Chapter 4
Support
This chapter describes the roles and functions of the AAMDC's key support staff. This staff includes the G1 and G4 sections, and other support elements such as the special staff and the headquarters and headquarters battery (HHB).
OVERVIEW
4-1. In order for the AAMDC to efficiently perform its mission, a number of critical support functions must be performed. These support functions include personnel management, logistic management, special staff functions, and battery headquarters administration. |
PERSONNEL SECTION
4-2. The personnel section (G1) is responsible for personnel administration and manpower management and is the focal point for all personnel-related matters. It ensures that the AAMDC and subordinate elements are manned at levels sufficient to accomplish their mission, provides health and personnel service support, and performs headquarters management functions. The section uses automated systems and personnel databases to support operations. The organizational structure is shown in Figure 4-1. |
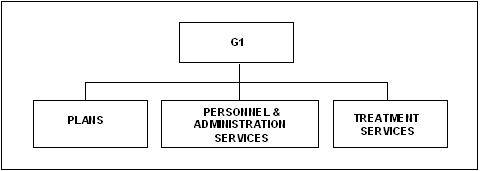
Figure 4-1. G1 Organization
OPERATIONS
4-3. To ensure the AAMDC is adequately manned, the G1 monitors, collects, and assesses information affecting soldier readiness and continually monitors and analyzes personnel strength using information technology systems. It also projects future requirements and develops plans to maintain strength. 4-4. To maintain personnel strength, the G1 actively manages personnel replacement. This involves:
4-5. The G1 also manages casualty operations. This involves casualty reporting, notification, and assistance; line-of-duty determination; reporting of status of remains; and casualty mail coordination. |
Health and Personnel Service Support
4-6. The G1 provides a variety of health and personnel support services. These include:
|
Headquarters Management
4-7. The G1 performs several headquarters management tasks including managing the organization and administration of the headquarters, recommending manpower allocation and coordinating and supervising movement and administrative support. |
Other Tasks
4-8. The G1 plans and supervises:
|
LOGISTICS SECTION
4-9. The logistics section (G4) is responsible for coordinating the logistic integration of supply, maintenance, transportation, and services for the command. The section uses automated systems and logistic databases to support operations. The organizational structure is shown in Figure 4-2. |
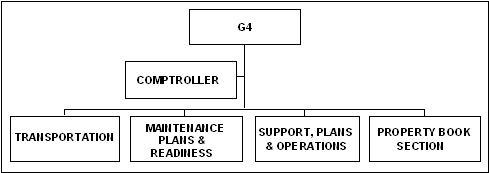
Figure 4-2. G4 Organization
OPERATIONS
4-10. The G4 develops the logistic plan to support operations and coordinates with the G3 and G1 to equip replacement personnel and units. The G4 provides the overall input on logistic requirements (less medical) to the theater support command. Current G4 structure does not support a logistic readiness center or logistic support operation functions and must be augmented to execute this mission. 4-11. The G4 section keeps track of the locations and numbers of ADA missiles (by type through total army asset visibility systems) and coordinates directly with the active defense cell to monitor current numbers. It also coordinates with supporting unit commanders on current and future support capability of those units and performs other tasks including:
|
Supply
4-12. The G4 performs a variety of supply-related activities including:
|
Maintenance
4-13. The G4 section monitors and analyzes the equipment readiness status and determines maintenance workload requirements with the theater support command and subordinate units. The section also coordinates maintenance, equipment recovery, and evacuation timelines. |
Transportation
4-14. The G4 section coordinates with the G3 to support strategic movements and conducts operational planning to support movement control and mode and terminal operations. The G4 section also performs the function of unit movement officer (UMO) for the AAMDC and intermediate UMO for subordinate units. It also coordinates with the G1 and G3 on transporting replacement personnel and enemy prisoners of war. |
Services
4-15. The G4 coordinates a variety of services including:
|
Other Tasks
4-16. The G4 section performs the property book function for the AAMDC. It also has staff planning and supervision responsibilities over:
|
SPECIAL STAFF SECTIONS
4-17. The special staff sections include the headquarters commandant, inspector general, public affairs, and staff judge advocate. These sections are described below. |
HEADQUARTERS COMMANDANT
4-18. The headquarters commandant section has operational control over soldiers assigned to the AAMDC who are not assigned or attached to subordinate commands. This includes responsibility for the following areas and activities:
|
INSPECTOR GENERAL
4-19. The inspector general (IG) section is responsible for advising the commander on the overall welfare and state of discipline of the command. Specific responsibilities include:
|
PUBLIC AFFAIRS
4-20. The public affairs section is responsible for understanding and fulfilling the information needs of soldiers and the public. Specific responsibilities include:
|
STAFF JUDGE ADVOCATE
4-21. The staff judge advocate (SJA) section is responsible for advising the command on all matters affecting the morale, good order, and discipline of the command. Specific responsibilities include:
|
HEADQUARTERS AND HEADQUARTERS BATTERY
4-22. The battery headquarters provides administrative, supply, food service, and maintenance support to the headquarters. This includes but is not limited to processing leaves and personnel actions; equipping soldiers with appropriate uniforms and supplies; feeding soldiers in both garrison and in the field; and maintaining assigned vehicles, weapons, communications items, and other required equipment. The organizational structure of the HHB is shown in Figure 4-3. |
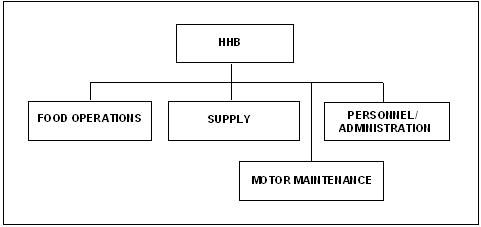
Figure 4-3. HHB Organization
OPERATIONS
4-23. The commander and the first sergeant are responsible for the health, welfare, and training of soldiers assigned or attached to the battery. The commander exercises nonjudicial punishment over personnel assigned or attached unless reserved by the AAMDC commander. The battery commander works for the chief of staff and the commanding general and maintains close ties to each staff section to deconflict training requirements and mission support activities. The first sergeant works for the battery commander, but coordinates closely with the command sergeant major and other staff sergeants major. All other members of the battery headquarters work for the battery commander and the first sergeant. |
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

