|
CHAPTER 4 WATER PURIFICATION DETACHMENT
|
Section I
THE DETACHMENT
This section is for the detachment commander.
MISSION
In areas where direct support water systems cannot provide enough water, general support units are brought in. The water purification detachment establishes and operates general support bulk water purification facilities in arid environments. It is collocated with base terminals. It is capable of producing 600,000 gallons of potable water per day from a freshwater source. When required to use saltwater sources, its production rate may be reduced. Your production capability will be based on the number of ROWPUs allocated your unit.
CAPABILITIES
Your detachment's capabilities are determined by the personnel strength levels prescribed by TOE 10469L. At full strength (TOE Level 1) and operating on a 24-hour basis, your detachment can--
- Operate up to ten 3,000-gallons-per-hour water purification units when grouped in banks with organic equipment at up to five locations.
- Produce 600,000 gallons per day when using a fresh or brackish water source.
- Produce 400,000 gallons per day when using a saltwater source.
- Store 90,000 gallons of water.
- Operate up to six bulk water purification units when augmented with personnel and equipment. The increase in capability that this provides depends upon the capabilities of the bulk purification units.
- Assist in coordinated defense of the unit area as well as the installation.
- Perform unit maintenance on all organic equipment except communications-electronic equipment.
Operational capabilities are reduced to approximately 90 percent for Strength Level 2 and 80 percent for Strength Level 3.
ATTACHED STRENGTH
Water purification teams ((TOE 10570) may be attached to your detachment when you cannot meet mission requirements. Your detachment can then purify, store, and issue more water per day More on water purification teams is presented later in this chapter.
REQUIRED SUPPORT
This detachment is capable of operating independently when provided administrative and supply support from a higher headquarters element or an adjacent unit. The elements that support the water purification detachment are as follows:
- Appropriate elements of the theater army provide medical, legal, financial, personnel, and administrative services.
- Preventive medicine teams approve water sources.
- Appropriate engineer units provide site and facility preparation and site maintenance.
- The battalion headquarters and headquarters detachment provides religious support.
ASSIGNMENT AND EMPLOYMENT
The water purification detachment will be assigned to a petroleum group. It normally is attached to a water supply battalion. The detachment will be employed in the corps or COMMZ area of operation near main lines of communications to support theater army units. Purified water is produced by the purification platoon and introduced into the water distribution system from locations onshore and offshore. The water purification detachment operates ten 3,000-gallons-per-day ROWPUs at up to five locations. The theater is fully mature when all committed forces are in place and operating. GS units provide water support where DS water systems cannot. Normally, water enters the system through the base terminal storage facility. Water is distributed to other terminals within the theater army area and forward into the corps area. The corps structure for water support is not fixed. It depends on the size of the force needed to support the mission and the specific geographic area of employment.
MOBILITY
The mobility of your detachment is determined by the number of organic vehicles authorized and the number of personnel and amount of equipment and supplies you move. If the whole detachment must move at one time, you must arrange for more vehicles. Your detachment has 74,206 pounds (3,979 cubic feet) of TOE equipment requiring transportation. The unit is capable of transporting 33,000 pounds (2,508 cubic feet) of TOE equipment with organic vehicles.
ORGANIZATION
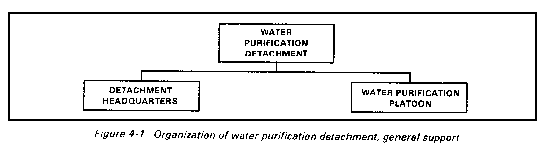
The water purification detachment (Figure 4-1) is organized into a detachment headquarters and a water purification platoon. The headquarters provides command and control. The platoon sets up and operates the assigned water purification equipment. Your detachment is organized to meet mission requirements in an arid environment. Water purification teams may be attached to your detachment when mission requirements exceed your purification capabilities.
Section II
DETACHMENT HEADQUARTERS
This section is for the detachment commander.
