|
RDL Homepage |
Table of Contents |
Document Information |
Download Instructions |
Lesson 1
THREAT HEAVY ARMORED VEHICLES
IDENTIFICATION and CAPABILITIES
OVERVIEW
LESSON DESCRIPTION:
In this lesson, you will learn to identify various threat heavy armored vehicles and their capabilities.
TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE:
| ACTION: | Identify threat heavy armored vehicles, and their capabilities. |
| CONDITIONS: | You will be given information from FM 100-2-3 (CD), Jane's Armour and Artillery 1989-1990, and the Soviet and Warsaw Pact Equipment Handbook, Revision 1. |
| STANDARDS: | Recognize and identify threat heavy armored vehicles and their capabilities in accordance with FM 100-2-3 (CD), Jane's Armour and Artillery 1989-1990, and the Soviet and Warsaw Pact Equipment Handbook, Revision 1. |
| REFERENCES: | The material contained in this lesson was derived from the following publications:
FM 100-2-3 |
INTRODUCTION
The various threat heavy armored vehicles have distinctive characteristics, and capabilities. This lesson will discuss the identification characteristics, and capabilities of threat heavy armored vehicles.
THREAT HEAVY ARMORED VEHICLES AND THEIR CAPABILITIES
Threat heavy armored vehicles are categorized as main battle tanks (MBTs), light tanks (LTs), and light amphibious tanks (LATs).
1. Main Battle Tanks (MBTs).
Heavy armored main battle tanks (MBTs) have individual characteristics and capability differences. A variety of MBTs are dealt with in this subcourse.
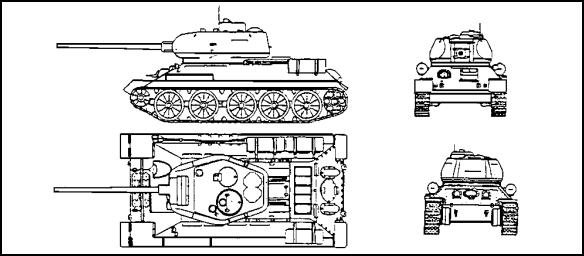
Figure 1-1. Czechoslovakian T-34/85 Medium MBT.
a. T-34/85 Medium Main Battle Tank (Figure 1-1). The Soviet built T-34/85 is primarily used for training and no longer is in front-line service with any of the Warsaw Pact countries. However, large quantities are being held in reserve.
(1) Variants. A number of T-34/85 variations have been observed and are discussed in the following subparagraphs:
(a) Anti-Aircraft Tank (China). This version is fitted with twin 37-mm automatic anti-aircraft guns, but is no longer known to be in service.
(b) 122-mm Self-propelled Gun (Syria). The mounts and guns of D-30 towed howitzers replaced the turrets on these versions. It too, is no longer known to be in service.
(c) 100-mm Field Gun M1944 (BS-3) (Egypt). This gun sits in a modified turret.
(d) 12.7-mm DShKM anti-aircraft machine gun. Some countries such as China, Egypt and Syria have fitted this gun on the turret roof.
(e) Armored Recovery Vehicles (ARVs). A variety of T-34s were modified to ARVs for towing, lifting, pushing, and pulling operations. Most modifications can be identified by the stowage platforms, winches, small and large cranes, pushbars, cable-drums, and spades mounted appropriately at strategic locations on the hull. Some of these modifications required the removal of the turret.
(f) Bridging Tanks. The Soviet version of the T-34 bridgelayer (BL) has been replaced by the T-54 (BL). A scissor type version, built by the Czechoslovaks, spans obstacles up to 15 meters wide. However, it is no longer known to be in service.
(g) Bulldozer Tanks. These tanks, developed for engineering and mine-clearing, are no longer known to be in service.
(h) Mine-clearing Tanks. The roller fitted T-34 mine-clearers were replaced by T-54 equipped mine-clearing tanks.
(i) Flamethrower Tanks. The T-34 flamethrowers were replaced by the newer T-54 equipped flamethrower tanks.
(2) Recognition Features. The T-34/85 has
- five large individually suspended dual rubbertired road wheels on each side with the drive sprocket at the rear and idler at the front. There are no track return rollers.
- a large three-man turret forward on the hull.
- optional drum-type fuel tanks that can be fitted on the sides and rear of the vehicle for an increased operational range. The drums mount before the main fuel tanks.
- a snorkel for deep fording on some models.
- two dome-shaped ventilators mounted in the roof of the turret toward the rear.
- three types of commander's cupolas: a circular fixed cupola with twin hatch covers that open front and rear, a single hatch cupola that can be traversed 360 degrees, and a similar single hatch cupola.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The T-34/85 has a four-man crew consisting of the tank commander, driver, gunner and loader. It also has an all-welded hull divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine and transmission at the rear. Specifications that apply to the T-34/85 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
T-34/85 Measurements
| Combat weight, 32,000 kg. Hull length, 6.19 meters. Hull width,2.997 meters. Overall height, 2.743 meters. Ground clearance, 0.38 meters. Track width, 500 mm. |
Fuel capacity, 590 liters. Maximum road range, 300 km. Cross country range, 209 km. Maximum speed, 55 km/h. |
Armor
| Hull Armor Thickness | Turret Armor Thickness |
| Front, 45/47 mm. Sides, 45/47 mm. Top, 18/22 mm. Floor, 18/22 mm. Rear, 47 mm. |
Mantlet, 90 mm. Sides, 75 mm. Rear, 60 mm. Roof, 18/22 mm. |
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The T-34/85 can
- cross a 2.5-meter trench.
- mount a 0.73-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- ford 1.32 meters without a snorkel.
- ford 5.5 meters with a snorkel
(5) Armament Characteristics. The T-34/85 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. The main gun is a 85-mm 54.6 caliber with a barrel length of 4.641 meters. It can fire three to four rds/min with an ammunition load of 56 rounds.
(b) Secondary Armament. Secondary armament consists of a 7.62-mm DTM machine gun mounted coaxially to the right of the main armament and a similar fixed weapon mounted in the bow, also on the right side.
(6) Countries Served. T-34 and T-38 tanks are in service with the following countries:
| Afghanistan Albania Angola Bulgaria China Congo Cuba |
Cyprus Czechoslovakia Ethiopia Germany, (East) Guinea Guinea, Bissau Hungary |
Korea, North Laos Mali Mongolia Mozambique Poland Romania |
Somalia Syria USSR Vietnam Yemen, North Yemen, South |
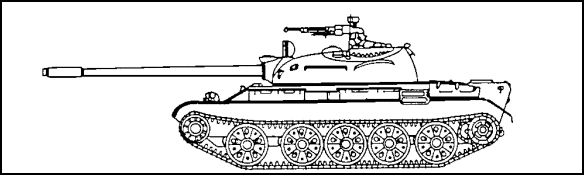
Figure 1-2. Soviet T-54B with 12.7-mm DShKM Anti-aircraft Gun.
b. T-54/55 Main Battle Tank (Figure 1-2). The T-54/55 is a non-amphibious MBT built in the Soviet Union, China (as type 59), Czechoslovakia and Poland.
