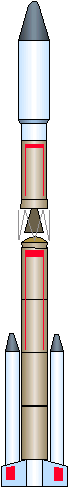
M-3SII
Targeting Halley's comet which made an appearance in 1985 after 76 years, ISAS started the development of the fifth generation Mu-launch system, M-3SII in 1981. The booster is a descendant of the M-4S first flown in 1970. It used the first stage of M-3S. however, the rest of the stages were replaced by new ones to enhance its payload capability. M-3SII-1 and -2, with a fourth kick stage, sent the first and second Japanese interplanetary probes, SAKIGAKE and SUISEI in 1985 toward encountering orbit with Halley's comet. Seven launches of M-3SII Iaunch system out of eight have been successful up to now.
The only flight during 1993-1994 occurred on 20 February 1993 when the 420-kg Astro-D (aka Asuka) X- ray observatory was inserted into an orbit of 534 km by 647 km with an inclination of 31.1 degrees. The maximum lift capacity for the M-3SII is approximately 800 kg into a 250 km circular, a 31 degree orbit (References 116 and 117).
The M-3SII is a 3-stage, all solid-propellant launch vehicle with two strap-on boosters and a family of optional fourth stages which are tailor made for specific mission profiles. All four stages as well as the strap-on boosters are manufactured by the Nissan Motor Company. In addition to LEO missions, the M-3SII has placed spacecraft on Earth escape trajectories (Sakigake and Suisei in 1985) and into extremely high altitude orbits with apogees beyond lunar distances (Muses-A in 1990). The final flight of the M-3SII took place in 1995 in support of the German Japanese-Russian microgravity recoverable satellite program, EXPRESS.
M-3S-II (Japan) | |
 |
Background Information
History
Description
Profile
|
The vehicle M-3SII-1 is described as follows
| 1st st. | SOB | 2nd st. | 3rd st. | 4th st. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total length | m | 27.785 | 9.140 | 13.1235 | 4.6661 | 2.0084 |
| Maximum diameter | m | 1.650 | 0.735 | 1.650 | 1.495 | 1.400 |
| Weight (ig.) | kg | 51952.6*1 | 10248.1 | 17267.2*3 | 4208.8 | 605.65 |
| Weight (b.o.) | kg | 24718.9*2 | 2225.1 | 6950.2*3 | 910.9 | 185.05 |
| Propellant weight | kg | 27098.0 | 8023.0 | 10317.0 | 3297.9 | 420.60 |
| Freon | kg | 271.46 | 87.6 | |||
| Hydrazine | kg | 40.0 | ||||
| Specific Impulse | sec | 266*4 | 266*4 | 282.0*4 | 293.1*4 | 284.6*4 |
| Center of gravity (ig.) | % | 63.3 | 61.7 | 55.1 | 49.5 | |
| Center of gravity (b.o.) | % | 44.5 | 47.0 | 36.2 | 29.4 | |
| Ix (ig.) | kg.m.sec2 | 3537.7 | 472.5 | 93.98 | 6.286 | |
| Ix (b.o.) | kg.m.sec2 | 919.2 | 206.0 | 13.04 | 3.536 | |
| Iy (ig.) | kg.m.sec2 | 295110.0 | 11754.0 | 304.4 | 14.27 | |
| Iy (b.o.) | kg.m.sec2 | 130310.0 | 5019.0 | 124.4 | 6.22 | |
| Net payload | kg | 247.4 | SA 138.1 | |||
| Nozzle expansion ratio | 7.80 | 9.13 | 23.24 | 51.84 | 49.00 | |
| Nozzle exit diameter | mm | 1270.4 | 725.0 | 1349.8 | 1094.4 | 504.0 |
*1:including Freon(271.46kg)
*2:including Freon(135.73kg)
*3:including Freon(87.6kg) & Hydrazine(40.0kg)
*4:in vacuum
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

