|
RDL Homepage |
Table of Contents |
Document Information |
Download Instructions |
LESSON 2
MILITARY INTELLIGENCE BATTALION ORGANIZATION
| CRITICAL TASKS: | None. |
OVERVIEW
LESSON DESCRIPTION:
In this lesson you will learn the organization of the MI battalion and the support it provides to the division.
Terminal Learning Objective:
| Tasks: | You will be able to describe the organization of the MI battalion and the support it provides to the division. |
| Conditions: | You will be given narrative information and illustrations from FM 34-1, FM 34-10, FM 34-20, FM 34-2, and FM 34-30. |
| Standards: | You will describe military intelligence battalion organization in accordance with FM 34-10, FM 34-20, and FM 34-30. |
| References: | The material contained in this lesson was derived from the following publications: FM 34-1FM 34-2 FM 34-10 FM 34-20 FM 34-30 |
INTRODUCTION
An MI battalion is found in each US Army division. This battalion provides intelligence collection, EW capability, and OPSEC support to the divisional units. The division MI Battalion is the primary intelligence gathering organization of the division. The ACE and ground based IEW assets are assigned to the battalion. The MI Bn commander and the G2 join forces to ensure that all IEW teams are well trained and prepared for the mission. This association also provides the division commander a capable and competent intelligence structure. The battalion can provide direct support (DS) to the division's brigades and general support (GS) to the division as a whole.
PART A - MI BATTALION HEAVY AND LIGHT DIVISION
The battalion in the heavy division has a Headquarters, Headquarters and Operations (HHOC) company, 3 Direct Support Companies, a General Support Company, an aerial recon platoon (when fielded), and an OPCON flight platoon from the aviation brigade (See Figure 2-1).
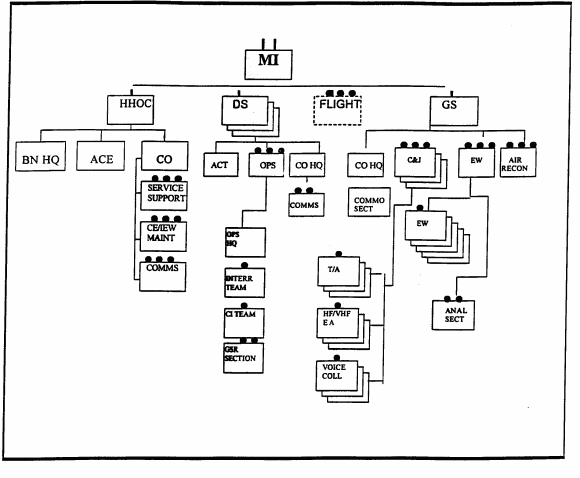
Figure 2-1. Military Intelligence Battalion Heavy Division.
The MI Bn in the light division is outfitted slightly different than the heavy division. It is organized with the philosophy of its parent division. It is light, easy to transport, and relies on additional assets from higher echelons for support during combat operations. The MI battalion relies on augmentation from corps for ground-based jamming and ELINT support. When the division is used in stability and support operations, additional CI and EPW interrogation augmentation from corps and EAC is required. The light battalion is organized as seen below in figure 2-2. A LRSD is in the light division but is not in the heavy.
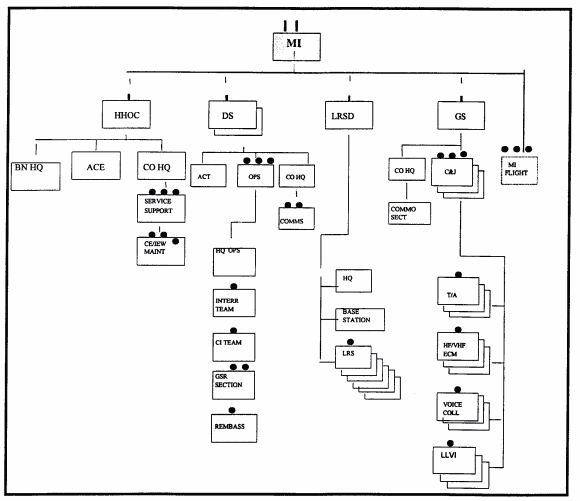
Figure 2-2. MI BN Light Division.
