TM 10-8340-205-13.
- Check supply quantity and condition of supplies during unloading.
- Store perishables at temperatures of 7 degrees Celsius (45 degrees Fahrenheit) or below or in a dry place with air circulation.
- Check all operating equipment according to FM 10-23 and TM 10-7360-204-13& P.
- Prepare food using the cook's worksheet and TM 10-412 or SB 10-495.
- Keep utensils and equipment clean.
- Dispose of solid and liquid waste and garbage according to FMs 10-23, and 21-10 and locally established environmental procedures and regulations.
Unit Supply
FM 10-14 and the Unit Supply Update provide guidance on unit supply operations. The supply sergeant issues and maintains organizational clothing and equipment. The supply sergeant also maintains property records. Under the guidance of the PBO, he-
- Arranges supplies so the unit can provide for fast and efficient support.
- Checks replenishment supplies and verifies them against the suspense file.
- Issues supplies promptly.
- Protects supplies from adverse weather, pilferage, and sabotage.
- Issues by subhand receipt procedures all property on the commander's hand receipt.
- Prepares shortage annexes for all missing components of end items issued on sub-hand receipts.
- Uses the procedures in DA Pamphlet 710-2-1 for handling supplies. Maintains unit's combat basic load of Classes I, II, and IV expendable supplies.
- Supervises the unit armor and provides the armor with assistance as needed.
- Manages hazardous materials IAW TC 5-400 and locally established environmental procedures and regulations
Requests for and Receipt of Ammunition
In a combat zone, Class V is provided on a push basis. A request for emergency resupply of ammunition will be sent through the group S4. The supply sergeant maintains the Class V basic load by hand receipt procedures IAW the unit supply update. In garrison, the requests for Class V will be submitted on a DA Form 581 through the group S2/S3 section for validation. Then the requests go to the supporting (ASP). Personnel handling ammunition should:
- Prepare four copies of DA Form 581 according to DA Pamphlet 710-2-1.
- Store ammunition according to quantity, class, and compatibility (maintain required distance between cells or areas) IAW locally established environmental and ammunition handling regulations and procedures.
- Check ammunition to make sure that it is not damaged and that it is marked by lot number, type, and quantity.
- Account for ammunition when received, when stored, and when issued.
- Use dunnage according to the guidance in TM 9-1300-206.
- Observe safety precautions at all times when handling ammunition. Manage wastes associated with ammunition (brass, used dunnage, and so forth) IAW locally established environmental regulations.
Discipline
The S1 officer is the point of contact for handling disciplinary actions administered under the uniform code of military justice. AR 27-10 gives further guidance.
Training
The unit training program should maintain a high state of operational readiness for the unit. Environmental stewardship training and safety training should be included in all phases of this training. The group executive officer and S2/3 officer will monitor the training program. FMs 25-100 and 25-101 gives guidance on training operations. Training must be "battle focused" and support the unit's approved METL. More on training is in Section V of Chapter 8.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|