(1) Variants. A number of variations are discussed in the following subparagraphs:
(a) T-54 Earlier Models. An early T-54 had a distinctive bulbous shape at its turret rear and lacked a snorkel. Another model had a 12.7-mm Dshkm machine gun at the right cupola and another version, the T-54A, was fitted with a D10TG gun. The T-54B, which followed, was fitted with a 100-mm D10T2S.
(b) T-55. The T-55, unlike the T-54, lacks a loader's cupola or 12.7-mm Dshkm anti-aircraft machine gun (fitted to some models) and a turret dome ventilator. A later model, the T-55A, has readily identifiable differences from earlier models. These differences include
- a 7.62-mm PKT gun replacing the 7.62-mm SGMT gun.
- the elimination of the 7.62-mm bow machine gun.
- a smooth, not bolted, commander's cupola.
- an improved deep-fording capability.
- raised loader and driver hatch covers.
(c) T-54/T-55 (Egyptian). Many of these T-54s/T55s were fitted with a German AEG infrared/white searchlight to the left of the main armament and a Yugoslav lskra laser rangefinder.
(d) Modernized T-54/T-55 MBTs. Some Warsaw Pact armies are upgrading their T-55 tanks to a new configuration called the T-55 AM, which includes smoke grenade launchers and a laser rangefinder mounted over the 100-mm gun. Horseshoe type armor is mounted around the front half of the turret and skirts for the upper part of the suspension are installed.
(e) Production Differences. Polish-produced tanks often have different stowage arrangements. The arrangement includes a rectangular box mounted on the left side of the turret, a smaller square stowage box on the left side of the turret-rear, and a slightly different rear decking.
(f) Armored Recovery Vehicles (ARVs). A variety of T-54/T-55s have been modified to ARVs for towing, pushing, and lifting operations. Most modifications are identified by tool and specialized equipment stowage and platforms, small and large cranes, winches, pushbars, cable-drums, spades, and dozer blades mounted strategically on the hull. Small tripod jib cranes can be erected on some versions and some modifications require the turret to be removed. Other versions have a distinctive commander's cupola on the forward right side of the hull.
(g) Bridging Tanks. Soviet, Czechoslovak, and Polish bridgelayers are built on earlier T-34 and T-54 tank chassis. The bridges launch hydraulically over the front of the vehicles and fold up when not in use to reduce vehicle length when travelling. Fully open, the bridges range in size from 12.3 to 21.6 meters and can span obstacles from 11 to 20 meters.
(h) Combat Engineer Vehicle (IMR). The IMR is essentially a T-55 that had its turret replaced with a hydraulically-operated crane. The crane can also be fitted with a small bucket or a pair of pincer type grabs for removing trees and other obstacles. A hydraulically-operated dozer blade mounts to the front of the hull; it can be used in a straight or Vconfiguration only and cannot angle doze.
(i) Dozer T-54. This T-54 can be fitted with bulldozer blades for clearing soil, obstacles and snow.
(j) Mine-clearing Tanks (Czechoslovakian and Soviet). T-54/T-55 Mine-clearing Tanks can be fitted with a wide range of mine-clearing equipment including singular and combined roller and plough type systems mounted on the front of the hull. Some lack turrets while others have built-up superstructures. On some versions, the driver sits at the front right of the turret while on others, the driver's position has been raised and moved to the rear as a new cupola with a 12.7-mm machine gun. Turrets on some models are believed to be armed with a 14.5-mm KPVT heavy machine gun replacing the normal 12.7-mm gun.
A more recent mine-clearing development is the rear-mounted rocket-propelled charges. The charges are launched across a minefield and once on the ground, are detonated.
(k) Flamethrower TO-55 (Soviet). The TO-55 flamethrower is in service with the Soviet Army and Naval infantry. The flamethrower has a maximum range of 200 meters and replaces the 7.62-mm coaxial machine gun while the 100-mm gun is retained.
(l) T-54 and T-55 (Israeli). Israel captured a number of T-54 and T-55 tanks and modified them for their own use. Some of the modifications included the replacement and/or installation of additional track storage and included replacing existing armament with some of the following armament types:
- 105-mm M68 rifled guns.
- 7.62-mm (0.30) Browning machine guns.
- 12.7-mm (0.50) Browning M2 HB machine guns.
- Browning 0.30 machine guns at loaders' stations.
- Modified 105-mm ammunition racks.
Israeli modified T-54s and T-55s are redesignated TI-67s.
(m) T-54/T-55/T-62 Model S (Israeli). These models have many other improvements including blazer explosive reactive hull and turret armor.
(n) Other Variances. Some T-54s have only four road wheels on each side. Others have a twin 57-mm self-propelled, automatic, anti-aircraft gun system sitting in an open-topped turret. A standard 12.7-mm (0.50) Browning M2 HB machine gun has replaced some Soviet equipped 12.7-mm DShKm anti-aircraft machine guns. In India, sheet steel tubes are placed on 100-mm barrels to distinguish Indian T-54/T-55 tanks from Pakistani T-59s.
(2) Recognition Features (Basic Models). Basic T-54/T55 models have
- five single rubber-tired road wheels each side with a distinctive gap between the first and second road wheels. The drive sprocket is at the rear, idler at the front and no track return rollers. Hydraulic shock absorbers are mounted on the first and fifth road wheel stations.
- four flat steel tanks on the right running board. Optional drum-type fuel tanks can also be fitted on the rear.
- three stowage boxes on the left running board.
- front climbing handles on the turret.
- an unditching beam mounted at the hull rear.
- a straight splash plate.
- a low-silhouetted, sloped hull.
- a half-egged shaped turret (view from side.)
- two snorkels: a thin one for operational use and a large diameter one for training. The operational snorkel mounts over the loader's periscope and when not used is disassembled and carried at the rear of the turret or hull. The large diameter snorkel mounts over the loader's hatch cover.
- a commander's cupola with a single hatch cover that has a periscope on each side and a infrared searchlight mounted on the forward part.
- an infrared searchlight to the right of the main armament.
- a driver's hatch cover with two periscopes mounted forward.
- a loader's hatch cover with a single periscope mounted to the right of the turret.
- an infrared light mounted to the right of the glacis plate.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics (Basic T-54/T-55 Models). T-54/T-55 basic models have all-welded hulls divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine at the rear. T-54/T55s have four-man crews with the tank commander and gunner sitting on the left side of the turret with the gunner in front. Both the T-54 and T-55 have smoke-laying capabilities. Specifications for the T-54/T-55 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
T-54/55 Measurements
| Combat weight, 36,000 kg. Hull length, 6.45 meters. Hull width, 3.27 meters. Overall height, 2.4 meters. Ground clearance, 0.425 meters Track width, 580 mm. |
Total fuel capacities, 812/960 liters. Maximum road ranges, 400/500 km. Ranges with long range fuel tanks, 600/600 km Maximum speed, 48/55 km/h. |
T-54/55 Armor
| Hull Armor Thickness | Turret Armor Thickness |
| Front upper, 97 mm. Front lower, 99 mm. Side upper, 79 mm. Side lower, 20 mm. Rear upper/lower, 46 mm. Front/rear floor, 20 mm. Top, 33 mm. |
Front, 203 mm Sides, 150 mm. Rear, 64 mm. Roof, 39 mm. |
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. Basic T-54 and T-55 models can
- cross a 2.85-meter trench.