PART B: COMMANDER AND STAFF
MI Battalion Commander. The MI Bn Commander is responsible for the performance of his battalion. Even though battalion elements are deployed throughout the division AO and parts of the battalion may be under the OPCON of other division elements, the commander retains command authority. He ensures all elements of the battalion perform their missions effectively. He sees that personnel are properly trained, equipment is maintained, and each element receives the support it needs. As the senior MI commander in the battalion, he coordinates and controls the deployment of all MI battalion elements operating in the division AO. The commander inspects deployed elements to identify and correct deficiencies and problems that may prevent or degrade mission accomplishment. He advises the division commander, G2, G3, and subordinate commanders and staffs on the most effective use of MI battalion assets.
Executive Officer. The executive officer supervises the staff and coordinates administrative and logistic support for the battalion. Normally, the commander delegates the authority the executive officer needs to direct the staff. While each staff officer has direct access to the commander, the executive officer is informed of matters addressed through direct coordination between the commander and staff officers. The executive officer serves as the deputy battalion commander and makes command decisions in the absence of the commander. He assumes command of the battalion when the commander is incapacitated or when directed by the battalion commander.
Battalion Staff.
The staff helps the commander accomplish the battalion mission. It provides information and recommendations concerning battalion operations and supervises subordinate companies in routine matters within the staff functional areas of responsibility. The staff responds to the needs of the companies and provides them with resources, support, and assistance is responsible for personnel management and administration.
S1. His responsibilities include:
- Keeping updated personnel records on all soldiers within the battalion.
- Coordinates finance support to units and their personnel.
- Maintains the battalion publications account.
- Maintains and runs the battalion mail service.
- Assists commanders with officer evaluation reports (OERs) and noncomissioned officer evaluation reports (NCOERs).
- Coordinates medical support.
- Acts as the interface with division Judge Advocate General (JAG).
- When required, operates frequency modulation (FM) communications on the administrative and logistics (ADLOG) net.
S2. The S2 is the principal intelligence staff officer within the battalion and serves as the security manager, overseeing the establishment of personnel security procedures within the battalion. He provides the commander all of the products required for mission analysis, wargaming, planning, and executing an operation. When deployed for combat, the S2 enters and monitors the division operations and intelligence net and maintains a current intelligence situation map (SITMAP) or overlay within the battalion TOC reflecting the current enemy situation. The S2 also assists the S3 in assessing CI and EPW interrogation mission priorities as received from the C&MM section and recommends to the S3 those tasks required by CI/EPW interrogation elements in general support (GS) of the division to satisfy these missions.
S3. As the battalion operations officer, the S3 has staff responsibility for operations, plans, and training in the battalion. He has staff responsibility for asset management for MI battalion resources, to include supporting or reinforcing MI assets and supervising battalion TOC operations. Battalion S3 Section supports the S3 in the execution of asset management.
The S3's responsibilities include:
- Continuous communications with CM.
- Planning for the employment of IEW assets to support division and brigade operations.
- Working with the CM to establish signals intelligence (SIGINT) asset priorities for tasking.
- Maintaining situation awareness and accurate logs as required by SOP.
- Reviews missions received from the division C&MM section
- Develops specific tasks, and identifies the assets that can best accomplish these tasks.
- It prepares and transmits tasking instructions for SIGINT/EW tasking prepared by the ACE.
- Developing plans for the use of assets based on projected division and brigade operations.
- Managing human intelligence, CI, ground surveillance, and signal security (SIGSEC) when attached from EAC assets.
- Monitoring task accomplishment and adjusting tasking when required.
- Communications-Electronics (C-E) Support Officer. The signal officer, working with the S3, develops the division intelligence communications architecture. He must be knowledgeable in all aspects of signal communications and special intelligence capabilities to execute signal requirements. The C-E officer manages the battalion communication security program.