MISSION
Personnel in the detachment headquarters command and control water supply operations. They direct and supervise technical and support activities of the detachment. They are responsible for unit readiness, site establishment, water reconnaissance, unit administration, food services, unit supply, unit maintenance, and training. Detachment headquarters personnel support the water purification platoon and, if augmented, the water purification teams. See Chapter 1 for more in-depth information on the headquarters functions.
PERSONNEL
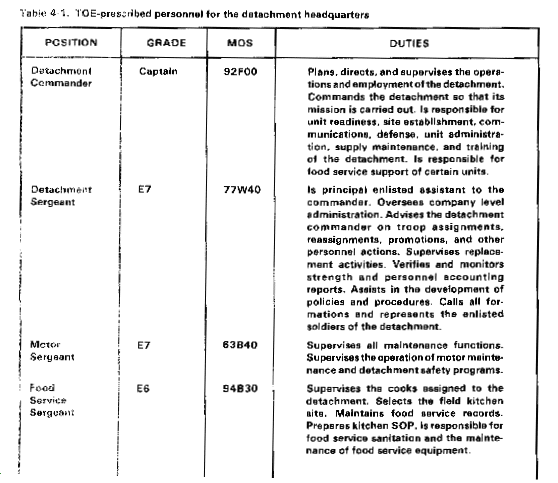
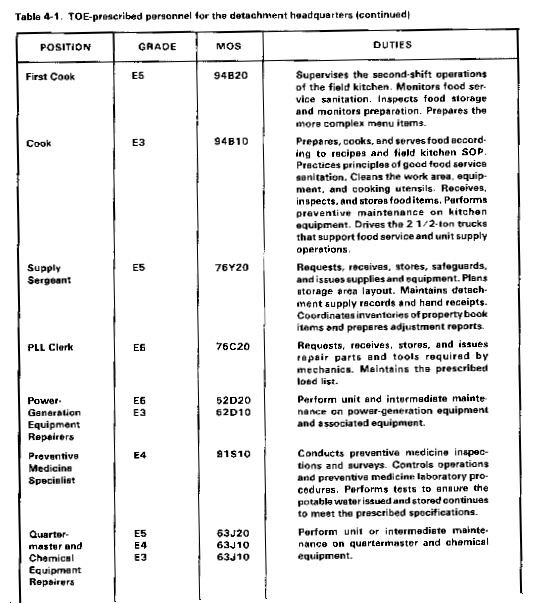
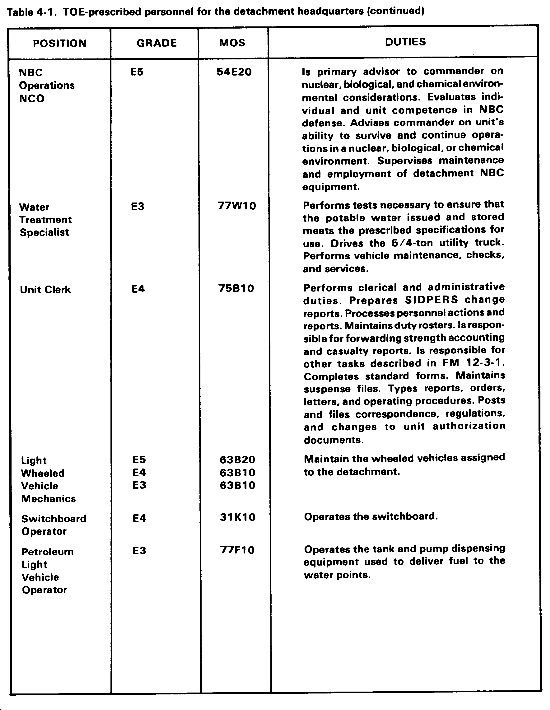
Your most valuable resources are your soldiers. To use them effectively, you must know their duties. Table 4-1 lists TOE-prescribed personnel of the detachment headquarters by position, grade, MOS, and duties.
