Defense Satellite Communications System Program
The DSCS's mission is to provide global communications capability to support the National Command Authority (NCA)/Joint Chief of Staff (JCS) under the operational control of Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA). The US Army has the responsibility for the acquisitions and fielding of both ground terminals and SATCOM control equipment.Modulation techniques include time division multiple access (TDMA), frequency division multiple access (FDMA), and spread spectrum multiple access (SSMA). Future modulation techniques will include demand assigned multiple access (DAMA).
The DSCS radio frequency portions are undergoing many upgrades to support its mission well into the 21st century. Some of the upgrades include:
Heavy/Medium Terminal Modification: This upgrade affects the AN/FSC-78 and AN/GSC-39 terminals. These terminal's RF components will be replaced with solid state devices for the transmitters and receive amplifiers. Included will be computer monitor, test and measurement, and control of the terminal functions.
Super High Frequency (SHF) Tri-band Range Extension Terminal (STAR-T): This developmental terminal will replace AN/TSC-85B/93B terminals at echelons above corps (EAC). The terminal will be mounted on a HMMWV. Its primary mission is to provide multiband communications and interface with commercial and military assets (dial central and satellite); DGM; TRI-TAC terminals at EAC; and with MSE terminals and ECB.
The DSCS Operational Control System (DOCS) controls all DSCS user terminals operating on DSCS spacecraft. This system also is undergoing upgrades that will allow higher control capability using less equipment and manpower resources.
The ground mobile forces (GMF) will use the DSCS II and DSCS III spacecraft to fulfill multichannel SHF initial system worldwide operational requirements. The DSCS II and III satellites are positioned in geostationary orbits and are continuously available for use by earth terminals located within 5,000 nautical miles of their subsatellite points. The SKYNET IV satellite will be available for GMF use in Europe.
- DSCS II: These satellites have two transponders, each having a bandwidth constrained by the nominal 2009 MHz bandwidth of the total usable bandwidth of 410 MHz. Each transponder is subdivided by filters in the RF diplexers to provide two operational channels, for example, four operational channels for each satellite. Four antennas are mounted on the despun platform. Two of them are earth coverage horn (ECH) antennas, one for uplink and one for downlink. The remaining two are parabolic dish type antennas. A single biconical horn is used to support the dedicated S-band telemetry and control link. It is mounted on the lower end of the spinning section of the satellite.
- DSCS III: The DSCS III program is a vital part of the comprehensive plan meeting national military communications needs. A six-channel communications transponder with each channel operating through its own RF amplifier serves the users. This allows compatible grouping of users for efficient use of the SHF frequency spectrum of 7.9 to 8.4 GHz. The DSCS III satellite carries two communications payload packages. The primary payload is at SHF, satisfying the space link requirements of standard military communications networks. The secondary payload is an US Air Force SATCOM UHF single transponder used to transmit emergency action messages between military command posts (CPs) and force elements. The communications system is supported by one receive multibeam antenna (MBA), two receive ECH antennas, two transmit MBA's, two transmit ECH antennas, and a gimballed dish antenna (GDA). Each of the six independent repeaters operates in the SHF region to relay telephone, data, wideband imagery, and secure digital voice signals using FM, BPSK, quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK), staggered quadrature phase shift keying (SQPSK) and frequency hopping pseudo noise (PN) spread spectrum modulation. Each terminal has access to any channel and each channel can relay, with minimum performance degradation, signal transmissions consisting of FDMA, TDMA, and spread spectrum multiple access (SSMA) via the PN carrier modulation technique. Linear, quasilinear, and saturated modes of operation are provided by means of selectable gain steps. The MBA with the beam forming the network can shape antenna patterns to arbitrary selected coverage areas.

DSCS Phase II Satellite
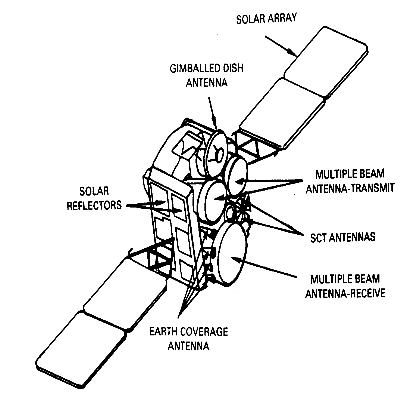
DSCS Phase III Satellite
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