Battalion TOC. The MI battalion TOC controls organic, attached, and supporting MI resources. It provides the battalion commander with the centralized management necessary to ensure rapid, efficient responses to mission requirements. The TOC tasks battalion assets in response to mission tasking received from the C&MM section. The TOC consists of the S2 and S3, and their staff sections. The S3 supervises all TOC operations. The functions of the MI battalion TOC are:
- Command and control of MI battalion assets.
- Control of subordinate company teams.
- Control of corps MI assets attached or operational control (OPCON) to the division MI battalion.
- Provision of SIGINT/EW tasking to both GS and DS assets.
- Provision of asset management/tasking for subordinate CI and EPW interrogation elements when deployed in GS.
S4. The logistics officer oversees the battalion's logistics needs, His responsibilities include:
- Combat service support supply.
- Map distribution.
- Coordinates logistical support from the maneuver brigade for DS and GS IEW assets located within their AO.
- Coordinates to handle any problems that arise with IEW maintenance.
- He works with the HHOC commander to ensure a feasible working plan to provide support for the entire battalion.
- Coordinates with division for all classes of supply.
- He establishes logistics supply priorities.
- Monitors the battalion command net.
PART C: HHOC
The HHOC provides command and control for elements of the battalion and supporting units. It contains the elements which provide asset management for IEW operations and performs technical analysis for SIGINT/EW activities. The HHOC company organization is shown in Figure 2-3. Discussed already was the battalion staff and the ACE. The rest of the HHOC is divided into the service support platoon and CE/IEW maintenance platoon, communications platoon, and the battlefield deception element. Specific functions of each are:
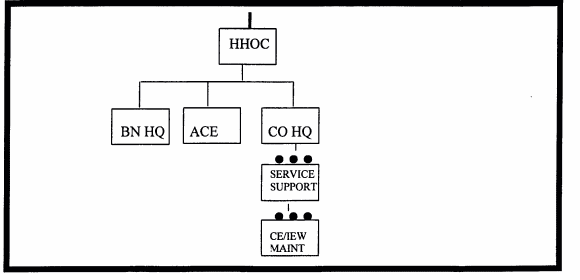
Figure 2-3. HHOC.
Service Support Platoon.
This platoon is divided into three sections: headquarters, food service, and mechanical maintenance. The HQ provides all tasking requirements for the platoon. It receives its requirements from the HHOC commander or the S4. The battalion maintenance officer (BMO) is the primary advisor to the XO and the MI battalion commander on maintenance requirements for wheeled vehicles, tracked vehicles, and generators. The BMO coordinates with the executive officer (XO) for maintenance priorities. The service support platoon provides equipment and personnel for the DS and GS maintenance contact teams. Specific team requirements will be based upon METT-T. The food service section provides support for the entire battalion. During dispersed operations the S4 will coordinate for Class I support by units in the vicinity of deployed MI companies or IEW teams. For more information on maintenance support refer to the appropriate TMs for each system and major end item listed on the tables of organization and equipment (TO&E).
CE/IEW Maintenance Platoon.
The CE/IEW maintenance platoon provides all support for IEW systems within the division and CE assets of the MI Battalion. It provides personnel and equipment for the DS and GS maintenance contact teams. Specific team requirements will be based upon METT-T. The IEW maintainers have responsibility for the electronic protection (EP) and electronic attack (EA) subsystems on the AN/ALQ-151 QUICKFIX IIB aircraft. The civilian maintenance contractors are required to provide systems specific actions per their individual contracts. Systems specific personnel must be placed on the battlefield so that they are close to the assets they repair. For example the ASAS software maintainers are located at the ACE so that they can facilitate rapid repair of down systems.
Communications Platoon.
The communications platoon works with the S3, develops the divisional intelligence communications architecture. They must have access to SCI to accomplish their duties. They work for the S3, but directly supports the ACE chief in the establishment of the assured communications architecture. They must be knowledgeable in all aspects of signal communications and special intelligence capabilities to execute their signal requirements.