COMMUNICATIONS
A combat communications system provides quick, reliable, and secure interchange of vital information within and between echelons. The goal is to maintain communications under all conditions. Two means of maintaining communications are wire and radio.
Wire
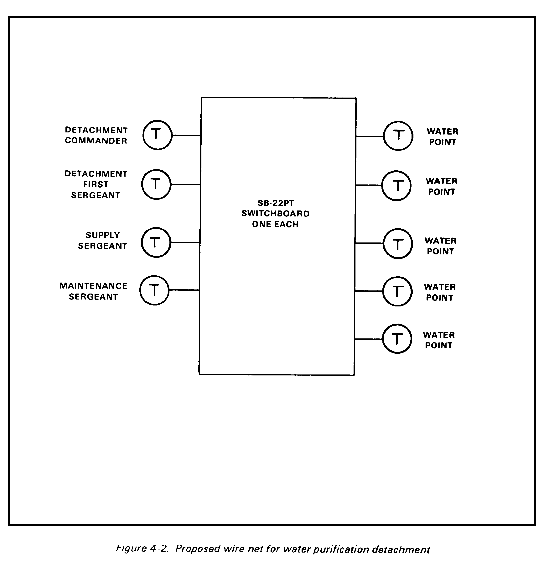
Wire is the primary means of communication provided the detachment. The organic wire net provides telephones and switchboards for internal communications and for entry into the common user system. Figure 4-2 shows a proposed detachment wire net.
Radio
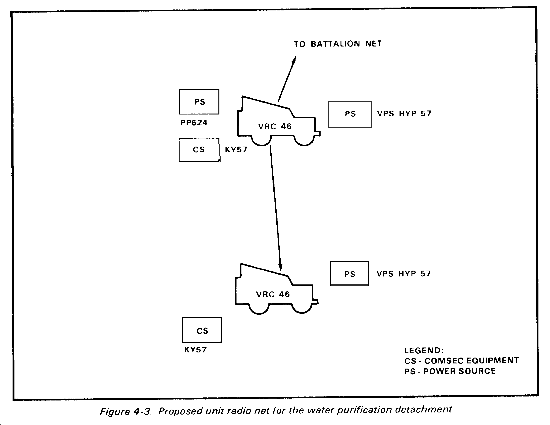
Day-to-day operations require continuous coordination with the headquarters and headquarters detachment, water supply battalion, supported and adjacent units. FM radio permits the detachment quick and accurate communication within its range. One AN/VRC 46 is required for the detachment commander to communicate with higher headquarters and with the water purification platoon. One AN/VRC 46 is required for the water purification platoon leader to receive orders from the detachment headquarters. Figure 4-3 shows a proposed radio net.
Section III
WATER PURIFICATION PLATOON
This section is for the platoon leader.
MISSION
The water purification platoon is responsible for operating the water purification facilities. The platoon can purify salt water pumped directly from the ocean, water from wells in the area, surface water, and water that may be contaminated. It is responsible for--
- Providing potable water for corps or COMMZ units in the field. The platoon produces about 600,000 gallons a day of potable water when all of its water purification equipment is available.
- Operating water supply points at up to five locations.
- Providing storage for up to 90,000 gallons of potable water.