- mount a 0.8-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- ford 1.27 meters without snorkel.
- ford 4.546 meters with preparation.
(5) Armament Characteristics (T-54/T-55 Basic Models). Basic T-54/T-55s have two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. The T-54 and T-55 basic models have the same main armament: a 100-mm D-10T (originally M1944) rifled tank gun with a length of 5.608 meters and a bore evacuator (fume extractor) at the end of the barrel. An average rate of fire for a T-54 is four rds/min with an ammunition load of 34 rounds for the T-54 and 43 rounds for the T-55.
(b) Secondary Armament. Secondary armament for the T-54 and T-55 is a 7.62-mm SGMT machine gun mounted coaxially to the main armament on the right side. The T-54 has two additional weapons: a similar 7.62-mm machine gun fixed in the center of the glacis plate and a 12.7-mm DShKM anti-aircraft machine gun mounted at the loader's position. The T-55 does not have an anti-aircraft machine gun installed.
(6) Recognition Features (T-54/T-55 105-mm Gun Models). When modified with the 105-mm gun, these T-54/T-55s share the same characteristics as stated above for basic models with some exceptions, which are discussed in the following paragraphs.
(7) Vehicle Characteristics (105-mm Gun Models). The combat weights of these T-54/T-55 versions are approximately 36,000 kg. Lengths of both versions forward are 9.20 meters and in travel, 8.20 meters. Overall heights for both vehicles are the same at2.85 meters. The width of each tank is 3.28 meters with a ground clearance of 0.45 meters and tracks of 2.63 meters.
(8) Vehicle Capabilities (105-mm Gun Models). Modified 105-mm T-54/T-55s can
- cross a 2.70-meter trench.
- mount a 0.8-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- climb a 30-percent side slope.
- ford 1.27 meters without snorkel.
The maximum speed of the modified T-54 is 43 km/h while the modified T-55 can attain a maximum speed of 45.48 km/h.
(9) Armament Characteristic (105-mm Gun Models). These modified T-54/T-55s have two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. Main armament for both the modified T-54 and T-55 is the 105-mm gun.
(b) Secondary Armament. Modified T-54 and T-55 tanks have identical secondary armament: a 7.62-mm machine gun mounted coaxially to the main armament and a 7.62-mm antiaircraft gun.
(10) Countries Served. T-54 and T-55 tanks are in service with the following countries:
| Afghanistan Albania Algeria Angola Bulgaria Central African Republic China Congo Cuba Czechoslovakia Germany, (East) |
Egypt Equatorial Guinea Ethiopia Bangladesh Finland Guinea Hungary India Iran Iraq Israel Kampuchea |
Korea, North Lebanon Libya Mali Mongolia Mozambique Nicaragua Nigeria Pakistan Peru Poland Romania |
Somalia Sudan Syria Tanzania Togo USSR Vietnam Yemen, North Yemen, South Yogoslavia Zambia Zimbabwe |

Figure 1-3. Soviet T-62 MBT.
c. T-62 Main Battle Tank (Figure 1-3). The T-62 MBT was developed from earlier T-54/T-55s. However, the T-62 has a longer and wider hull, different spacing on the road wheels (A distinct gap is located between the third and fourth and fourth and fifth road wheels.), different turret shape, and a longer and fatter gun barrel with a fume extractor towards its muzzle.
(1) Variants. A number of T-62 variations are discussed in the following subparagraphs:
(a) T-62M (NATO T-62A). The main recognition differences between the T-62 and the T-62M are the contour and size of the turret and the replacement of the fixed loader's hatch with a rotating cupola mounting a 12.7-mm DShKM antiaircraft machine gun. The 12.7-mm DShKM can only be used from outside the tank. Some machine gun ammunition boxes are stored externally on the right of the turret. The T-62 can be fitted with mine-clearing equipment like that fitted to the T-54/T-55. Currently, the T-62 is being updated with new components.
(b) Egyptian T-62s. Some of these T-62s are fitted with Sakr ground-to-ground smoke rocket launchers.
(c) T-62K Command Tank. T-62K variances are specifically in the areas of internal communications and navigation.
(d) TO-62 Flamethrower. The TO-62 flamethrower is in Soviet service. The flame gun has an effective range of 100 meters and is mounted coaxially with the 115-mm gun.
(e) Modified T-62 MBTs. A number of T-62 tanks have been fitted with additional armor protection for the fuel tanks, above the road wheels, glacis plate, and each side of the 115-mm gun halfway round the turret. The additional turret armor is fitted passively to the turret. Some T-62 tanks were fitted with missile launchers on the rear of the turret for air defense, but it is not known if these were ever deployed operationally.
(f) RO 115-mm Tank Barrel. British Royal Ordnance has provided substantial quantities of 115-mm tank barrels to Egypt for replacement of the existing T-62 115-mm U-5TS guns.
(g) T-62 with 105-mm L7 Gun. In this conversion, a 105-mm L7 rifled tank gun replaces the standard 115-mm U-5TS gun.
(h) T-62 with GIAT 120-mm Smoothbore Gun. In this conversion, a GIAT 120-mm smoothbore gun replaces the 115-mm gun.
(i) M1977 Armored Recovery Vehicle (ARV). These ARVs are limited to towing operations and as far as it known, they are not fitted with winches or other specialized recovery equipment.
(2) Recognition Features. The T-62 has
- five twin rubber-tired road wheels on each side with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and no track return rollers. A hydraulic shock absorber is also provided at the first and last road wheel stations.
- three external diesel fuel tanks on the right side and a single auxiliary oil tank on the left side. The T-62 also has two optional drum-type fuel tanks that can be fitted on the rear of the vehicle for an increased operational range.
- an unditching beam mounted at the hull rear.
- two snorkels, a thin one for operational use and a large diameter one for training. The operational snorkel is disassembled and carried at the turrets rear when not in use.
- a longer hull and gun tube than the T-54/T-55.
- a rounded turret (view from side).
- a low-silhouetted hull.
- a commander's cupola that is further back on the turret than the loader's hatch. The cupola has four periscopes; two in the hatch cover and two in the forward part of his cupola.
- a drivers single-piece hatch cover.
- two periscopes for the gunner, one of which is used in conjunction with the main searchlight mounted coaxially to the right of the main armament.
- a loader's single hatch cover to the right of the turret with a periscope that can be used to the front or rear.
- a straight splash plate mounted on the front of the vehicle with a white light and an infrared headlamp mounted to the rear of the deflector.
- front-climbing curved handles on the turret.
- turret rails for infantry or personal equipment.
- a box-like radiation detector/actuator mounted on the right side of the turret behind the compressed air tanks.