The Communications-Electronics Support Officer (CESO) is also the COMSEC custodian for the battalion. They maintain the keylist requirements list and updates it as necessary. They provide keylists and COMSEC fills to each of the companies during operations. During operations they monitor the MI battalion command net.
Battlefield Deception Element (BAT-DE)
The BAT-DE is OPCON to the division G3 for operations. Its personnel assist in deception planning and execution. The element advises the commander and the G3 on deception capabilities and limitations as they pertian to certain contingencies, OPLANs or OPORDs.
Subordinate sections are plans and operations; communications signature; physical signature; and electronic signature. Each of these sections provides a different capability to deception operations. Examples include:
Plans and operations.
- Provides planning guidance to the G3.
- Incorporates the following team capabilities and other assets into the deception plan.
Communications signature team.
- Conduct communications deception by emulative and imitative measures.
Physical signature team.
- Provides two and three dimensional equipment displays.
- Establishes false CPs, forward area refueling and rearming points (FARRPs), and other false installations.
Electronic signature team.
- Provides two and three dimensional equipment displays.
- Establishes false CPs, FARRPs, and other false installations.
Electronic signature team.
- Provides false SIGINT signals.
For more information on the BAT-DE and electronic deception, refer to the appropriate FM 90-2 and FM 90-2A(S).
PART D-- DS MI COMPANY
This company provides the division ground surveillance, EPW interrogation, and limited CI capabilities. See figure 2-4 for the DS Company Organization.
- Company HQ. The company HQ provides administrative and logistical support to the DS company. It collocates with the supported brigade forward support battalion (FSB) in the brigade trains area. The HQ is normally comprised of the commander, 1SG, NBC NCO, Supply NCO, and operations NCO. In the absence of the commander, the 1SG executes all classes of support and maintenance activities. He also provides analysis support to the analysis and control team (ACT).
- Analysis and Control Team (ACT). The ACT is a small analytical team which provides DS support to the supported brigade S2. Through the use of its ASAS remote work station the ACT can access the ACEs databases. It can provide direct digital connectivity to other S2s within the division, in adjacent divisions as necessary. This team is organized with an all source intelligence officer and all source intelligence analysts. The ACT is the tasking and reporting authority for all assets organic, assigned, or attached to the DS MI company. It executes missions authorized by the brigade commander or brigade S3 and issued by the S2 as SORs. The ACT does not work for the brigade S2 but with him. The DS company commander is responsible for the execution of tasked missions. If the DS company is augmented with any EW assets the ACT will need support from the supported unit transcription and analysis section. The ACT must be trained in the receipt and tasking of SIGINT specific SORs and technical data. It must establish a standard relationship with SIGINT assets so that it can fully understand their inherent limitations and capabilities. It also:
- Provides technical control of SIGINT and electronic warfare support (ES) assets in response from tasking.
- Maintains the enemy electronic order of battle, including SIGINT and technical databases.
- Analyzes and correlates ES and SIGINT data from all sources to update the technical database and produce SIGINT.
- SIGINT data is passed to the All-Source Production of the ACE.
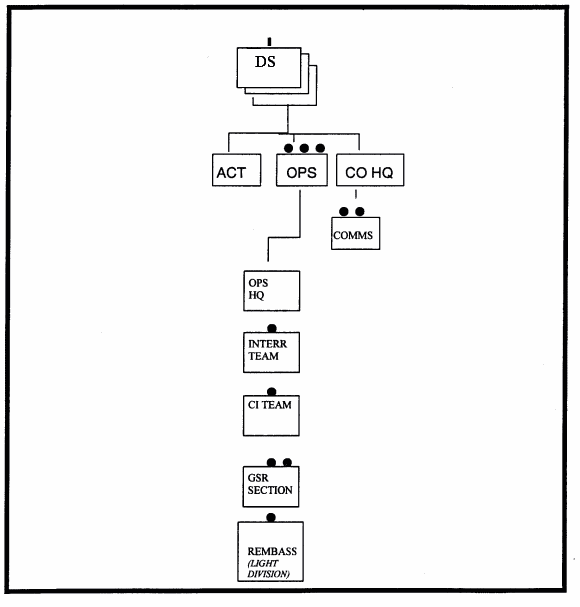
Figure 2-4. DS MI Company.