PERSONNEL
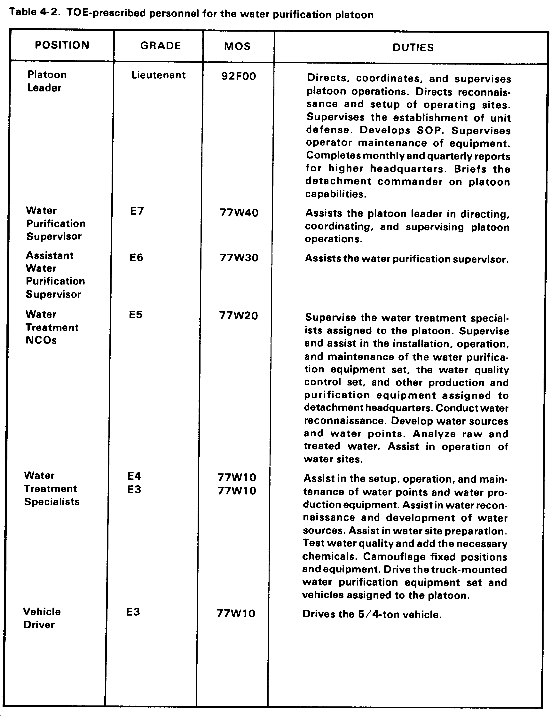
Your most valuable resources are your personnel. To use them effectively, you must know their duties. Table 4-2 lists TOE-prescribed personnel of the platoon by position, grade, MOS, and duties.
OPERATIONS
Your duties as the platoon leader fall into two general categories--tactical operations and water operations. They are described below.
Tactical Operations
You reconnoiter sites and develop layout plans, loading plans, and contingency plans for demolition. You also direct the placement and camouflage of supplies and equipment. One of your most important duties involves determining how to use personnel and equipment to accomplish your platoon mission. You are also tasked with consolidating, preparing, and reviewing technical, personnel, and administrative reports. As platoon leader, you must contribute to and update those portions of the detachment SOP dealing with platoon operations.
Water Operations
Your duties in water operations include advising the detachment commander on the selection of a site for water production. You direct the survey team on layout requirements, prepare personnel and equipment for movement, and move personnel and equipment to the operating site. You direct the setting up of an operating site. You must also coordinate with the commander of the water supply company operating the supporting water distribution and storage system.
ORGANIZATION FOR OPERATIONS
After a general operating area for the detachment is designated by the battalion headquarters, your detachment commander may ask you and your platoon sergeant to assist in a reconnaissance of the area to determine the best location for your platoon activities. It is then your responsibility to develop a layout plan for the platoon. Below are important points you and your platoon sergeant must consider in establishing your operating areas and setting up your equipment.
Reconnaissance
Preliminary planning is needed for air and ground reconnaissance. If air reconnaissance is used, get information about routes of communication, cover, concealment, inclement weather, infiltration, and avenues of attack. The use of aircraft for reconnaissance is limited by adverse weather and security considerations. Ground reconnaissance is the only positive way of getting accurate information. Table 4-3 shows ground reconnaissance factors to be considered. More information on air and ground reconnaissance is in FM 10-52.
Layout
You should prepare a layout plan for platoon operations as part of the detachment movement plan. Your first concern is the need to produce potable water as soon as possible. Your site should be reasonably level and well drained. Concealment is important also. The site should have easy access to road nets, and at least one road should run through the water supply point. During the point reconnaissance, a sketch of the site, keyed to the map and terrain features, is made. If the water source requires site improvement, complete block 10 of DA Form 1712-R (Water Reconnaissance Report). The report must be prepared carefully and on time. The data presented must be legible, clear, complete, and concise. Forward a copy of the report to the S3 at battalion headquarters. Personnel there will send it to the engineer corps for site or road work required. More on completing a reconnaissance report is in FM 10-52. A sample of the report may be found in the appendix of this FM.
WATER PRODUCTION OPERATIONS
The water purification platoon establishes and operates the general support water purification sites onshore and offshore. The platoon purifies and stores water, but has very limited distribution capabilities. The platoon is responsible for installing, operating, and performing operator maintenance on the water purification equipment sets, the water quality analysis set, and other related equipment. It is also responsible for maintaining the ROWPU. When required, the platoon production capability can be increased by attaching water teams, TOE 10570.