- a blower mounted at the rear of the turret to the left of the spent cartridge ejection door.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The T-62 has an all-welded hull divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine and transmission at the rear. The T-62 has a four-man crew consisting of the tank commander, driver, gunner and loader. The tank commander is seated on the left and the driver is seated in the front of the vehicle on the left side. The T-62 also has smoke-laying capabilities. Specifications that apply to the T-62 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
T-62 Measurements
| Combat weight, 40,000 kg. Hull length, 6.63 meters. Hull width,3.3 meters. Overall height, 2.395 meters. Ground clearance, 0.43 meters. Track, 2.64 meters Track width, 580 mm. Track length on ground, 4.15 meters. |
Total capacity internal/external/supplemental fuel tanks, 675/285/400 liters. Normal on/off-road range, 450/320 km. Maximum on/off-road range with long range fuel tanks, 650/450 km Maximum speed, 50 km/h. |
T-62 Armor
| Hull Armor Thickness | Turret Armor Thickness |
| Front upper, 102 mm. Front lower, 102 mm. Sides upper, 79 mm. Sides lower, 15 mm. Rear upper/lower, 46 mm. Front/rear floor, 20 mm. Top, 31 mm |
Front, 242 mm Sides, 153 mm. Rear, 97 mm. Roof, 40 mm. Hatches, 30/31 mm. |
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The T-62 can
- cross a 2.85-meter trench.
- mount a 0.8-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- ford 1.4 meters without snorkel.
- ford 5.5 meters with snorkel.
(5) Armament Characteristics. The T-62 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. The main gun is a U-5TS (2A20) 115-mm smoothbore gun with an average rate of fire of four rds/min and a main ammunition load of 40 rounds.
(b) Secondary Armament.T-62 secondary armament consists of a 7.62-mm PKT machine gun mounted coaxially to the right of the main armament.
(6) Countries Served. T-62 tanks are in service with the following countries:
| Afghanistan Algeria Angola Cuba Egypt |
Ethiopia Germany, (East) Iran Iraq Israel |
Korea, North Libya Mongolia Syria USSR |
Vietnam Yemen, North Yemen, South |

Figure 1-4. T-64 with 12.7-mm machine gun.
d. T-64 Main Battle Tank (Soviet) (Figure 1-4). Initially, problems were encountered with a number of T-64 components, which resulted in the T-64 not being considered a satisfactory design. However, the T-64A and T-64B, later production models, are in service with the Western Group of Forces. In this lesson the T64B, although a T-64 variant, is presented as the primary T-64 model. Both vehicles are basically the same and have
- a modified gunner sight.
- a bump stop for the fourth road wheel.
- hinges for the attachment of side skirts.
- six smoke mortars on each side of the turret.
(1) Variant. The T-64K command version, when stationary, is fitted with a 10-meter telescopic mast that is erected over the turret and held in position by stays that are pegged to the ground. The T-64K command version is not normally fitted with the 12.7-mm anti-aircraft gun.
(2) Recognition Features. The T-64B has
- six small evenly-spaced dual road wheels on each side with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and four return rollers. A hydraulic shock absorber is also provided at the first, second, fifth and sixth road wheel stations.
- a sharply-sloped upper glacis with V-shaped water and debris deflector.
- ammunition/storage boxes on the turret sides.
- optional drum-type fuel tanks that can be fitted.
- an infrared searchlight mounted on the left side of the main armament.
- integrated fuel cells and storage containers that give a streamlined appearance to the fenders.
- two snorkel types for deep fording, one fitted to the turret and the other over the engine compartment. The snorkels are carried on the top of the turret at the rear.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. At least two versions of the T-64B are in operation: the new construction version, which lacks the forward gunner's sight, and the rebuilt version, which retains the gunner's sight. The T-64B has an all-welded hull divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine and transmission at the rear. The T-64B has a crew of three. Specifications that apply to the T-64B are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
T-64B Measurements
| Combat weight, 42,000 kg. Hull length, 7.4 meters. Hull width with/without skirts,4.64/3.38 meters. Height without AA MG, 2.2 meters. Ground clearance, 0.377 meters. Track width, 580 mm. |
Track length on ground, 4.4 meters. Total fuel capacity all tanks, 1,000 liters. Normal road range, 400 km. Maximum road range with long range fuel tanks, 600 km Maximum road speed, 75 km/h. |
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The T-64B can
- cross a 2.72-meter trench.
- mount a 0.8-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- climb a 40-percent side slope.
- ford 1.4 meters without snorkel.
- ford 5.5 meters with snorkel.
(5) Armament Characteristics. The T-64B has two layers of armament: main and secondary. The T-64B also has explosive reactive armor (ERA).
(a) Main Armament. Main armament is a 125-mm 2A26 smoothbore gun/missile launcher. The 125-mm gun can achieve a rate of fire of six to eight rds/min. The 125-mm ordnance can also fire the AT-8 Songster ATGW missile.
(b) Secondary Armament. The T-64B's secondary armament consists of a 12.7-mm anti-aircraft gun machine gun that can be aimed and fired from within the tank and a 7.62-mm machine gun mounted coaxially to the main armament. Two or three boxes of 12.7-mm ammunition are mounted on the left side of the turret.
(6) Country Served. The T-64 is in use only with the Soviet Union.
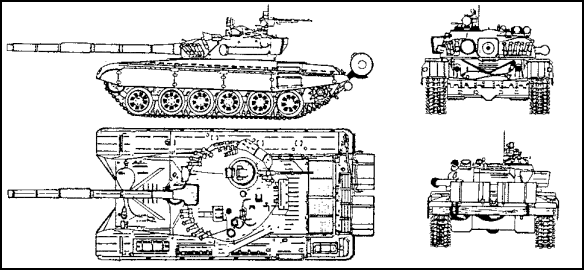
Figure 1-5. T-72M1 MBT with smoke dischargers.
e. T-72 Main Battle Tank (Figure 1-5). Since the Soviet built T-72 entered production, many improvements have been made to the vehicle, making it difficult to distinguish individual versions of the tank. Improvements include: increased protection, better mobility, and enhanced firepower. A late production model, the T-72M1 (Figure 1-5), is fitted with smoke dischargers on the turret: seven on the left side and five on the right side.
(1) Variants. The following variants summarize some of the key distinguishing features:
(a) T-72 with ERA. This T-72 is fitted with explosive reactive armor (ERA) arrays similar to those installed on the T-64 and T-80 series MBTs. To fit the mounting points for ERA, eight forward-firing smoke mortars have been repositioned to the left side of the turret and the distinctive V-shaped splash plate on the glacis has been removed.
(b) BREM-1 Armored Recovery/Repair Vehicle (ARRV). This ARRV is equipped with a hydraulic crane, capable of lifting 12 tons, mounted at the front of the hull on the left side. Other equipment includes a main winch with a capacity of 25 tons that can be increased to 100 tons, an auxiliary winch, a hydraulically operated dozer/stabilizing blade at the front of the hull, towing equipment, and a complete range of tools and recovery equipment. This vehicle is known to be used in (East) Germany.
(c) IMR-2 Combat Engineer Vehicle. The IMR-2 is believed to be the replacement for the T-55 IMR. A crane is mounted that can be fitted with a number of attachments including pincers for uprooting trees. At the front of the vehicle is a dozer blade that can be used in a straight or V-configuration.
(2) Recognition Features. The T-72 has
- six large evenly-spaced road wheels on each side with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and three return rollers.
- two optional drum-type fuel tanks that can be fitted to the vehicle for an increased operational range.
- a unditching beam carried at the rear.
- a snorkel for deep fording that is carried on the left side of the turret to the rear.