Operations/I&S Platoon.
The DS MI Company for a Heavy Division has an Operations Platoon with a GSR Team. The DS MI Company for a Light, Airborne and Air Assault Division has an intelligence and surveillance (I&S) Platoon.
CI Team. The CI team is used in an area support role. It provides multidiscipline counterintelligence support for brigade operations. The team can provide risk assessments and OPSEC proposals for the brigade operation. The CI team coordinates with other CI teams and intelligence agencies for additional HUMINT support to their brigade.
Interrogation Team. An interrogation team may be attached temporarily to one of the brigades. The initial interrogation of EPW takes place at the forward holding facility of the division in the brigade area. Initial interrogation is strictly tactical with requirements changing with the current situation. The tactical unit is responsible for initial security of EPW. As soon as possible, the tactical unit moves the EPW to the division collection point for interrogation for additional tactical information. At the division collecting point, EPW come under the control of military police, releasing tactical personnel for return to their units. The interrogation team expedites any interrogation and forwards results to the ACT and the corps EPW holding area with the EPW so corps interrogators have a starting point for their interrogations. This division interrogation team is very limited in communications and tactical movement capabilities. The team will not maintain EPWs at the brigade but will speed them to the division or corps supporting facility. The EPW team is not responsible for EPW support. These activities are provided by the supporting MP platoon.
Imagery Processing Team. Upon activation of the Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System (JSTARS) aircraft this section will be fielded with a JSTARS ground station module (GSM).
Remotely Employed Battlefield Sensor System Team. The REMBASS team provides early warning, surveillance, target acquisition, force protection, and economy of force support to the light / airborne / air assault MI Battalion. The team emplaces its sensor family along suspected avenues of approach, in or near named areas of interest (NAIs) or around the HVT's to provide early warning in a force protection mission. The sensors are expendable but should be recovered and reused if the situation permits. The REMBASS team reports its collected information directly to the ACT. If attached to a maneuver battalion for operations, it provides all collected information directly to the supported S2.
Ground Surveillance Radar (GSR) Squad. DS company GSR squads are equipped with either AN/PPS-5 or AN/PPS-15 GSR systems. The GSR provides early warning, target location, and targetable information to its supported brigade or battalion. The squad is normally attached to a maneuver unit for operations. Collected information is reported directly to the maneuver S2. GSS sections located in light / airborne / air assault MI Battalions may task organize REMBASS teams and GSR teams together to form a GSS squad in order to satisfy changing battlefield conditions to satisfy intelligence requirements.
PART E: GS MI COMPANY
The GS MI company provides SIGINT/IEW support to the division. It is organized as seen in Figure 2-5 and 2-6.
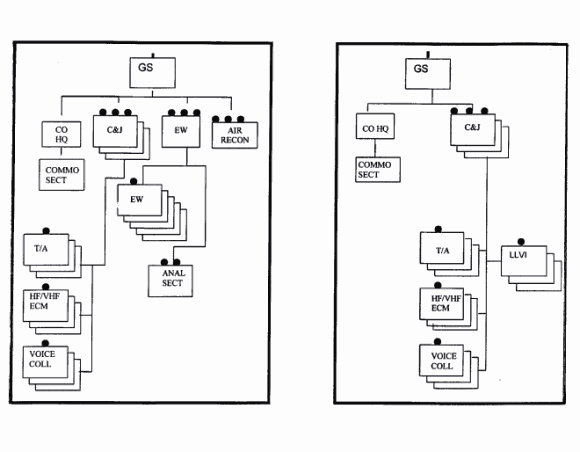
Figure 2-5. GS MI Company (Heavy). Figure 2-6. GS MI Company (Light).