STANAG 2885 (Edition One). |
Water Points
Water supply points are established as far forward as possible, considering the location of available water sources, the location of consuming units, and the commander's tactical plan. However, in arid regions, available water sources are limited and widely dispersed. There is little or no surface water. The availability of subsurface water varies within geographic regions. The lack of water sources necessitates an extensive purification, storage, and distribution system. STANAG 2885 (Edition One) provides the following guidance on water supply in arid areas:
- Collection of water by unit transport will be made direct from water points in administrative areas wherever possible, but the scarcity of sources of supply and the long distances between them will often make this impossible. In such cases, distribution will have to be in cans delivered with the rations by air or land transport. Distribution in this manner is not an engineer task.
- At times it may be necessary to establish water points where there are no local sources of water and to keep these water points filled by bulk road, rail transport, or by pipelines.
Water Purification, Storage, and Distribution
The water purification platoon, equipped with its 3,000-gallons-per-hour ROWPUs, will be collocated with base terminals. The base terminals serve as the point of entry for water into the theater. They are located in the rear areas near ports or other tanker off-loading facilities. The platoon will be responsible for purifying water at the base terminals. Water purification teams will operate ROWPUs to purify surface or well water when it is available. Each site will have storage tanks and a chlorinator. Purified water from these sites may be transferred to the tank farms or to the sup ported divisions by tanker trucks or a TWDS.
Water Documents
Water point personnel submit daily reports on their water production using DA Form 1713-1-R (Daily Water Production Log--ROWPU). Platoon headquarters personnel then consolidate the information on DA Forms 1716-R (Water Point Daily Production Summary) and send them to the appropriate supply section of higher headquarters. DA Form 1715-R (Water Point Inspection Report) is completed daily by supervisory personnel and preventive medicine teams who periodically test the water for chlorine and bacteria content and inspect the water point for sanitation. The appendix to this FM shows samples of these forms. Blank forms suitable for reproduction are provided in FM 10-52. The forms are designed to coordinate the operation of widely separated water points. Their use also helps to safeguard water quality, improve efficiency of water treatment, and decrease equipment maintenance.
Physical and Chemical Tests
The main purpose of field water purification is to make water safe for humans to drink. The amount and type of treatment depends upon the quality of the raw water, the quantity of purified water needed, and the degree of purification required. The water must be treated to the degree required to make it potable. Potable water may still contain some impurities, but only impurities that will not affect the health of those who drink the water. Water treatment specialists test and analyze the available water and measure impurities to determine if they are within established limits according to TB Med 577. Usually, there are three water purification specialists in each water production squad. They operate the ROWPU and such related equipment as the water quality analysis set and the chemical agent detector kit. The water quality analysis set can detect and quantify selected naturally occurring contaminants. The chemical agent detector kit detects agents at or above concentrations that could cause casualties or reduce soldier performance. More on chemical tests is in TMs 3-6665-319-10 and 5-6630-215-12. See FM 10-52 for tests on different types and sources of water. FM 10-52 also discusses water supply under NBC conditions. STP 10-77W1-SM and STP 10-77W24-SM-TG describe water purification and treatment operations.
Operation and Maintenance of Equipment
The water treatment specialists at each water point install, operate, and perform operator maintenance on the water purification equipment sets. The water treatment NCO oversees the water specialists in their duties. The platoon sergeant makes rounds at each water point inspecting the condition of all the water treatment equipment. He also inspects supporting storage and housing facilities and materials-handling and traffic control procedures. Maintenance plays a key part in the smooth operation of the water purification unit and the support equipment. The platoon sergeant must inspect the maintenance practices of the water point personnel. He should--
- Check the condition of the support equipment. This includes checking for stripped threads, cracks, rips, and broken parts.
- Check the condition of all support areas and personnel at the water point.
- Recommend appropriate measures for damaged equipment on DA Form 2404.
- Check the water point bivouac area.
Section IV
WATER PURIFICATION TEAM
This section is for the water treatment supervisor.
MISSION
The water purification team (TOE 10570) is a specialized team that produces and issues potable water in the field. It also provides augmentation capabilities as required. Usually the team is assigned to the division, corps, or TAACOM.