- a commander's cupola with a periscope and an infrared searchlight on each side.
- a gunner's hatch mounted with two observation periscopes. An infrared searchlight is mounted in front and to the left of this hatch along with a laser rangefinder.
- another infrared searchlight mounted on the right side of the main armament.
- a single loader's hatch to the right of the turret with a periscope that can operate to the front or rear.
- a driver's single hatch cover, in front of which is a wide-angle observation periscope.
- two light-steel stowage boxes mounted on the turret, one at the rear and the other on the right.
- integrated fuel, oil and storage containers along each side of the hull that give the fenders a streamlined shape.
- an oil cell and stowage boxes on the top left side of the hull.
- four removable armored skirt plates fitted over the forward part of the track for additional protection.
- a dozer blade mounted under the nose.
- optional mine-clearing equipment.
- a searchlight and infrared headlamp mounted to the rear of the deflector, on the right side.
- turret rails.
- a box-like radiation detector/actuator mounted on the right side of the turret behind the compressed air tanks.
- a blower mounted at the rear of the turret.
- a sharply-sloped glacis made of a new laminate armor 200-mm thick and a V-shaped water and debris deflector mounted to the glacis plate.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The T-72's all-welded hull is divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine and transmission at the rear. The T-72 has a three-man crew. The tank commander and gunner sit in the turret with the commander on the right and the gunner on the left. Specifications that apply to the T-72 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
T-72 Measurements
| Combat weight, 41,000 kg. Hull length, 6.95 meters. Hull width with/without skirts,4.75/3.6 meters. Height without AA MG, 2.37 meters. Ground clearance, 0.47 meters. Track width, 580 mm. |
Track length on ground, 4.25 meters. Total fuel capacity all tanks, 1,000 liters. Normal road range, 480 km. Maximum road range with range fuel tanks, 700 km. Maximum road speed, 80 km/h. |
Turret armor is believed to be 280-mm thick while the nose is 80mm thick.
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The T-72 can
- cross a 2.7-meter trench.
- mount a 0.85-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- climb a 40-percent side slope.
- ford 1.4 meters without snorkel.
- ford 5.5 meters with snorkel.
(5) Armament Characteristics. The T-72 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. Main armament is a 125-mm 2A46 smoothbore gun which can fire eight rds/min with an ammunition load of 39 rounds and a range of 2,000 meters.
(b) Secondary Armament. T-72 secondary armament consists of a12.7-mm anti-aircraft NSVT machine gun mounted on the commander's cupola and a 7.62-mm PKT machine gun mounted coaxially to the main armament. (The 12.7-mm gun is a new design turret machine gun that has no provision for firing from inside the tank. It can only be used with the commander exposing the upper part of his body.)
(6) Countries Served. T-72 MBTs are service with the following countries:
| Algeria Angola Bulgaria Cuba |
Czechoslovakia Finland Germany, (East) Hungary |
India Libya Iraq Poland |
Romania Syria USSR Yugoslavia |

Figure 1-6. T-80 Main Battle Tank with Explosive Reactive Armor.
f. T-80 Main Battle Tank (Soviet) (Figure 1-6). The T-80 is the main battle tank in first echelon threat units and has been deployed to units in (East) Germany and other Soviet units which had not been supplied T-64 MBTs. Apparently the T-80 is only being deployed with Soviet rather than Warsaw Pact forces. The track of the T-80 is slightly wider than the T-64 and has a longer length of track on the ground. The T-80 is believed to have reverted to torsion bar suspension like that fitted to the T-72 as opposed to the T-64, which has hydro-pneumatic suspension. A distinct spacing is noted between the second and third, fourth and fifth, and fifth and sixth road wheels.
(1) Variants. A number of variants have been observed and are discussed in the following subparagraphs.
(a) T-80 M-1981/3. This version was first thought to be another variant of the diesel-powered T-72.
(b) T-80 M-1983/1. A gas-turbine-powered version.
(c) T-80 Model 1984. This version can be fitted with smoke grenade launchers on each side: five on the left and four on the right of the main armament.
(d) T-80 Command Version. While unknown, there is probably a command version of the T-80 with a laser designation system mounted on the commander's cupola; the system would be protected by a rectangular armored box cover.
(2) Recognition Features. The T-80 is very similar to the older T-72 and incorporates some features of the T-64. It also has its own unique characteristics. The T-80 has
- six large evenly-spaced rubber-tired road wheels that are bolted together in two halves with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and three track return rollers. The new tracks are fitted with rubber pads.
- two snorkels: a large one for the gas turbine, and another one for the radiator grill. Both are carried at the turret rear in a large circular container.
- a distinct oblong exhaust at the hull rear.
- a dozer blade under the vehicle's nose.
- a unditching beam carried across the hull rear.
- a laser warning device at the rear hull.
- three rather than four deflection bars in front of the driver's hatch.
- an infrared searchlight mounted on the right side of the main armament.
- enhanced frontal armor and side skirts.
- twelve turret-mounted smoke dischargers, seven on the left side and five on the right.
- optional fuel tanks for rear hull mounting.
- integrated fuel cells and storage containers that give the fenders a streamlined shape.
- a sharply-sloped laminate type glacis plate for improved protection against kinetic energy and HEAT attack.
- a removable missile guidance box mounted on the right side of the turret roof in front of the commander's cupola.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The overall layout of the T-80 is similar to the T-64 series with the driver's compartment at the front, two man turret in the center and engine and transmission at the rear. The T-80 has a three-man crew. The tank commander and gunner sit in the turret with the commander on the right and the gunner on the left. Specifications that apply to the T-80 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
T-80 Measurements
| Combat weight, 42,000 kg. Hull length, 7.4 meters. Hull width, 3.4 meters. Height without AA MG, 2.2 meters. Ground clearance, 0.38 meters. Track width, 580 mm. |
Track length on ground, 4.4 meters. Total fuel capacity all tanks, 1,400 liters. Normal road range, 400 km. Maximum road range with long range fuel tanks, 600 km Maximum road speed, 75 km/h. |
When fitted with explosive reactive armor, the smoke grenade launchers are moved from each side of the main armament back to each side of the turret and positioned between the turret side and the explosive reactive panels. The T-80 is virtually immune to penetration from all current NATO ATGWs which rely on a HEAT warhead to penetrate armor. The armor does not provide protection against APDS or APFSDS attack.
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The T-80 can
- cross a 2.9-meter trench.
- mount a 0.9-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- climb a 40-percent side slope.
- ford 1.4 meters without snorkel.
- ford 5.5 meters with preparation.
(5) Armament Characteristics. The T-80 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. The T-80 uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore gun that can fire four types of separate loading ammunition with a range of 2,500 meters. The T-80 also fires the AT-8 Songster ATGW missile. The 125-mm gun/missile launcher tube is fitted with a thermal sleeve and a fume extractor. There is a possibility that only a part of the T-80 fleet is equipped to fire the AT-8 Songster ATGW. The ammunition load for the 125-mm gun depends on mission requirement for standard rounds and the AT-8 Songster ATGW. A normal 125-mm ammunition load is 40 rounds.