Company HQ.
The company HQ provides administrative and logistical support to the GS company. It locates itself on the battlefield where its position will provide the commander with easy access to the subordinate platoons and IEW systems. The HQ is comprised of the commander, 1SG, NBC NCO, Supply NCO and operations NCO. The 1SG oversees support and maintenance activities in the absence of the commander.
Collection and Jamming (C&J) Platoon x3.
PLT HQ. The C&J Platoon HQ provides asset management for the Platoon's collection, analysis, and jamming teams. It is responsible for all tasking and reporting within the platoon. It conducts all interfaces with the company, subordinate teams, MI battalion S3, and the single source cell (SSC) of the ACE for technical data. C&J platoons may be attached to a DS company under the tenet of tactical tailoring the IEW force.
Transcription Analysis (TA) Section. The TA section is not normally deployed as part of the GS company HQ. It performs very selective scanning and gisting of voice intercepts recorded by the various collection teams. The team provides limited transcription and analysis for the company and Platoon. It reports collected information via the C&J net to the SSC of the ACE and the MI battalion S3. The ACT of the DS company also monitors this net so that they can provide near-real time communications intelligence (COMINT) reporting to the supported brigade S2 and commander. The section:
- Maintains historical data on enemy communication, including net structures.
- Examines intercepted traffic for exploitable information.
- Develops enemy net diagrams to develop subordination within threat formations.
- Isolates individual transmitters.
- Correlates DF results to locate transmitters.
Voice Collection Team. The voice collection team intercepts and gists high frequency (HF) and very high frequencey (VHF) voice communications using the AN/TRQ-32(V)2 or 3 system. It also provides DF and line of bearing (LOB) information. Recordings, gists, LOB, and DF are sent to the TA team for further processing and dissemination. The vehicle mounted and manportable systems each provide HF or VHF or a combination of the two. The team is manned to position the two vehicle mounted intercept positions. The manportable system, AN/PRD-12 is dismounted for surge or maintenance deadline.
Low Level Voice Intercept (LLVI) Team X 3 (LT/ABN/AASLT MI Battalion). The LLVI, AN/PRD-12, LMRDFS, teams are resourced by TO&E so that they can provide additional DF baselines in support of division operations. They are capable of independent and full time operations. These teams can be attached to maneuver units for a specific mission or kept in GS to the division. Their use is METT-TC dependent. They provide all collected data to the C&J platoon. They are capable of LOB and DF. Systems can be netted to extend the baseline and cue one another to a target. The team is tasked by and reports to the TA team. It receives technical data from the SSC of the ACE. This data can be received directly by the sensor or relayed if not within line of sight of the ACE.
HF/VHF Electronic Attack Team. Electronic attack teams use the AN/TLQ-17 (V) 2 or 3 and are capable of jamming HF and VHF communications. They can also perform ES tasks when not conducting jamming missions. The team receives its tasking via the G3 - S3 - C&J Platoon - team route. All mission reporting is provided back along the tasking route and to the SSC of the ACE.
Electronic Warfare Platoon (Heavy MI Battalion ONLY).
Plt HQ. The EW Platoon HQ provides asset management for the platoon's collection and analysis teams. It is responsible for all tasking and reporting within the platoon. It conducts all interfaces with the company, subordinate teams, MI battalion S3, and the SSC of the ACE for technical data.
Analysis Section. The analysis section deploys on the battlefield so that it can adequately support and employ the five AN-TSQ-138 TRAILBLAZER systems. It performs very selective scanning and jisting of voice intercepts recorded by the various collection teams. The team provides limited transcription and analysis for the company and platoon. It reports collected information via the EW T/R net to the SSC of the ACE and the MI battalion S3. The ACT of the DS company also monitors this net so that it can provide near-real time COMINT reporting to the supported brigade S2 and commander. Under certain conditions this section may execute asset tasking responsibilities for the AN/ALQ-151 QUICKFIX IIB system. The team tasks SORs to specific sensors and coordinates for technical data from the SSC of the ACE.
