|
RDL Homepage |
Table of Contents |
Document Information |
Download Instructions |
LESSON TWO
PRACTICE EXERCISE
INSTRUCTIONS: The following items will test your grasp of the material in this lesson. There is only one correct answer for each item. When you complete the exercise, check your answers with the asnwer key that follows. If you answer any item incorrectly, study that part of the lesson again before continuing. Answer the following questions. Choose the BEST answer for each question, and select the corresponding letter.
General Situation: You are an infantry officer stationed in Europe or the Middle East. As an infantry officer it is vital that you recognize and know some of the capabilities of the various THREAT light armored vehicles that Soviet, Warsaw Pact, and Middle East forces could deploy against you. Use this situation to answer the questions in this practice exercise.
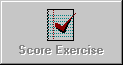
| 1. | You are in charge of a reconnaissance mission along the border of a Warsaw Pact country and observe a number of similar type vehicles (shown in Figure 2-39) deployed in self-propelled howitzer battalions. You identify the vehicles as
|
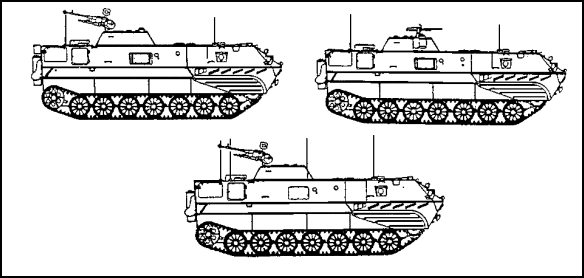
Figure 2-39.
| 2. | Refer to Figure 2-39. The vehicles position is significant because it is mainly concerned with
|
| 3. | Refer to Figure 2-39. You know the vehicles fall under the designation of 1V12s and are used solely by the
|
| 4. | You are watching a command training film of Soviet light armored vehicles and recognize the considerably smaller than average light tracked vehicle shown in Figure 2-40 as a
|

Figure 2-40.
| 5. | Refer to Figure 2-40. For amphibious operations, this vehicle is propelled through the water by
|
| 6. | You observe an Iraqi light armored vehicle (shown in Figure 2-41) fitted with a 12.7-mm open-mounted machine gun, a crew of two, and twenty troops standing by to enter an open troop compartment. You identify the vehicle as a
|
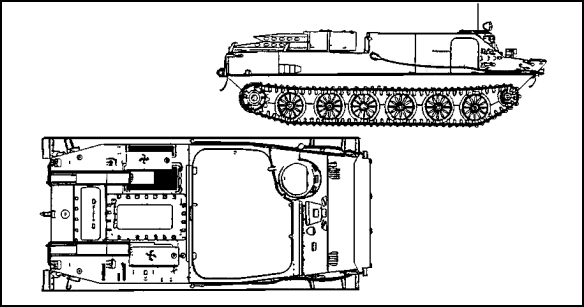
Figure 2-41.
| 7. | The vehicle identified in Figure 2-41 is amphibious and propelled through the water by
|
| 8. | Refer to Figure 2-42. You recognize the vehicle and know it is deployed as the standard APC by the
|
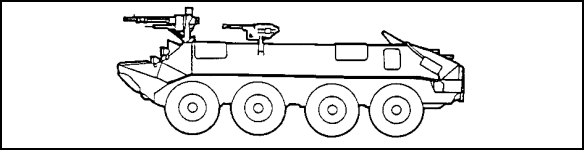
Figure 2-42.
| 9. | You see two vehicles of the type shown in Figure 2-42 offloading troops. Knowing the troop carrying capacity of the vehicles, you expect to see
|