(b) Secondary Armament. Secondary armament consists of a12.7-mm anti-aircraft NSVT machine gun mounted on the commander's cupola. This weapon can only be used with the commander exposing the upper part of his body. Also, a 7.62-mm PKT machine gun is mounted coaxially to the right of the main armament.
(6) Countries Served. T-80 MBTs are in service with Soviet forces only in the Soviet Union and (East) Germany
g. M-84 Main Battle Tank (Yugoslavian). Recognition features and vehicle characteristics for the Yugoslavian built M84 are virtually the same as those stated for the late production Soviet T-72 MBT (Figure 1-5) with two banks of smoke dischargers mounted on the turret front: seven on the left and five on the right.
(1) Vehicle Characteristics. Specifications for the M-84 are presented in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
M-84 Measurements
| Hull length Forward with (without unditching beam or long range fueltanks), 9.53 meters. Width overall, 3.57 meters. |
Height to turret roof, 2.19 meters. Ground clearance, 0.428 meters. Track, 2.79 meters. Track length on ground, 4.27 meters. |
(2) Vehicle Capabilities. The M-84 can
- cross a 2.8-meter trench.
- mount a 0.85-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- climb a 40-percent side slope.
- ford 1.2 meters without snorkel.
- ford 1.8 meters with five minutes preparation.
- ford 5 meters with 20 minutes preparation.
(3) Armament Characteristics. M-84 main and secondary armament is the same as that for the T-72 MBT.
(4) Countries Served. The M-84 MBT is in service with the Yugoslavian Army and is being offered for export.
h. T-74 Main Battle Tank (Soviet). Recognition features and vehicle characteristics for the T-74 are the same as those stated for the late production T-72 MBT (Figure 1-5) and the M-84 stated above. No further recognition and vehicle characteristics or exceptions for the T-74 will be discussed in this lesson.

Figure 1-7. Type 59 MBT with 100-mm Gun.
i. Type 59 Main Battle Tank (China) (Figure 1-7). The Type 59 MBT was developed from earlier Soviet supplied T-54s and later model T-54As. In many aspects, the Chinese Type 59 and Soviet T54s are similar.
(1) Variants. A number of Type 59 modifications and variations are presented in the following subparagraphs:
(a) NORINCO Type 59 Retrofit Package. In addition to internal engineering and equipment changes, a new 100-mm gun stabilized in both elevation and traverse has been installed on this version.
(b) Type 59 with 105-mm gun. This gun is believed to be a western 105-mm rifled tank gun fitted with the normal fume extractor and thermal sleeve.
(c) Type 59 with 105-mm L7 gun. The United Kingdom has fitted this type 59 with the 105-mm L7A3 rifled tank gun.
(d) Type 59 MBT with IR18 Thermal Imager (UK). This United Kingdom owned Type 59 was fitted with a IR18 based thermal fire control system. The thermal sensor for the system was mounted on a bracket on the left side of the mantlet and moves with the 105-mm gun.
(e) Type 59 Chassis with Marksman Turret. This type 59 version was fitted with a twin 35-mm air defense turret.
(f) Type 59 Basic ARV. This ARV is essentially a Type 59 with its turret removed. The vehicle is armed with a single 12.7-mm machine gun. This ARV is not believed to have a winch and is limited to towing operations.
(2) Recognition Features.The Type 59 is similar to the Soviet T-54 and shares many of the same characteristics. More recent T-59 production models have
- infrared searchlights for the commander and gunner.
- a larger infrared searchlight mounted above the main armament that moves in elevation with the main armament.
- a laser rangefinder (fitted to some models) right of the infrared searchlight mounted over the main armament.
- new night vision equipment that includes new periscopes for the commander, gunner and driver (fitted on thirty models only).
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The overall layout of the Type 59 is similar to the T-54 series with the driver's compartment at the front, fighting compartment in the center and engine and transmission at the rear. The Type 59 has a four-man crew. Specifications that apply to the Type 59 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
Type 59 Measurements
| Combat weight, 36,000 kg. Hull length, 6.04 meters. Hull width, 3.27 meters. Height,2.2 meters. Ground clearance, 0.425 meters. Track, 2.855 meters Track width, 580 mm. Track length on ground, 3.84 meters. |
Fuel capacity main tanks, 815 liters. Fuel capacity external tanks, 400 liters. Normal road range, 420-440 km. Maximum road range with long fuel tanks, 600 km Maximum road speed, 40-50 km/h. |
Type 59 Armor
| Hull Armor Thickness Front upper, 97 mm. Front lower, 99 mm. Sides upper, 79 mm. Sides lower, 20 mm. Rear upper/lower, 46 mm. Front/rear floor, 20 mm. Top, 33 mm |
Turret Armor Thickness Front, 203 mm Sides, 150 mm. Rear, 64 mm. Roof, 39 mm. |
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The Type 59 can
- cross a 2.7-meter trench.
- mount a 0.79-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- ford 1.4 meters without snorkel.
- ford 5.5 meters with preparation.
(5) Armament Characteristics. The Type 59 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. Main armament for the Type 59 consists of a 100-mm Type 59 rifled gun that fires both Chinese and NORINCO developed rounds. Normal ammunition load for the main armament is 34 rounds.
(b) Secondary Armament. Secondary armament consists of three weapons: a12.7-mm anti-aircraft Type 54 machine gun, a 7.62-mm Type 59T machine gun at the bow and another 7.62-mm 59T machine gun mounted coaxially to the right of the main armament.
(6) Countries Served. Type 59 tanks are in service with the following countries:
| Albania Bangladesh China |
Congo Kampuchea North Korea |
Pakistan Tanzania |
Vietnam Zimbabwe |

Figure 1-8. Type 69-II MBT with 100-mm Gun and Side Skirts.
j. Type 69 Main Battle Tank (China) (Figure 1-8). The Type 69 MBT was first produced with both smoothbore (Type 69-I) and rifled (Type 69-II) guns. After extensive testing, the rifled gun proved to be more accurate and had greater armor penetration characteristics. Smoothbore production was discontinued after only 150 such equipped Type 69s were built. The Type 69-I is a further development of the Type 59 and differs from it mainly in the areas of armament, fire control and night vision equipment. In this lesson, the Type 69-I is discussed as the basic type 69 and the Type 69-II is discussed as a variant. Actual layouts of the Type 69-I and Type 69-II MBTs are virtually identical and are not repeated in this lesson.
(1) Variants. The following variants summarize some of the key distinguishing features:
(a) Type 69-II. The Type 69-II is fitted with a 100-mm rifled gun firing Chinese developed ammunition. The gun is stabilized both horizontally and vertically and has an increased hit probability due to a new fire control system. In addition to basic equipment, the Type 69-II has side skirts and a laser rangefinder mounted externally above the 100-mm gun. Some Type 69s are fitted with an external stowage bin on the turret rear and armor protection for the anti-aircraft machine gun.
(b) Thai Army Type 69-II. The Thai Army have replaced the 12.7-mm armament on their Type 69-II with the US 12.7-mm M2 Browning machine gun.
(c) Twin 37-mm SPAGG. There are two versions of the Twin 37-mm SPAGG. The first version sits in a power operated two man turret that is essentially built on a Type 69 tank chassis. This version has a four-man crew with the commander seated on the left and the gunner on the right with the Twin 37mm cannon between them. No radar is fitted to this version, making it a fair weather system only. The second version is armed with the same twin 37-mm cannon fitted with flash suppressors and a surveillance radar mounted on the turret rear. As far as is known, this version has yet to enter production.