Electronic Warfare Team x5. The EW team provides DF reports to the analysis team via its internal UHF data link. It provides collected data and reports directly to the SSC of the ACE if within line of sight (LOS). The AN/TSQ-138 system can establish a ultra high frequency (UHF) data link with the QUICKFIX aircraft. The teams report on their T/R net to the analysis section, MI battalion S3 and to the SSC of the ACE. The system can conduct net radio protocol (NRP) with the AN/TRQ-32 (V)3, TIGER relay, and the communications control set (CCS) of the ACE.
I&S Platoon (LT/ABN/AASLT MI Battalion ONLY).
PLT HQ. The Operations platoon HQ provides asset management for the platoon's collection teams. It is responsible for all tasking and reporting within the platoon. It conducts all interfaces with the company, subordinate teams, MI battalion S3. It coordinates with maneuver unit S2s for GSR and REMBASS requirements.
CI Team. The CI team is used in a General Support role to the division. It provides detailed intelligence in the division rear area. It provides multidiscipline counterintelligence support for division operations. The team can provide risk assessments and operations security (OPSEC) proposals for division planning requirements and execution. The CI team coordinates with other CI teams and intelligence agencies for additional HUMINT support to their division. Additional GS CI teams are normally deployed from the CI company/tactical exploitation battalion/corps MI brigade. For more information on CI operations refer to FM 34-60.
Interrogation Team. The interrogation team is located at the division interrogation prisoners of war (IPW) collection facility. The team conducts limited interrogation for tactical information and sends results to the ACE. The team sends IPW and reports to the corps IPW compound. The interrogation team is not a guard unit. Guarding IPW and moving them to the rear must be accomplished by the capturing unit or the military police. The capturing unit is responsible for IPW they capture until the IPW can be turned over to MP at the division collection point. MPs coordinate the speeding of IPW to the corps supporting facility. The IPW team does not own nor is it responsible for IPW support. These activities are provided by the supporting MP platoon. Additional GS interrogation teams are normally deployed from the interrogation company of the tactical exploitation battalion of the corps MI brigade.
Air Reconnaissance Platoon (HVY/ABN/AASLT MI Battalion ONLY).
Platoon HQ. The air reconnaissance platoon HQ provides asset management for the platoon's aircraft (UAVs). It is responsible for all tasking and reporting within the platoon. It conducts all interfaces with the company, MI battalion S3, and the CM of the ACE for specific asset reporting or collection requirements.
Mission Planning. This section prepares mission plans from tasked SORs. In addition to briefing collection requirements, mission planning includes time over target, flight path, and routes to and from the target. The mission planning section ensures Army airspace Command and Control (A2C2) has cleared the appropriate airspace by effecting coordination and verifying their mission on the air coordination order (ACO).
Ground Control. Ground control assumes responsibility for the mission as soon as the aircraft is in flight. It executes the mission and ensures reporting is completed.
Launch and Recovery. Places the aircraft in flight and recovers them at the end of mission. They pass-off control of the aircraft to the ground control section.
Air Vehicle Service Support Section. This section provides service support for the aircraft and UAV specific ground control equipment. The maintenance section of the HHOC provides regular motor and C-E support.
PART F: THE LONG RANGE SURVEILLANCE DETACHMENT (LIGHT/ABN/ASSLT ONLY).
Long range surveillance (LRS) detachments are a unique addition to the MI battalion because they are composed mainly with infantrymen who perform a human intelligence (HUMINT)-like role in front of the forward line of own troops (FLOT). The detachment contains six surveillance teams, two base stations, and a headquarters section. The LRS detachment organization is seen in Figure 2-7.