CAPABILITIES
The water purification team, on a two-shift basis, can operate four water purification points. It can produce up to 240,000 gallons per day when the water source is fresh water. Use of a saltwater source reduces the production rate. Production capability will be based on the number of ROWPUs allocated to the team. The team can store up to 36,000 gallons of potable water and can issue up to 240,000 gallons per day. With organic vehicles, the team can transport 10,000 pounds (604 cubic feet) of TOE equipment. The team has 21,172 pounds (1,120 cubic feet) of TOE equipment that requires transportation.
PERSONNEL
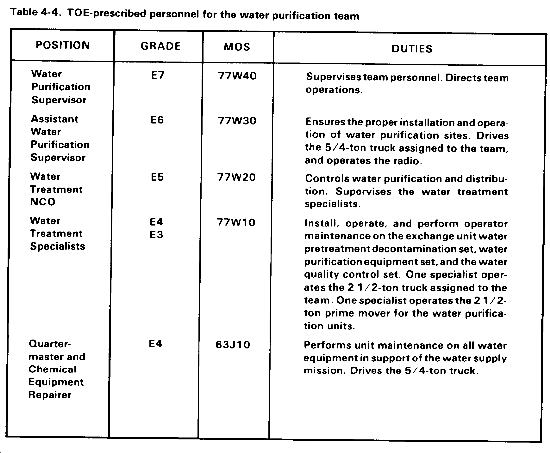
The water purification supervisor (E7, 77W40) supervises the establishment and operation of the water purification site. Table 4-4 lists TOE prescribed personnel of the water purification team by position, grade, MOS, and duties.
OPERATIONS
The water purification team issues mainly to units at the water supply points. It issues up to 240,000 gallons of water per day. If the water team is attached to the water purification detachment, the detachment platoon leader is responsible for organizing personnel and equipment in the operating area. He coordinates activities with supported units to ensure that the mission is accomplished and that correct procedures are used. He also ensures that plans and operations are carried out using correct operating procedures. Water production operations for the water purification team are the same as those described for the water purification platoon.
Water Distribution
When the water purification team is assigned a DS mission, the team will provide water by supply point distribution. When given a GS mission, the team will feed water to a water supply company for distribution. Water is distributed by a system of hoses, pipes, or pipelines to tanks, trucks, or trailers. It is normally necessary to provide a separate water point where water cans may be filled either singly or by the trailer load or truckload. The water point may consist of a distribution system with hoses. See AR 700-136 for distribution and management of water resources. Some general considerations for water distribution are described below.
Schedule. A schedule should be made giving the time of distribution for each supported unit. The schedule should specify the water point to be used.
Containers. New tanks, trailers, or other containers should be cleaned thoroughly before they are used. They should be cleaned with a calcium hypochlorite solution and rinsed with water.
Water cans and trailers. Water containers must be kept clean. They should be inspected periodically for rust and chips in the internal enamel. Water cans should be filled with water only. Water trailers must be clean when they arrive at a water point. Cleanliness is a responsibility of the using unit. Water point supervisors should refuse to fill containers that are not clean.
Lead poisoning. Lead is an accumulative poison. Lead-lined tanks or pipes should not be used in water storage, treatment, or distribution equipment.
Reports
The water team submits daily reports on water production and distribution. DA Form 1713-1-R is used by water treatment specialists to determine the daily water production. This information is submitted to headquarters personnel for consolidation on DA Form 1716-R. The water team also submits daily reports on its water distribution to using units on DA Form 1714-R. Headquarters personnel then consolidate the DA Form 1714-R and submit a DA Form 1717-R to higher headquarters. This summary should be studied to detect any unusual consumption of water by using units. Blank forms suitable for reproduction are provided in FM 10-52. See the appendix in this FM for samples of DA Form 1714-R and DA Form 1717-R.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|