(d) Twin 57-mm Type 80 SPAGG. The twin 57-mm Type 80 SPAGG is fitted on a modified Type 69-II MBT chassis with an open-topped turret. This vehicle has a six-man crew.
(e) Type 84 Armored Vehicle Launch Bridge (AVLB). The Type 84 AVLB is essentially a Type 69 MBT with its turret replaced with a bridge launching mechanism. The bridge launches over the front of the vehicle and when fully open can span a gap of up to 16 meters and support tracked and wheeled vehicles weighing up to 40 tons.
(f) Type 653 Armored Recovery Vehicle (ARV). The Type 653 ARV is based on the chassis of the Type 69 MBT. Besides recovering other vehicles on the battlefield, this ARV is designed to undertake major repairs such as changing powerpacks, clearing obstacles and preparing fire positions. Type 69 ARV standard equipment includes a front-mounted hydraulically-operated dozer blade, a hydraulic crane on the right side, a main winch with a capacity of 70 tons, an auxiliary winch, tools, tow bars and cables. A small quantity have been sold to Thailand.
(2) Recognition Features. The Type 69-I has
- a laser rangefinder mounted externally over the main armament in front of the mantlet.
- an infrared searchlight on the commander's cupola.
- an infrared searchlight above and to the immediate right of the main armament.
- an infrared driving light on each running board. o a coating of infrared reflecting paint.
- side skirts.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The Type 69-I has an all-welded hull that is divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine at the rear. The Type 69-I has a four-man crew. Specifications that apply to the Type 69-I are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
Type 69-I Measurements
| Combat weight, 36,500-37,000 kg. Hull length, 6.243 meters. Width over skirts/hull, 3.298/3.27 meters. Height to axis of AA MG, 2.807 meters. Ground clearance, 0.425 meters. |
Track, 2.64 meters. Track width, 580 mm. Track length on ground, 3.845 meters. Maximum road range, 420/440 km. Maximum road speed, 50 km/h. |
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The Type 69-I can
- cross a 2.7-meter trench.
- mount a 0.8-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- climb a 40-percent side slope.
- ford 1.4 meters.
(5) Armament Characteristics. The Type 69-I has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. Main armament is a 100-mm smoothbore gun with a bore evacuator near the muzzle. The ammunition load for the 100-mm gun is 34 rounds.
(b) Secondary Armament. Type 69-I secondary armament consists of a 12.7-mm anti-aircraft Type 54 antiaircraft machine gun mounted on the loader's cupola. A 7.62-mm machine gun is mounted coaxially to the main armament and another similar weapon is mounted in the bow. The Type 69-I can lay a smoke screen through the exhaust system on the left side.
(6) Countries Served. Type 69 MBTs are in service with China, Iraq and Thailand.
k. Type 79 Main Battle Tank (China). Recognition features and vehicle characteristics for the Type 79 are similar to some of the features on Type 59, Type 69 and Type 80 MBTs shown in Figures 1-6, 1-7 and 1-8.
(1) Variants. None.
(2) Recognition Features. The Type 79 MBT has
- towing eyes under the nose of the tank.
- headlamp arrangements similar to the Type 80 MBT.
- a turret (slightly different than the Type 59/ 69) with a large rectangular window forward of the commander's cupola that could be an internally-mounted laser rangefinder.
- a bank of four electrically-operated smoke dischargers mounted on each side of the turret.
- a metal stowage box mounted to the rear of the smoke dischargers that is believed to house additional grenades.
- slight differences in the rear of the hull suggests a powerpack unlike the one used on the Type 59/Type 69.
- five removable skirts on the upper suspension.
- new tracks with removable rubber pads replacing the more normal all-steel tracks fitted to other Chinese MBTs.
- night vision equipment for the commander, gunner and driver.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The Type 79 chassis is similar to the Type 59/Type 69 and weighs 37.5 tons compared to the 36 tons on the Type 59. The Type 79 has a maximum road speed of 50 km/h. Other specifications of the Type 79 are presented in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
(4) Armament Characteristics. The Type 79 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. Type 79 main armament is a 105mm rifled tank gun that is provided with a fume extractor and a thermal sleeve.
(b) Secondary Armament. Type 79 secondary armament consists of a12.7-mm machine gun mounted on the loader's cupola for local and anti-aircraft defense and a 7.62-mm machine gun mounted coaxially with the main armament.
(5) Countries Served. The Type 79 MBT is in service in China.
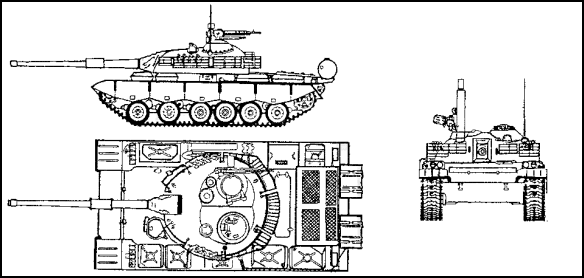
Figure 1-9. Type 80 Main Battle Tank.
l. Type 80 Main Battle Tank (China) (Figure 1-9). The Type 80 is a brand new chassis with a turret similar to that installed on the Type 69 MBT but with different armament.
(1) Variants. The following variants summarize some of the Type 80s key distinguishing features:
(a) Type 80-II. The Type 80-II is virtually identical to the basic Type 80 except that it has a slightly greater combat weight and a greater overall length. Other specifications are internal and will not be discussed in this lesson.
(b) Type 85-II and Type 85-IIA. These two vehicles have been developed with a welded turret that can be fitted with additional armor protection. Exact differences between the Type 85 and Type 85-II are unknown; although the Type 85-II is slightly heavier and shorter in length. Armament is the same as in the Type 80 except that the Type 85-II can carry 46 rounds of 105-mm ammunition while the Type 85-IIA can carry 44 rounds. Other differences are internal and will not be discussed further.
(2) Recognition Features. The Type 80 has
- six dual rubber-tired road wheels on each side with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and three track return rollers. The first, second, fifth and sixth road wheel stations have hydraulic shock absorbers.
- two optional drum-type fuel tanks that can be mounted on the rear for an increased operational range.
- a snorkel for deep fording mounted on the loaders hatch when in use.
- a commander's cupola with a forward-opening hatch cover with two integral periscopes for side observation.
- three frontal observation periscopes mounted forward of the commanders hatch.
- a loader's left opening circular hatch cover.
- four forward-firing electrically-operated smoke dischargers on each side and a stowage basket that runs around the sides and rear of the turret.
- a splash board mounted on the glacis plate.
- a driver's single left opening hatch cover, in front of which are two day periscopes, one of which can be replaced by an infrared periscope for night driving.
- two circular exhaust outlets on the right side of the hull.
- armored track skirt plates with hinged wavy bottoms to allow for suspension maintenance.
(3) Vehicle Characteristics. The Type 80 all-welded hull is divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine and transmission at the rear. The Type 80 has a four-man crew. The tank commander, gunner and loader sit in the turret with the commander on the left, gunner forward and below the commander, and the loader on the right. Composite armor can also be added to the vehicle's front and turret for increased protection. Additionally, the Type 80 has smoke laying capabilities. Specifications that apply to the Type 80 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
Type 80 Measurements
| Combat weight, 38,000 kg. Hull length, 6.325 meters. Hull width over tracks, 3.354 meters. Hull width over skirts, 3.372 meters. Height to turret roof, 2.290 meters. Ground clearance, 0.48 meters. |
Track, 2.7 meters. Track length on ground, 4.064 meters. Fuel capacity, 1,400 liters. Maximum road range, 430 km. Maximum road speed, 55-60 km/h. |
(4) Vehicle Capabilities. The Type 80 can
- cross a 2.7-meter trench.
- mount a 0.8-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- climb a 40-percent side slope.
- ford 1.4 meters without snorkel.
- ford 5 meters with preparation.
(5) Armament Characteristics. The Type 80 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(a) Main Armament. Main armament for the Type 80 is a 105-mm rifled gun fitted with a fume extractor and a thermal sleeve. The ammunition load for the 105-mm gun is 44 rounds.
(b) Secondary Armament. The Type 80s secondary armament consists of a 12.7-mm anti-aircraft machine gun mounted on the loader's hatch and a 7.62-mm machine gun mounted coaxially to the main armament.
(6) Countries Served. Chinese development of the Type 80 MBT is complete and the vehicle is ready for production.
2. Light Tank (LT) (China).
Type-62. The Type 62 LT is virtually a scaled down Type 59 MBT (Figure 1-7) and is believed to be used in place of the Type 59 in rugged terrain such as that encountered in southern China. The Type-62 LT is the only threat light tank discussed in this subcourse.
a. Variants. None.
b. Recognition Features. The Type 62 light tank has the same basic recognition features as the Type 59.
c. Vehicle Characteristics. The layout of the Type 62 is identical to the Type 59. It has a four-man crew with the driver at the front of the hull on the left and the other three crew members in the turret. The commander and gunner are seated on the left of the turret with the loader on the right. The engine and transmission are at the rear of the hull. Specifications that apply to the Type 62 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
Type 62 Measurements
| Combat weight, 21,000 kg. Hull length, 5.55 meters. Hull width, 2.86 meters. Height, 2.25 meters. Ground clearance, 0.42 meters. |
Track, 2.39 meters. Track width, 380 mm. Track length on ground, 3.53 meters. Fuel capacity, 730 liters. Maximum road range, 500 km. Maximum road speed, 60 km/h. |
d. Vehicle Capabilities. The Type 62 can
- cross a 2.55-meter trench.
- mount a 0.7-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- ford 1.3 meters without snorkel.
e. Armament Characteristics. The Type 62 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(1) Main Armament. Main armament is a 85-mm gun, probably identical to that on the Type 63 light amphibious tank. Main ammunition load for this weapon is 47 rounds.
(2) Secondary Armament. Secondary armament consists of a12.7-mm anti-aircraft Type 54 heavy machine gun mounted at theloader's position for anti-aircraft use and a 7.62-mm machine gun mounted coaxially to the right of the main armament. Another 7.62-mm machine gun is mounted at the bow.
f. Countries Served. Type 62 tanks are in service with the following countries:
| Albania China |
Congo North Korea |
Mali Sudan |
Tanzania Zaire |
3. Light Amphibious Tank LAT (China).
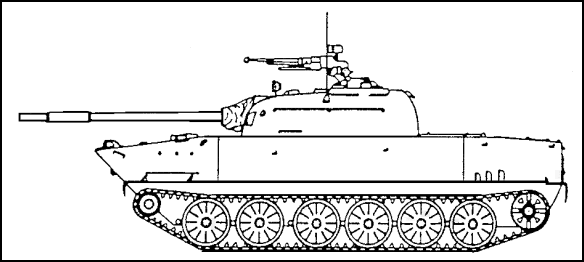
Figure 1-10. Type 63 Light Amphibious Tank (China).
Type 63 LAT (Figure 1-10). This is a redesigned version of the Type 60. The Type 63 LAT uses automotive components of the Type 77 series APC, which is the Chinese version of the Soviet BTR50KP vehicle, both of which are discussed in Lesson Two.
a. Variants. None.
b. Recognition Features. The Type 63 LAT has
- a fully amphibious capability.
- six rubber-tired road wheels with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and no track return rollers.
- a shallow glacis plate.
- a trim board folded back onto the glacis plate that is erected at the front of the hull before entering the water.
- a single-piece driver's hatch cover that has three periscopes mounted forward of the hatch.
- a infrared driving light on the right side of the hull front.
- a commander's hatch that opens forward and a loader's hatch that opens to the rear.
- a dome-shaped ventilator mounted in the turret roof to the rear of the commander's and gunner's hatches.
- optional fuel tanks that can be fitted on top of the hull to increase operational range.
- a Chinese designed laser rangefinder (fitted on some models) over the rear part of the 85-mm gun. This is identical to the laser rangefinder found on some Chinese Type 59 MBTs.
- no NBC system or night vision equipment for commander and gunner.
c. Vehicle Characteristics. The Type 63 LAT has an all-welded rolled-steel hull divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine and transmission at the rear. The turret is in cast-steel sections welded together. The Type 63 has a four-man crew consisting of the tank commander, driver, gunner and loader. The tank commander sits on the left side of the turret with the gunner on the same side in front and the loader to the right. The Type 63 is fully amphibious, being propelled in the water by two water jets of Soviet design. Specifications that apply to the Type 63 are provided in the lists and paragraphs that follow.
Type 63 Measurements
| Combat weight, 18,000 kg. Hull length, 7.15 meters. Hull width, 3.2 meters. Height to turret top, no AAMG,2.522 meters. Height to turret top, with AAMG, 3.122 meters. |
Ground clearance, 0.4 meters. Track. 2.82 meters. Track length on ground, 4.44 meters. Fuel capacity, 545 liters. Maximum road range, 370 km. Maximum road speed, 64 km/h. Maximum water speed, 12 km/h. |
Type 63 Hull Armor
| Front, 11 mm. Sides upper, 14 mm. Top, 10 mm. |
Floor, 10 mm. Rear, 10 mm. Mantlet, 11 mm. |
d. Vehicle Capabilities. The Type 63 can
- cross a 2.9-meter trench.
- mount a 0.87-meter vertical step.
- climb a 60-percent grade.
- ford amphibiously.
e. Armament Characteristics. The Type 63 has two layers of armament: main and secondary.
(1) Main Armament. The Type 63 has a 85-mm gun, probably identical to that installed in the Type 62 light tank. A normal ammunition load for the main armament is 47 rounds.
(2) Secondary Armament. Secondary armament consists of a12.7-mm anti-aircraft machine gun, a 7.62-mm Type 54 (Soviet M1938/46 DShKM) heavy machine gun mounted at the loader's station for anti-aircraft defense and another 7.62-mm machine gun mounted coaxially to the main armament.
f. Countries Served. Type 63 LATs are in service with the following countries:
| China North Korea |
Pakistan | Sudan | Vietnam |
GO TO:
Practice Exercise 1
Lesson 2
Table of Contents