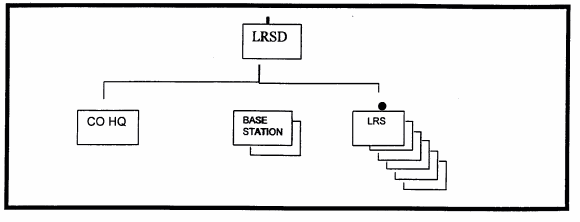
Figure 2-7. Typical LRS Detachment.
Company HQ. The company HQ is responsible for providing administrative and logistical support to the LRS detachment. The unit deploys to a location on the battlefield where it can provide the commander access to team communications. The HQ is comprised of the commander, 1SG, NBC NCO, Supply NCO and Operations NCO. The 1SG directs support maintenance activities in the absence of the commander. The LRS detachment has an operations officer to assist the commander in planning and executing LRS missions. The operations officer establishes reporting and tasking windows for each team. He oversees the execution of each mission, from conception and employment to extraction. He ensures adequate air lift is available by coordinating directly with the G3 Air for mission support.
Base Radio Station. Provide all tasking and receive the reports from the individual teams. Each team has an individual reporting window. Teams use HF burst communications systems to reduce the possibility of DF by enemy forces. Base stations report all traffic directly to the G2 and the ACE. LRS traffic is normally provided a divisional internal code word so that it can be distinguished from other HUMINT reporting.
Surveillance Teams. Each team consists of six highly trained infantryman skilled in identification and observation techniques. They are experts in vehicle identification by sight and sound. Teams use various types of spotting scopes and weapons. Weapons are to be used only as a last resort so as not to give away hide sites. They move mainly at night or in hours of limited visibility from their hide site to their surveillance site. Teams use HF digital communications to report all intelligence traffic. Teams normally have specific tasking and reporting windows in which to establish communications with the base radio station. Teams are employed out to approximately 50 KMs in support of division taskings. Teams carry rations for up to eight days when they will either need a resupply at a distant site or be extracted. The optimum is to extract the team, refit, and redeploy to a new location.
PART G: THE QUICKFIX PLATOON
The QUICKFIX platoon, from the division aviation brigade, has one organization for all types of divisions and regiments.
Platoon Headquarters. The QUICKFIX platoon is part of the aviation brigade and deploys to the airfield used by the brigade. The platoon HQ provides administrative and logistical support to the platoon. The platoon headquarters coordinates with the MI battalion S3 and the chief of the SSC for all required mission briefs. The MI battalion S3 executes OPCON of the QUICKFIX assets and tasks SORs to the platoon. The aircraft receive technical data from the SSC of the ACE. The platoon headquarters and the MI battalion S3 work with the A2C2 of the division to deconflict airspace for ingress and egress and operational collection tracks. The MI battalion S2 tracks enemy ADA assets and knows the capabilities of hostile missile systems. If he believes an operational track to be at risk for interception he immediately advises the S3 and the platoon headquarters so that they can shift the aircraft to another collection track.
Flight Section. The flight section consists of three AN/ALQ-151 equipped helicopters, (EH 60A- Blackhawks). These aircraft provide GS EA and ES to the division. Aircraft belong to the division aviation brigade. They are OPCON to the MI battalion for operations. The development of the ACE has left the S3 with limited communications assets and personnel to fully execute this mission. The EW platoon of the GS company may execute this mission for the battalion S3. The flight platoon can provide HF and VHF DF and EA in support of division operations. It can also establish a data link with the AN/TSQ-138 system, thereby extending the range and width of the division baseline.
Flight operations. The platoon leader manages flight operations to:
- Receive, analyze and plan mission taskings from the MI battalion. Coordinate and interface with USAF and other combined arms members to synchronize mission execution.
- Submit an airspace control measure request through aviation channels to G3 (Air).
- Task personnel and flight crew to perform the mission.
- Monitor the execution of the mission.
- Manage flight hours and mission resources.
Mission operations. Voice intercept operators conduct signal intercept and EW missions.
Maintenance operations. Aircraft and EW system repairers maintain on-board mission capability.
Practice Exercise

