|
RDL Homepage |
Table of Contents |
Document Information |
Download Instructions |
LESSON 1
PRACTICE EXERCISE
ANSWER KEY AND FEEDBACK
1. You are conducting spotting operations along the border of a Warsaw Pact country who is engaged in training exercises. You observe a number of vehicles of the same type with large turrets and bow-mounted machine guns. You identify the vehicles (shown in Figure 1-11) as
A. T-54/T-55 MBTs
B. T-62 MBTs
C. T-34/85 MBTs
D. T-64 MBTs
The T-34/85 is primarily used for training and no longer is in front-line service with any of the Warsaw Pact countries. Besides its large (three-man) turret and coaxial mounted machine gun, it has another very distinctive bow-mounted 7.62-mm gun machine gun.

Figure 1-11.
2. The vehicle in Figure 1-11 carries two layers of armament consisting of a
A. 85-mm main gun, a 12.7-mm AA MG, and a 7.62-mm MG.
B. 12.7-mm main weapon and a 7.62-mm secondary gun.
C. 85-mm main gun and two 7.62-mm secondary weapons.
D. 100-mm main gun and one 12.7-mm secondary weapon.
The T-34/85 carries two layers of armament: a 85-mm 54.6 caliber main weapon and two7.62-mm machine guns; one is coaxially mounted to the right of the main armament and the other is mounted in the bow also on the right side.
3. With snorkel installed, the vehicle shown in Figure 1-11 can ford a maximum of
A. 6.0 meters
B. 4.3 meters
C. 5.0 meters
D. 5.5 meters.
The T-34/85 can ford up to 5.5 meters with a snorkel and is limited to 1.32 meters without a snorkel. (page 4, paragraph (4))
4. While you are on field maneuvers in the Middle East, one of your men points out an Iraqi vehicle across the border. Using your binoculars, you notice that in addition to its armament, the vehicle has two snorkels mounted at the rear. You identify the vehicle (shown in Figure 1-12) as a
A. Basic made T-54 MBT
B. Basic made T-62 MBT
C. Basic made T-64 MBT
D. Basic made T-72 MBT
One of the key distinguishing features of the basic T-54 is its two snorkels: a thin operational one and a larger one for training.
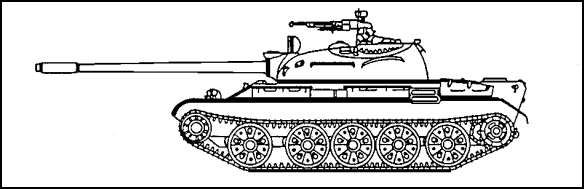
Figure 1-12.
5. Refer to Figure 1-12. Two other main features or characteristics of the vehicle that most enabled you to correctly identify it was the
A. 100-mm main gun and 12.7-mm anti-aircraft gun.
B. three tanks mounted on the left running board.
C. 85-mm main gun and 7.62-mm secondary weapon.
D. five evenly-spaced road wheels.
Two of the T-54s most distinguishing features is its 100mm D-10T rifled tank gun with a bore evacuator at the end of the barrel and its 12.7-mm DShKM anti-aircraft machine gun mounted on the turret at the loader's position.
6. The vehicle shown in Figure 1-12 arrives at the edge of a small lake. You know the water is a maximum of 4-meters deep. The vehicle
A. can ford amphibiously.
B. cannot ford under any circumstance.
C. must wait for a bridging unit.
D. can ford safely.
The basic T-54 is not amphibious, but with the proper snorkel it can ford 4.546 meters. Without a snorkel it can only ford 1.27 meters.
7. You are on a reconnaissance mission in a Middle Eastern desert and spot a vehicle (shown in Figure 1-13) with a distinct spacing between the third and fourth and fourth and fifth road wheel. You also observe what appears to be a 115 mm turret-mounted main gun. You identify the vehicle as a
A. Type 59 MBT.
B. T-72 MBT.
C. T-80 MBT.
D. T-62 MBT.
One feature of the T-62 is the pronounced space between the third and fourth and fourth and fifth road wheels. Another important feature is its long fat-barrelled 115mm smoothbore gun with a fume extractor towards its muzzle.
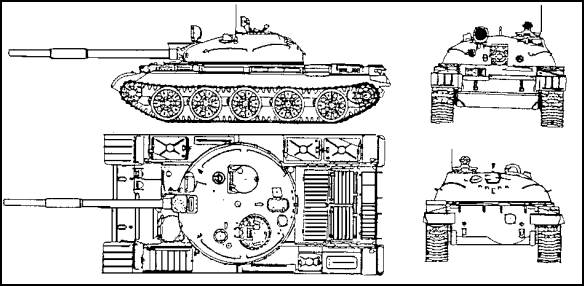
Figure 1-13.
8. Refer to Figure 1-13. Other recognition features of the vehicle that most enabled you to correctly identify it was its
A. smoke discharges and secondary armament.
B. four tanks: three on the right and one on the left.
C. large infrared searchlight left of the main armament.
D. squared front and rear hull.
The T-62 carries three external diesel fuel tanks on the right side and a single auxiliary oil tank on the left side.
9. Refer to Figure 1-13. You are directing a construction unit to dig an anti-tank ditch to prevent the vehicle type shown in Figure 1-13 from crossing into your holding zone. Knowing the capabilities of the vehicle, you instruct the team to dig a deep trench with straight vertical walls and a minimum width of
A. 1.5-meters
B. 3.5-meters
C. 2.5-meters
D. 2.0-meters
The T-62 can cross a trench 2.85 meters and climb a vertical step of 0.8 meters. Therefore, the trench must be deep enough and wide enough to prevent crossing.
GO TO:

