FM 34-81-1: Battlefield Weather Effects
APPENDIX B
WEATHER EFFECTS ON AIR DEFENSE ARTILLERY
Air defense artillery (ADA) requires weather information for both deployment and employment. Deployment requires climatological data, trafficability, and severe weather forecasts. Weather conditions affecting employment vary according to the type of weapon system used. When missle systems require radar surveillance, elements such as refractive index and precipitation must be known. Other systems require visual target acquisition. Listed below are weather effects for ADA that are not contained in the WTDA tables.
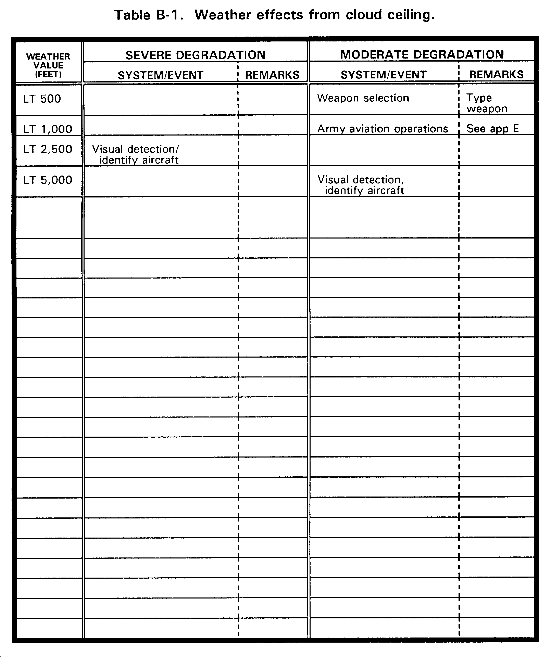
CLOUDS AND SKY COVER. Overcast skies degrade visual acquisition and tracking. Low overcast limits the effectiveness of aerial illumination devices. Clouds limit the use of NVD by blocking natural light from the moon and stars.
HUMIDITY. Moisture in the air affects the refractive index and may degrade radar effectiveness.
ILLUMINATION. Most NVD require about a quarter (23 percent) of the moon, 30 degrees above the horizon, scattered clouds, and the sun more than 5 degrees below the horizon. Detailed products dealing with the use of E-O devices are available from the SWO.
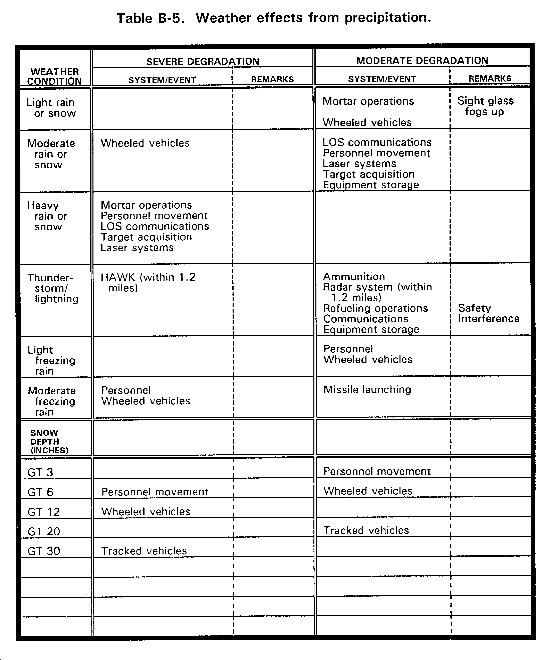
PRECIPITATION. Rain, sleet, or snow prevents visual target acquisition and tracking. Precipitation attenuates radar signals and degrades or prevents infrared homing.
REFRACTIVE INDEX. This index (see glossary for a description) degrades target acquisition and tracking radar.
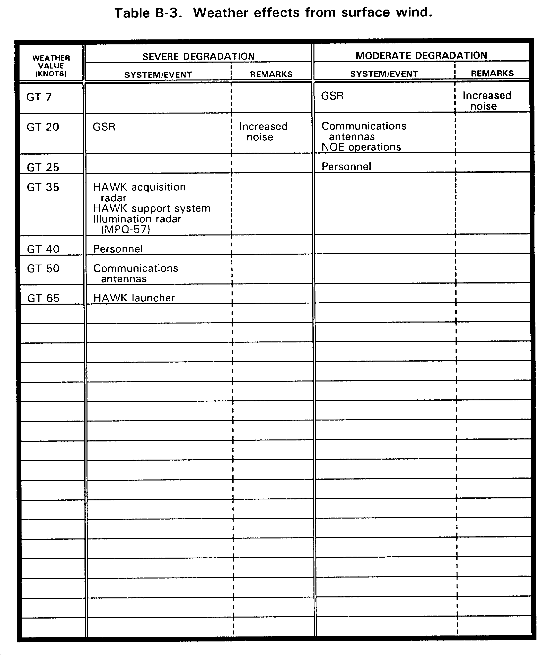
SURFACE WIND. Strong surface winds produce blowing dust, sand, or snow and may cause computers to malfunction.
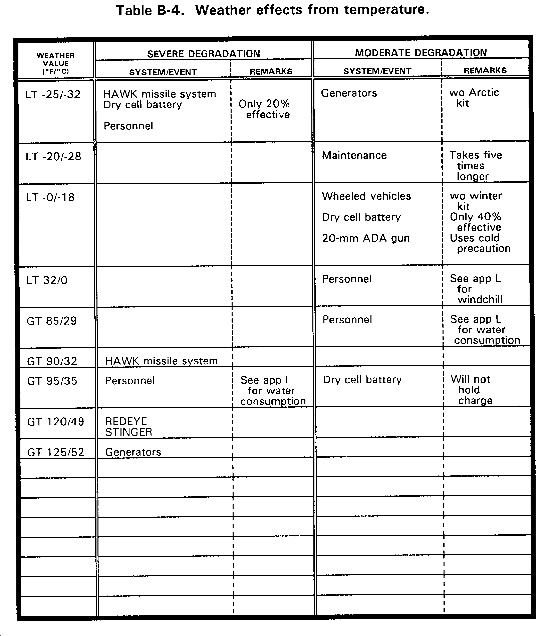
TEMPERATURE. High temperatures can degrade the effectiveness of electronic systems, and very low temperature may affect mechanical devices. Extreme cold produces detectable ice-fog exhaust trails from certain weapon systems and vehicles.
THUNDERSTORMS AND LIGHTNING. Intense electrical storms will probably mean that electronic systems will be out of service.
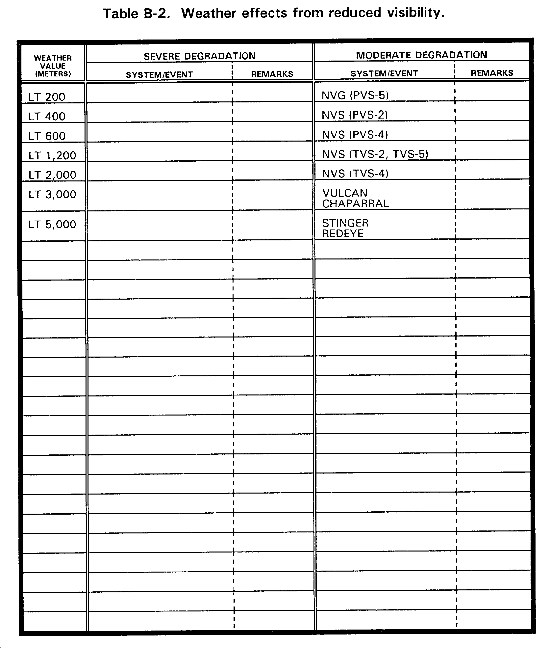
VISIBILITY. Low visibility decreases the effectiveness of visual collection systems.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

